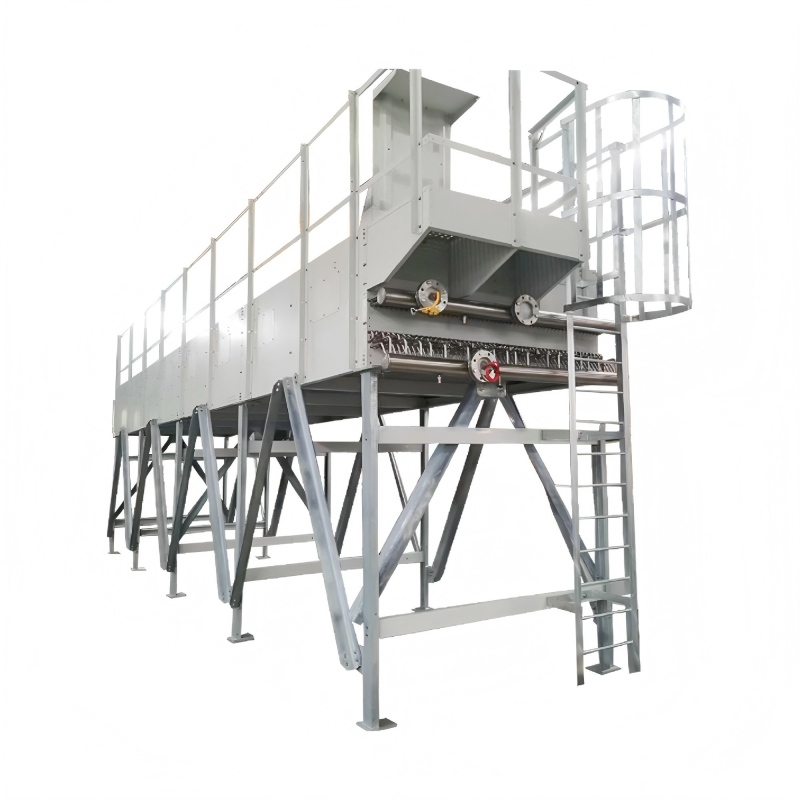
This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of horizontal dry cooling factories, examining their design, operation, and selection. We delve into the various factors you should consider when choosing a system for your specific needs, providing practical advice and real-world examples to help you make an informed decision. Learn about the advantages and disadvantages of different types of horizontal dry cooling factories and how to optimize their performance for maximum efficiency.
What is a Horizontal Dry Cooling Factory?
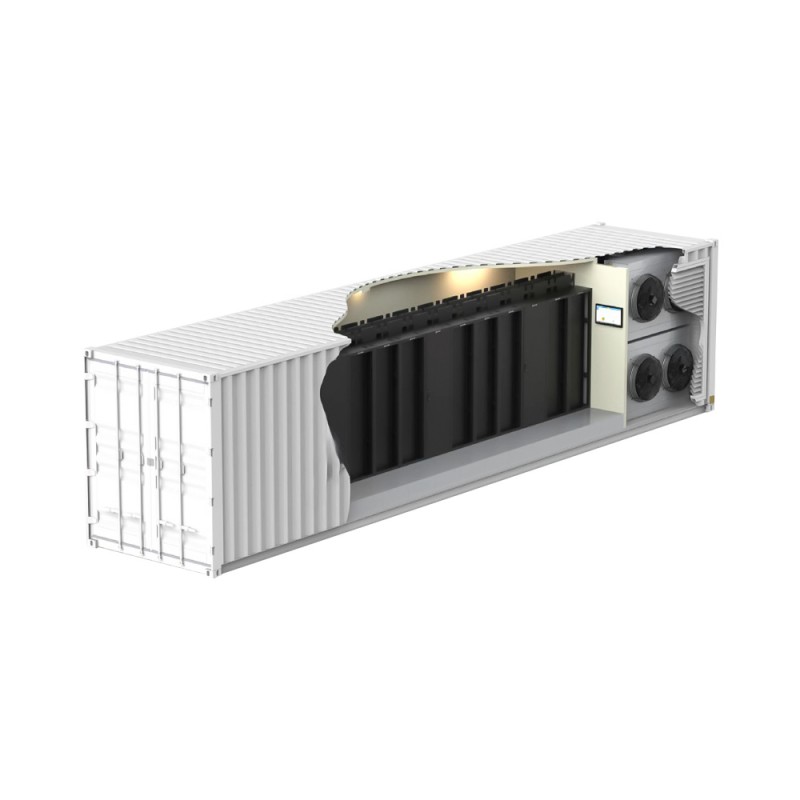
A horizontal dry cooling factory refers to a facility that utilizes horizontal dry cooling towers or systems for industrial cooling applications. Unlike traditional wet cooling towers, these systems employ air as the primary cooling medium, eliminating the need for water. This significantly reduces water consumption and minimizes the environmental impact associated with water evaporation and scaling. The factory aspect refers to the scale and complexity of such systems, often integrated into larger industrial processes.
Types of Horizontal Dry Cooling Systems
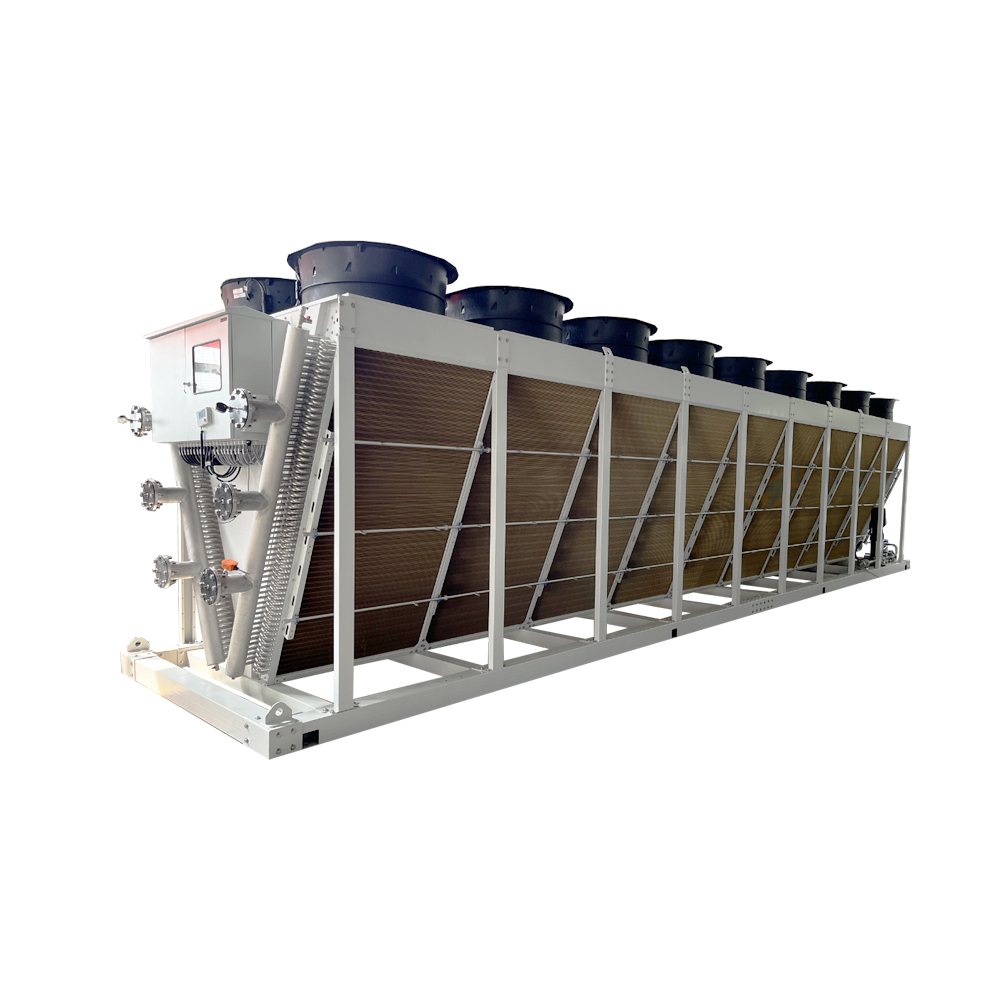
Air-Cooled Condensers
Air-cooled condensers are a common type of horizontal dry cooling system. They directly transfer heat from a process fluid to the ambient air via finned tubes. They are typically robust and reliable, suitable for various applications. Factors to consider include the fin density, tube material, and fan design to optimize heat transfer and efficiency.
Indirect Dry Cooling Towers
These systems employ a heat exchanger to separate the cooling water from the ambient air. This indirect approach reduces fouling and allows for more efficient heat transfer compared to direct air-cooled condensers in certain applications. The choice between direct and indirect systems often depends on the specific process fluid and environmental conditions.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Horizontal Dry Cooling Factory
Selecting the right horizontal dry cooling factory requires careful consideration of several key factors:
Capacity and Efficiency
The system's cooling capacity must meet the demands of your specific application. Efficiency is crucial, as it directly impacts energy consumption and operational costs. Consider the ambient temperature, process fluid flow rate, and desired cooling temperature when assessing capacity and efficiency requirements.
Space Requirements
Horizontal dry cooling factories generally require a larger footprint compared to wet cooling towers with equivalent cooling capacity. Careful site planning is essential to ensure adequate space for the system and facilitate maintenance access.
Maintenance and Operating Costs
Evaluate the long-term maintenance and operational costs. Factors to consider include the frequency of cleaning, fan maintenance, and potential repairs. Some systems might require less frequent maintenance, offsetting higher initial investment costs over time.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of horizontal dry cooling factories is significantly lower than that of wet cooling towers due to reduced water consumption. However, noise and air emissions from fans should also be considered. Selecting a system with effective noise reduction measures is vital for minimizing environmental impact.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Horizontal Dry Cooling Systems
| Feature | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Water Consumption | Significantly reduced water usage | Not applicable |
| Environmental Impact | Lower environmental impact compared to wet cooling towers | Potential for higher energy consumption and noise pollution |
| Space Requirements | Can be modular and adapted to site constraints | Generally requires larger footprint than wet cooling towers |
Choosing the Right Partner for Your Horizontal Dry Cooling Factory
Partnering with a reputable supplier is crucial for the successful implementation of your horizontal dry cooling factory. Look for a company with extensive experience, a proven track record, and a commitment to quality. Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd offers a range of solutions tailored to diverse industrial needs. Their expertise in designing, manufacturing, and installing advanced cooling systems ensures optimal performance and longevity.
This guide provides a starting point for understanding and selecting a suitable horizontal dry cooling factory. Remember that thorough planning and consultation with industry experts are key to ensuring a successful project outcome.