This guide provides a detailed overview of OEM heat exchanger type shell and tube units, covering their design, applications, advantages, disadvantages, and selection criteria. We explore various aspects crucial for understanding and choosing the right shell and tube heat exchanger for your specific needs. Learn about different materials, configurations, and best practices for optimal performance and longevity.
Understanding Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
What is a Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger?
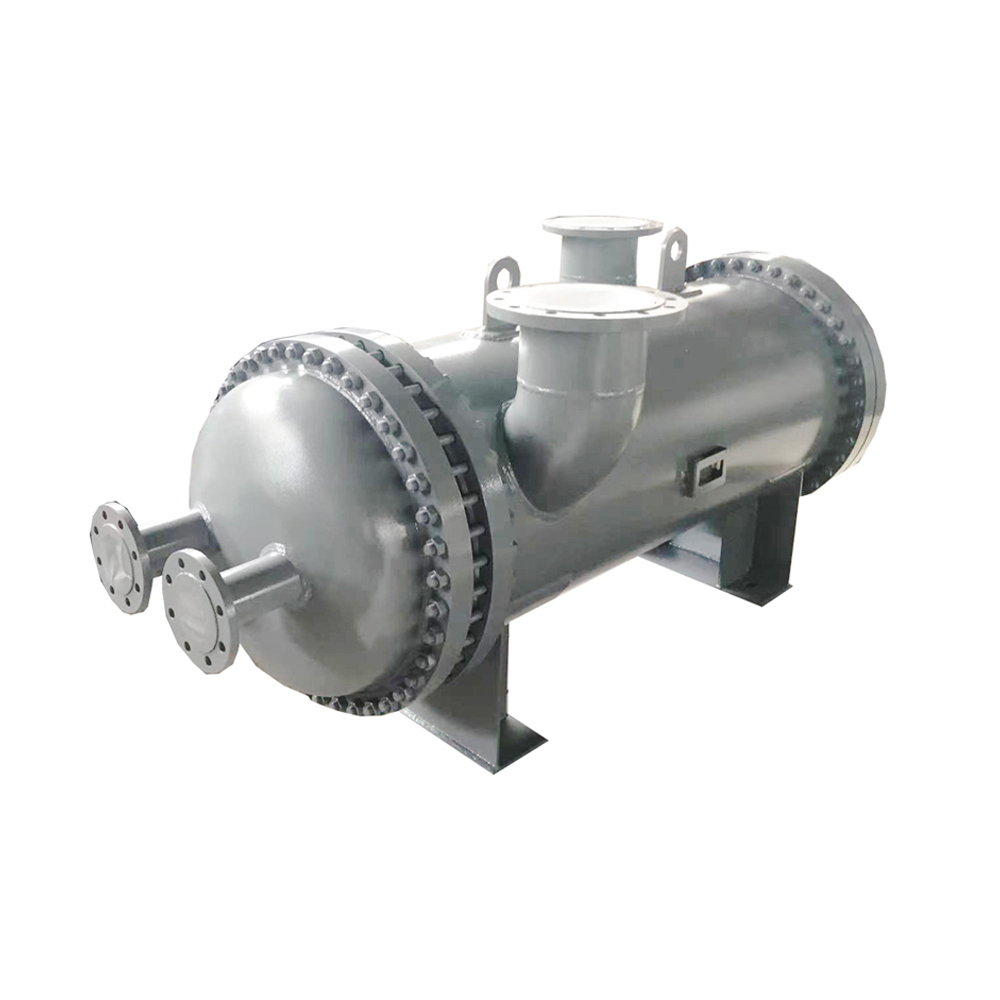
A shell and tube heat exchanger is a type of heat exchanger widely used in various industries for efficient heat transfer between two fluids. It consists of a cylindrical shell containing a bundle of tubes. One fluid flows through the tubes, while the other flows over the outside of the tubes within the shell. The heat exchange occurs through the tube walls. This design allows for a large surface area for heat transfer, making it effective for various applications.
Types of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Several variations exist within the OEM heat exchanger type shell and tube category, each optimized for specific applications. These variations often involve different baffle configurations, tube arrangements, and shell designs. Common types include:
- U-Tube Heat Exchangers
- Fixed Tube Sheet Heat Exchangers
- Floating Head Heat Exchangers
The choice of type depends on factors such as pressure, temperature, fouling potential, and ease of maintenance. For example, U-tube designs offer easy tube cleaning but might have limitations with high pressure differentials. Fixed tube sheet designs are simpler and more cost-effective but may require more complex cleaning procedures.
Applications of OEM Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Diverse Industries
OEM heat exchanger type shell and tube units find applications across a broad spectrum of industries, including:
- Power Generation
- Chemical Processing
- Oil and Gas Refining
- HVAC Systems
- Refrigeration
Their versatility and adaptability make them suitable for various heat transfer needs, from large-scale industrial processes to smaller-scale applications. The specific design and materials used can be customized to meet the requirements of each industry.
Material Selection for OEM Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Material Considerations
Selecting appropriate materials is critical for the longevity and performance of your OEM heat exchanger type shell and tube. Factors to consider include:
- Corrosion Resistance
- Temperature Limits
- Pressure Ratings
- Compatibility with the fluids being used
Common materials used include stainless steel, carbon steel, copper alloys, and titanium, each offering unique properties and suitability for specific applications. Choosing the wrong material can lead to premature failure and costly repairs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Pros and Cons
Like any technology, shell and tube heat exchangers offer both advantages and disadvantages.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| High heat transfer efficiency | Can be expensive |
| High pressure and temperature capabilities | Can be bulky and require significant space |
| Can handle a wide range of fluids | Cleaning and maintenance can be complex |
| Long lifespan with proper maintenance | Difficult to repair individual tubes |
Selecting the Right OEM Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
Key Selection Criteria
Choosing the right OEM heat exchanger type shell and tube requires careful consideration of several factors. These include the:
- Fluid properties (viscosity, flow rate, temperature, pressure)
- Required heat duty
- Available space
- Budgetary constraints
- Maintenance requirements
Consulting with experienced engineers is recommended to ensure you select a unit that meets your specific needs and operates efficiently.
For high-quality OEM heat exchanger type shell and tube solutions, consider contacting Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd. They offer a wide range of customized options to meet your specific requirements.
Note: This information is for general guidance only. Always consult with qualified engineers and refer to manufacturer specifications for specific applications.