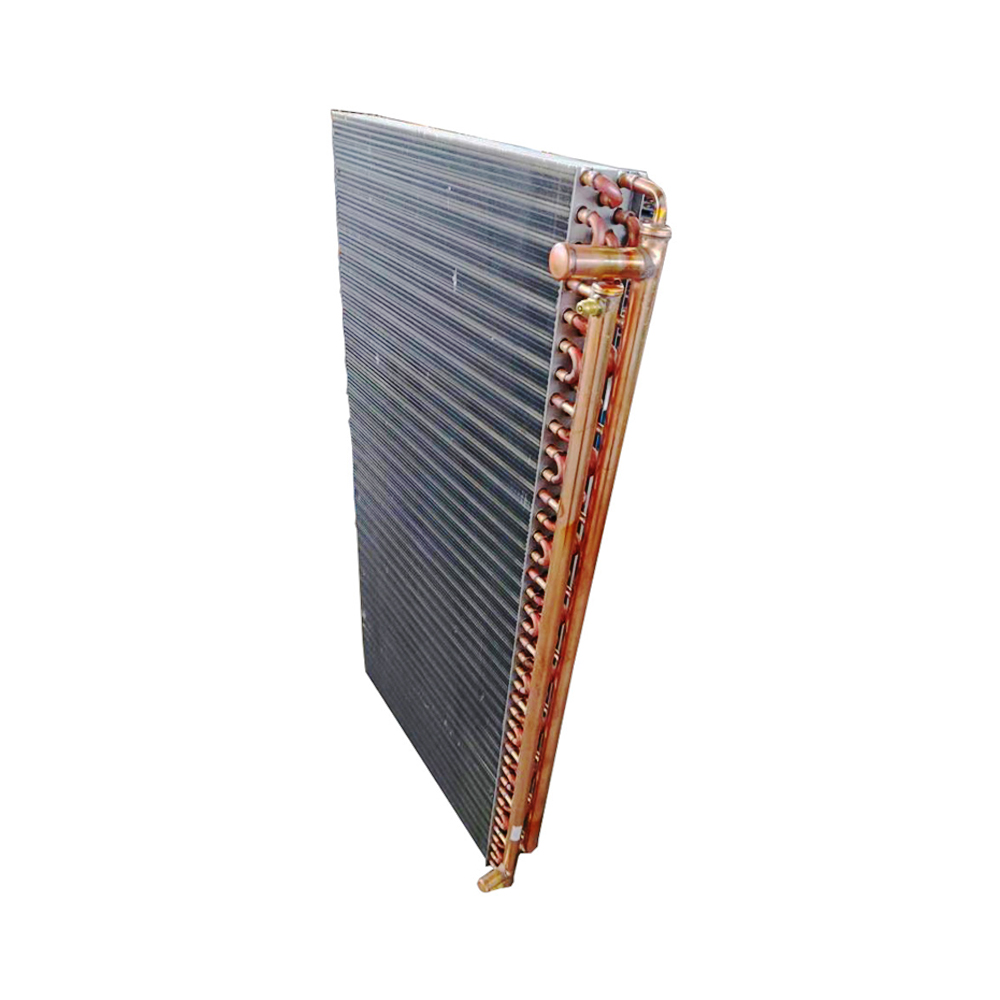
OEM refrigerant evaporators are crucial components in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. Understanding their functionality, selection, and maintenance is essential for ensuring optimal system performance and efficiency. This guide delves into the intricacies of these evaporators, providing insights for professionals involved in design, manufacturing, or maintenance of refrigeration systems.
Types of OEM Refrigerant Evaporators
Plate Evaporators
Plate evaporators are known for their high efficiency and compact design. They consist of multiple thin plates brazed together to create a large surface area for heat exchange. This design is particularly suitable for applications where space is limited, such as in smaller refrigeration units. The choice of refrigerant often influences the material and design of the plates to ensure compatibility and performance.
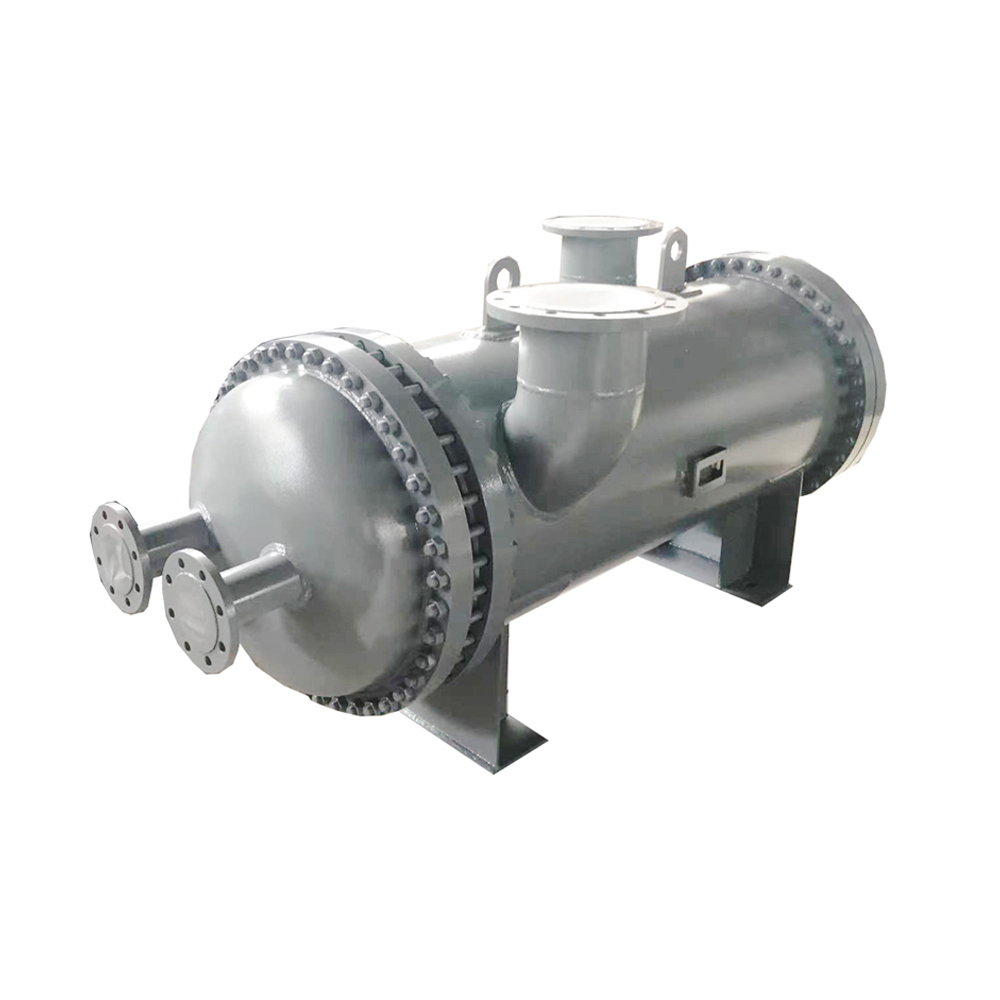
Shell and Tube Evaporators
Shell and tube evaporators are a robust and versatile type, often used in larger industrial refrigeration systems. They involve a shell containing a bundle of tubes through which the refrigerant flows. The refrigerant absorbs heat from the surrounding medium as it evaporates. These evaporators are typically more durable and can handle higher pressures and flow rates than plate evaporators. The selection of appropriate tubing material is critical for compatibility with different refrigerants and operating conditions.
Microchannel Evaporators
Microchannel evaporators utilize small diameter tubes to maximize heat transfer efficiency. Their compact size and high performance make them suitable for applications such as automotive air conditioning and small commercial refrigeration. The intricate design and manufacturing process require specialized techniques. Proper maintenance is critical due to the small channel dimensions.
Selecting the Right OEM Refrigerant Evaporator
Choosing the right OEM refrigerant evaporator depends on several factors:
- Refrigerant Type: The evaporator must be compatible with the chosen refrigerant (e.g., R-134a, R-410A, R-32). Material compatibility is crucial to prevent corrosion and leaks. Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd offers a range of evaporators compatible with various refrigerants.
- Capacity: The evaporator's capacity must match the cooling load requirements of the system.
- Operating Pressure: The evaporator must be able to withstand the operating pressures of the system.
- Space Constraints: The physical dimensions of the evaporator must be suitable for the available space.
- Cost: The initial investment and long-term operational costs should be considered.
Maintenance of OEM Refrigerant Evaporators
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of OEM refrigerant evaporators. This includes:
- Regular inspection for leaks and damage.
- Cleaning the evaporator to remove dirt and debris.
- Checking the refrigerant levels and pressure.
- Ensuring proper airflow around the evaporator.
Key Specifications and Considerations
Understanding key specifications is crucial for selecting the appropriate OEM refrigerant evaporator. These often include:
| Specification | Description |
| Capacity (BTU/hr or kW) | The amount of heat the evaporator can remove. |
| Refrigerant Type | The type of refrigerant used (R-134a, R-410A, etc.). |
| Operating Pressure (PSI or kPa) | The pressure at which the evaporator operates. |
| Dimensions (length, width, height) | The physical dimensions of the evaporator. |
| Material | The material of construction (copper, aluminum, etc.). |
Remember, proper selection and maintenance are critical for efficient and reliable system operation. Always consult the manufacturer's specifications and guidelines for optimal performance.