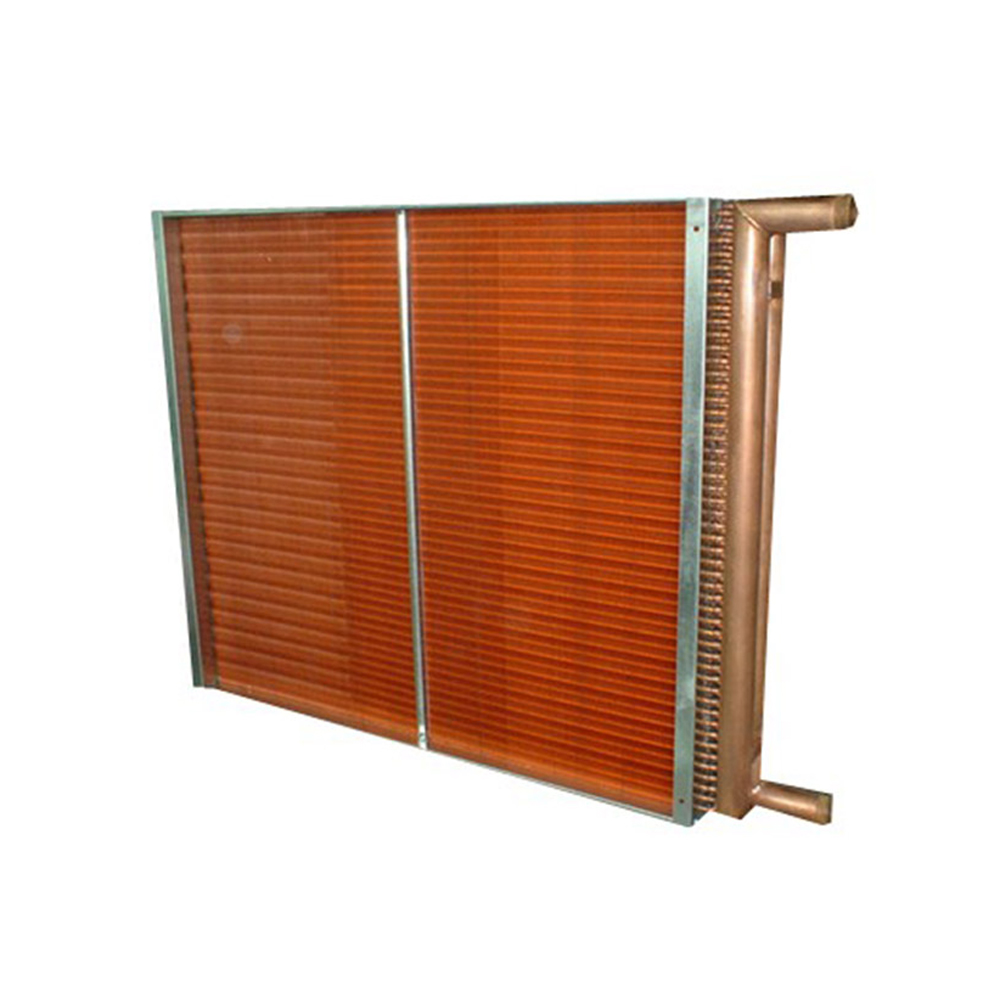
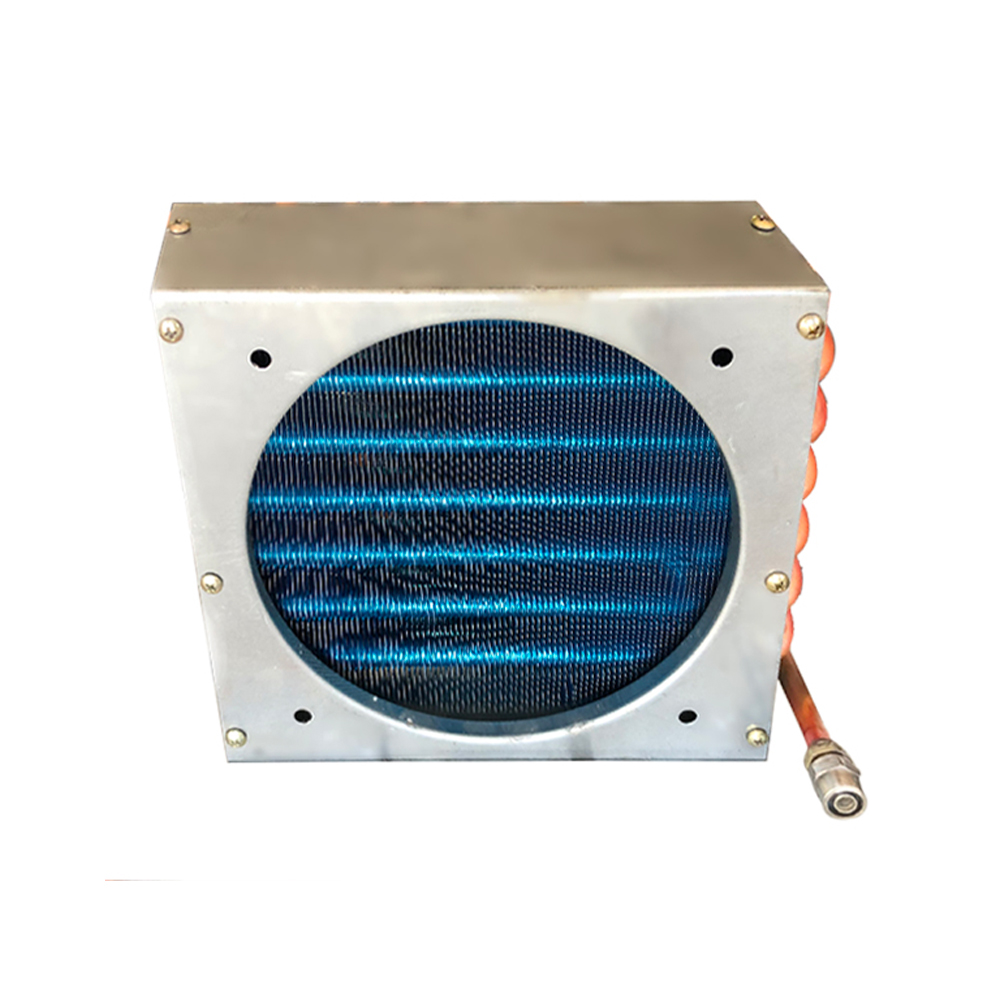
This article delves into the world of OEM Tube Fin Heat Exchangers, providing a detailed understanding of their functionality, selection, and application across various industries. We'll explore their design characteristics, benefits, and considerations for optimal performance and longevity. Learn how to choose the right exchanger for your specific needs and discover best practices for maintenance and troubleshooting. Whether you're an engineer, a procurement specialist, or simply curious about these essential components, this guide offers valuable insights.
Understanding OEM Tube Fin Heat Exchanger Design
Construction and Materials
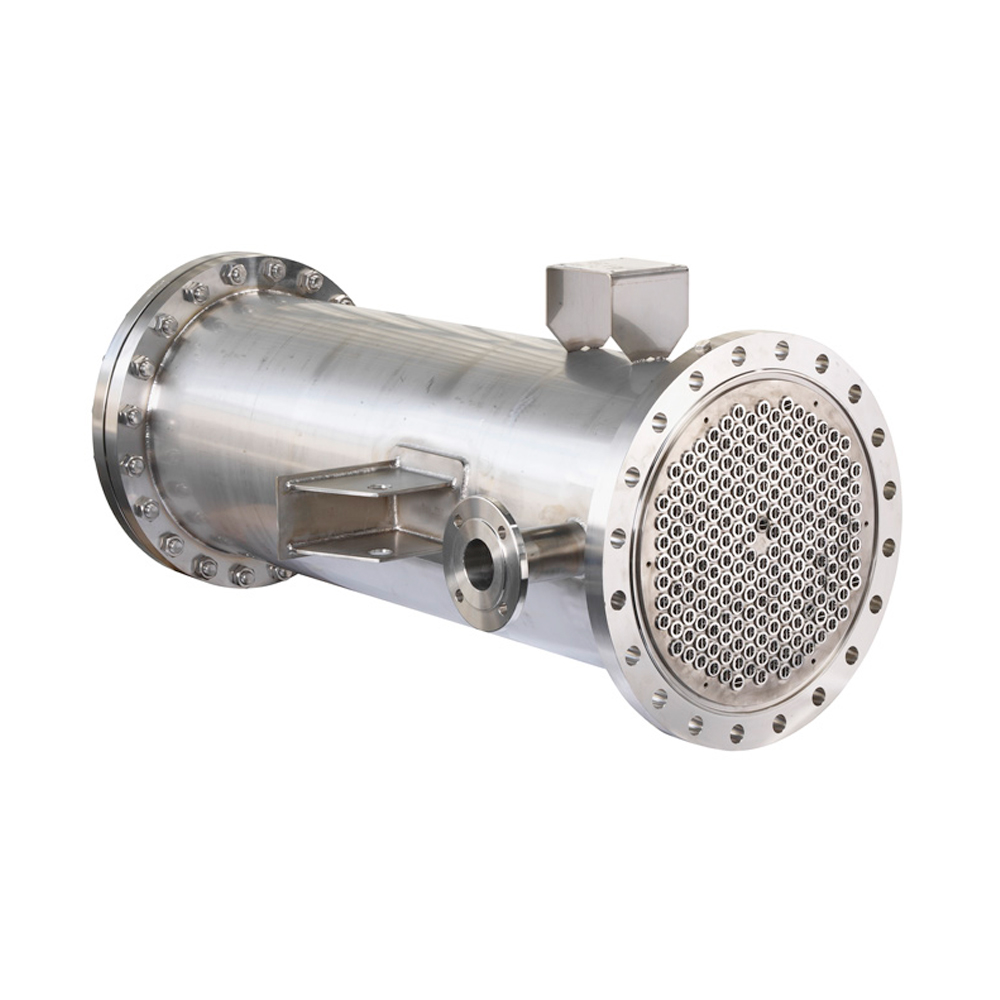
OEM Tube Fin Heat Exchangers are constructed using a network of finned tubes. These tubes, typically made of copper, aluminum, or stainless steel, offer excellent heat transfer capabilities. The fins, often aluminum, increase the surface area for enhanced heat exchange efficiency. The choice of materials depends on factors such as the operating temperature, pressure, and the nature of the fluids involved. Corrosion resistance is a key factor, especially in applications involving aggressive chemicals.
Types and Configurations
Several configurations of OEM Tube Fin Heat Exchangers exist, each tailored to specific applications. These include parallel flow, counterflow, and crossflow designs. The choice depends on factors like required heat transfer rate, pressure drop, and space constraints. For example, counterflow designs generally offer higher effectiveness but might require more space.
Applications of OEM Tube Fin Heat Exchangers
HVAC Systems
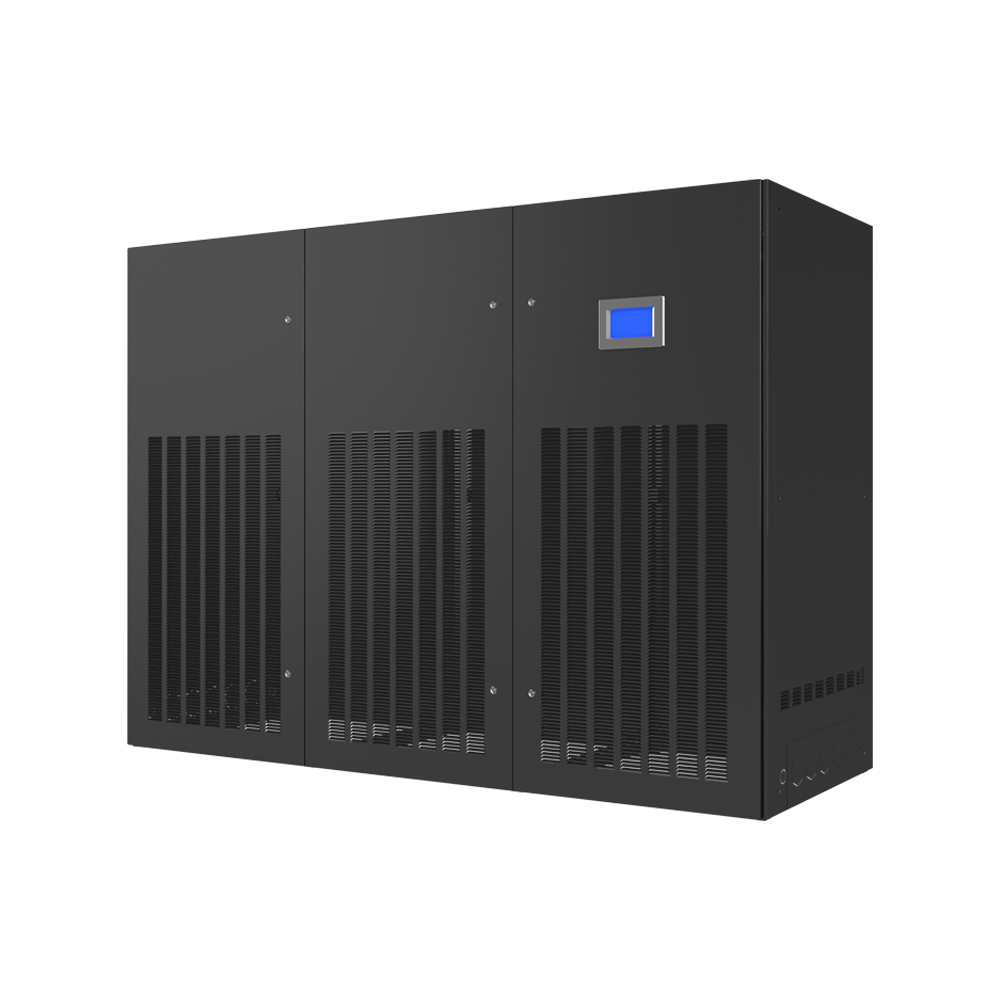
OEM Tube Fin Heat Exchangers are widely used in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems for heating and cooling applications. Their compact design and high efficiency make them suitable for both residential and commercial buildings. In these applications, they often form part of larger units provided by OEM manufacturers.
Industrial Processes
Various industrial processes rely on OEM Tube Fin Heat Exchangers for efficient heat transfer. These include chemical processing, power generation, and refrigeration. The ability to handle high temperatures and pressures makes them crucial in demanding environments. For example, they're essential in heat recovery systems, maximizing energy efficiency.
Automotive and Transportation
The automotive industry uses OEM Tube Fin Heat Exchangers in applications such as engine cooling and climate control. Their compact size and lightweight design are significant advantages in this sector. The need for reliable and efficient heat management makes them a vital component in modern vehicles.
Selecting the Right OEM Tube Fin Heat Exchanger
Selecting the appropriate OEM Tube Fin Heat Exchanger requires careful consideration of several factors, including:
- Heat transfer requirements (duty)
- Fluid properties (temperature, pressure, viscosity, etc.)
- Operating conditions (ambient temperature, pressure drop limitations)
- Space constraints and physical dimensions
- Material compatibility (corrosion resistance)
- Maintenance requirements and accessibility
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. This includes inspecting for leaks, cleaning fouling deposits, and ensuring proper airflow. Early detection of problems can prevent costly repairs or replacements. Refer to the manufacturer's guidelines for specific maintenance recommendations. For comprehensive solutions and high-quality OEM Tube Fin Heat Exchangers, consider exploring options from reputable suppliers like Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd.
Comparison of Different OEM Tube Fin Heat Exchanger Materials
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Copper | Excellent thermal conductivity, good corrosion resistance | Relatively expensive |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, good thermal conductivity, cost-effective | Lower corrosion resistance compared to copper |
| Stainless Steel | Excellent corrosion resistance, high strength | Lower thermal conductivity compared to copper and aluminum |
Note: This information is for general guidance only. Specific product details and performance data should be obtained from the respective manufacturer's specifications.