This guide provides a detailed overview of pipe in pipe heat exchangers, covering their design, applications, advantages, disadvantages, and selection criteria. Learn about the different types available and how to choose the right one for your specific needs. We'll also explore real-world applications and considerations for optimal performance.
Understanding Pipe in Pipe Heat Exchangers
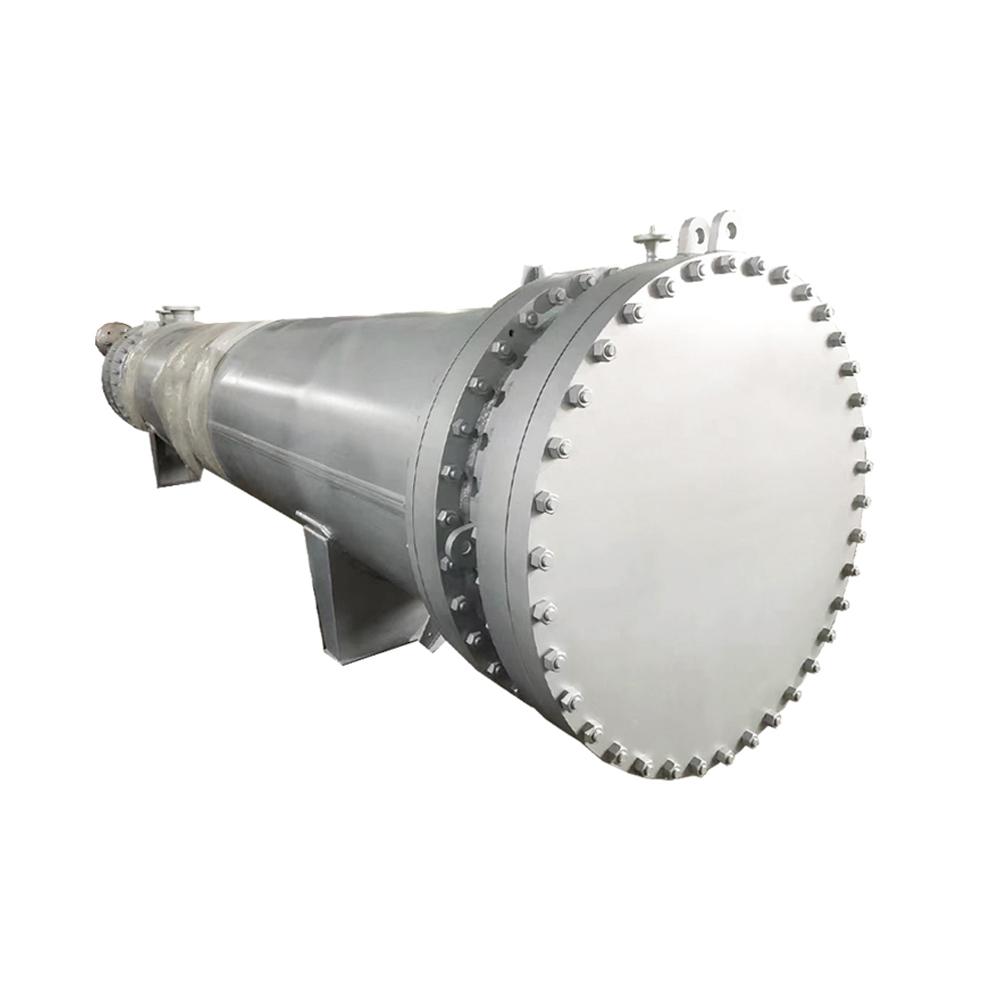
What are Pipe in Pipe Heat Exchangers?
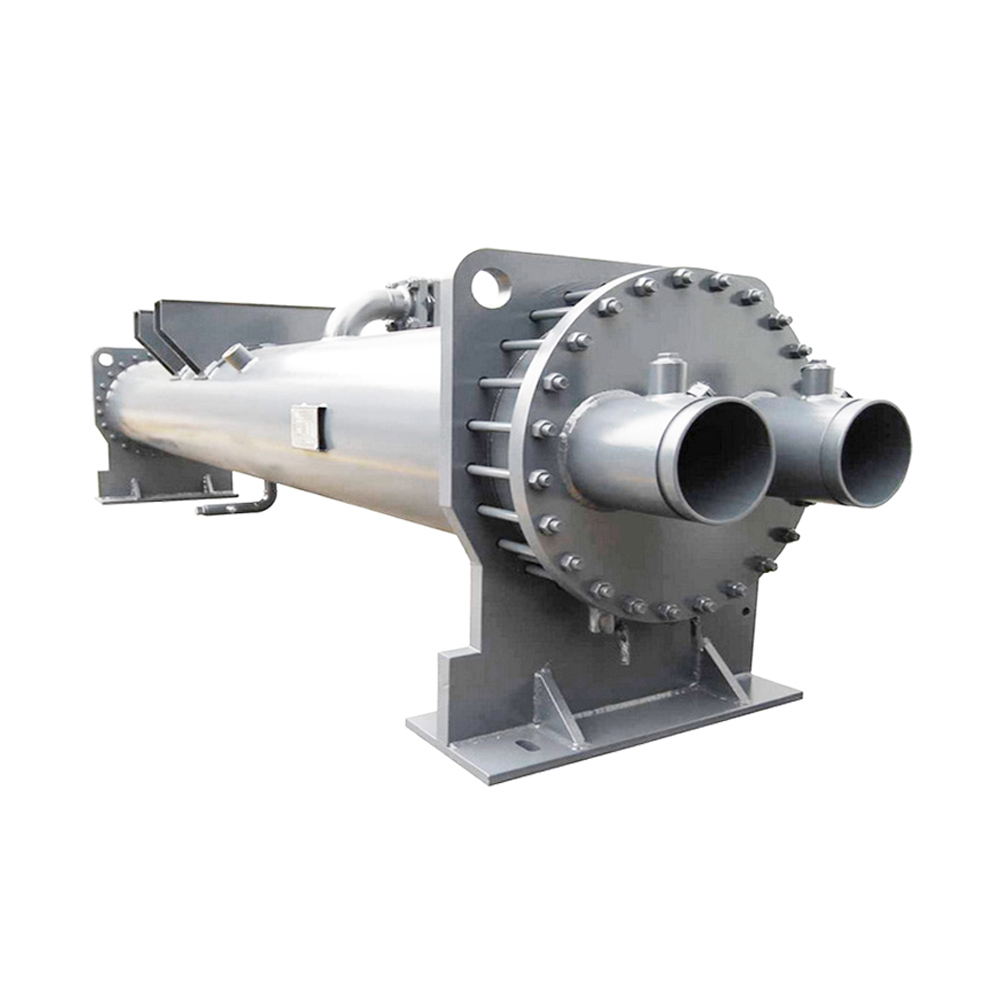
A pipe in pipe heat exchanger, also known as a double-pipe heat exchanger, consists of two concentric pipes. The fluid to be heated or cooled flows through the inner pipe, while the heating or cooling medium flows through the annular space between the inner and outer pipes. Heat transfer occurs through the pipe wall via conduction. This simple design makes them cost-effective and easy to maintain. The efficiency of a pipe in pipe heat exchanger depends heavily on factors such as the flow rate, temperature difference, and the thermal conductivity of the pipe material.
Types of Pipe in Pipe Heat Exchangers
Several variations exist to optimize heat transfer and suit diverse applications. These can include:
- Counterflow: Fluids flow in opposite directions, maximizing heat transfer.
- Parallel flow: Fluids flow in the same direction, resulting in less efficient heat transfer.
- Types based on pipe material: Stainless steel, copper, and other materials are chosen based on compatibility with the fluids and the operating temperature.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Pipe in Pipe Heat Exchangers
Like any heat exchanger technology, pipe in pipe heat exchangers have both strengths and weaknesses. Let's consider them:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Simple design and construction | Lower heat transfer efficiency compared to more complex designs |
| Easy to clean and maintain | Limited surface area for heat transfer, especially for high heat duty applications |
| Relatively low cost | Not suitable for high-pressure or high-temperature applications (depending on material) |
| Versatile applications | Can be susceptible to fouling if not properly cleaned |
Applications of Pipe in Pipe Heat Exchangers
Pipe in pipe heat exchangers find applications across various industries. Some common examples include:
- Chemical processing: Heating or cooling chemical streams.
- Food processing: Pasteurization, chilling, and other temperature-controlled processes.
- Pharmaceutical industry: Sterile fluid handling and temperature control.
- HVAC systems: Smaller-scale heating or cooling applications.
- Renewable energy: Preheating or cooling fluids in solar thermal systems.
Selecting the Right Pipe in Pipe Heat Exchanger
Choosing the appropriate pipe in pipe heat exchanger requires careful consideration of several factors, including:
- Fluid properties (viscosity, thermal conductivity, etc.)
- Required heat transfer rate
- Operating temperature and pressure
- Material compatibility
- Budget and space constraints
For expert advice and high-quality pipe in pipe heat exchangers, consider contacting Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd for more information on their capabilities and product range. They're a leading provider of efficient and reliable heat exchange solutions.
Conclusion
Pipe in pipe heat exchangers offer a simple, cost-effective solution for various heating and cooling applications. Understanding their advantages, disadvantages, and selection criteria is crucial for successful implementation. Remember to carefully consider the factors outlined above to ensure optimal performance and longevity.