This guide provides a comprehensive overview of refrigerant evaporators, exploring their function, types, applications, and key considerations for selection and maintenance. We'll delve into the critical role they play in refrigeration systems and offer practical insights for various industries.
What is a Refrigerant Evaporator?
A refrigerant evaporator is a heat exchanger component in a refrigeration system. Its primary function is to absorb heat from the surrounding environment, causing a phase change in the refrigerant from a low-pressure liquid to a low-pressure gas. This process cools the space or substance being refrigerated. The efficiency of a refrigerant evaporator directly impacts the overall performance of the refrigeration system.
Types of Refrigerant Evaporators
Several types of refrigerant evaporators cater to different applications and refrigerants. The choice depends on factors such as the cooling capacity required, the refrigerant used, and the application's specific needs. Some common types include:
Flooded Evaporators
Flooded evaporators are characterized by a complete submersion of the evaporator coil in the refrigerant. This design promotes efficient heat transfer, particularly suitable for applications requiring high cooling capacity, such as large industrial chillers. However, they require more complex control systems and careful monitoring to prevent flooding issues.
Dry Evaporators
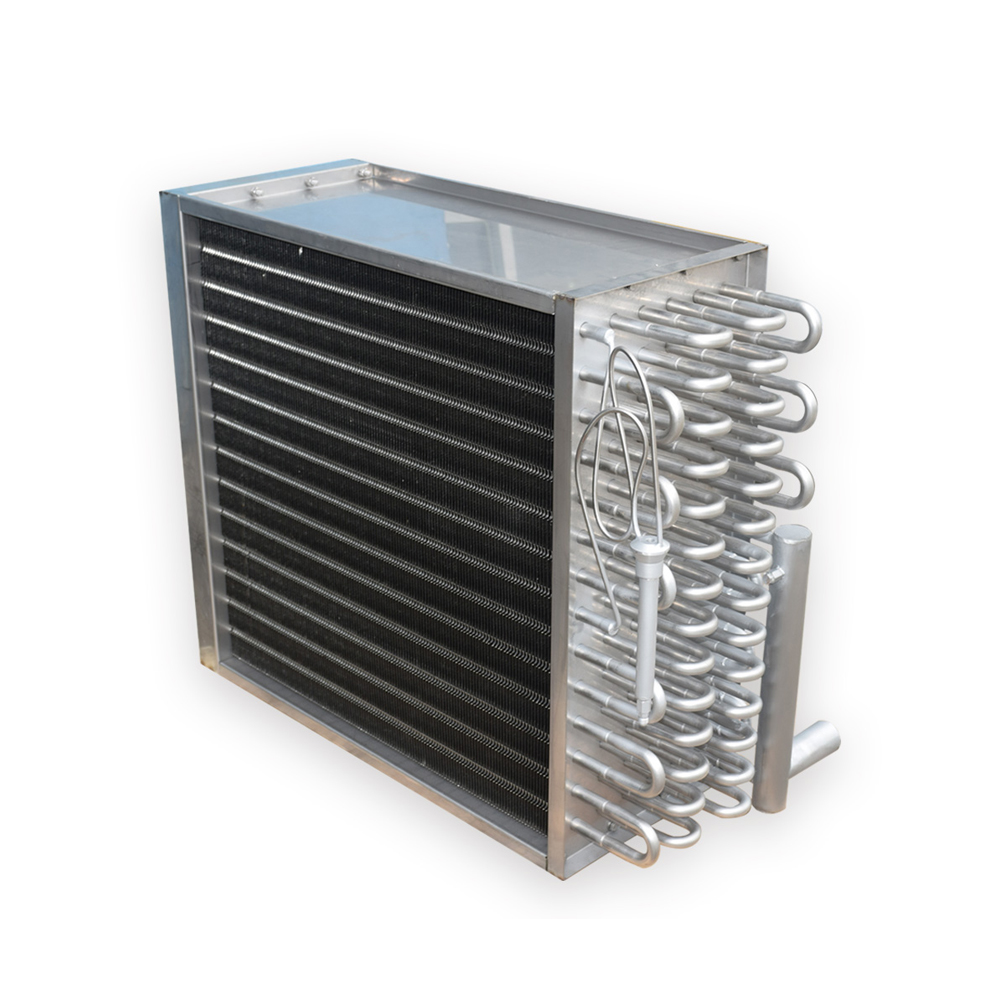
Dry evaporators, in contrast, maintain a low refrigerant charge within the tubes. They typically feature a smaller refrigerant volume compared to flooded evaporators. Dry evaporators are known for their simpler design and reduced risk of flooding, making them suitable for various applications, from smaller commercial refrigeration units to residential air conditioning systems. Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd (https://www.ShenglinCoolers.com/) offers a range of high-quality dry evaporators.
Plate Evaporators
Plate evaporators use a series of thin, flat plates to maximize surface area for heat transfer. This design is compact and efficient, commonly found in smaller refrigeration systems and specialized applications. The efficient heat transfer makes them ideal for scenarios demanding rapid cooling.
Other Types
Other types of refrigerant evaporators include shell and tube evaporators, used extensively in industrial applications; and air-cooled evaporators, which are common in air conditioning systems. The selection of the optimal refrigerant evaporator type hinges on a careful assessment of several factors.
Factors Affecting Refrigerant Evaporator Performance
The performance of a refrigerant evaporator depends on several crucial factors. These include:
Refrigerant Type and Properties
Different refrigerants have varying thermodynamic properties, directly impacting the evaporator's efficiency. The selection of the right refrigerant is critical for optimal performance and environmental considerations.
Evaporator Design and Construction
The design and construction of the refrigerant evaporator significantly influence its heat transfer capability. Features like fin spacing, tube diameter, and material selection all play a role.
Operating Conditions
Environmental factors such as ambient temperature and airflow can affect the evaporator's performance. Proper insulation and air circulation are crucial for maintaining optimal efficiency.
Refrigerant Evaporator Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your refrigerant evaporator. This includes:
- Regular inspection for leaks, corrosion, or other damage.
- Cleaning the evaporator coils to remove dirt and debris that can impede heat transfer.
- Monitoring refrigerant levels and pressure.
Choosing the Right Refrigerant Evaporator
Selecting the appropriate refrigerant evaporator requires careful consideration of several factors. These include the cooling capacity needed, the type of refrigerant used, the operating conditions, and the overall system design. Consulting with a refrigeration specialist is recommended to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd can provide expert guidance and solutions for your specific needs.
For a more detailed comparison of different evaporator types, refer to the table below. Note that these values are illustrative and may vary depending on the specific model and manufacturer.
| Evaporator Type | Typical Application | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Flooded | Large industrial chillers | High efficiency, large capacity | Complex control, potential for flooding |
| Dry | Commercial and residential refrigeration | Simple design, low risk of flooding | Lower efficiency compared to flooded |
| Plate | Small refrigeration systems | Compact, efficient | Lower capacity compared to other types |
Remember to always consult the manufacturer's specifications and safety guidelines before installing or operating any refrigerant evaporator. Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety.