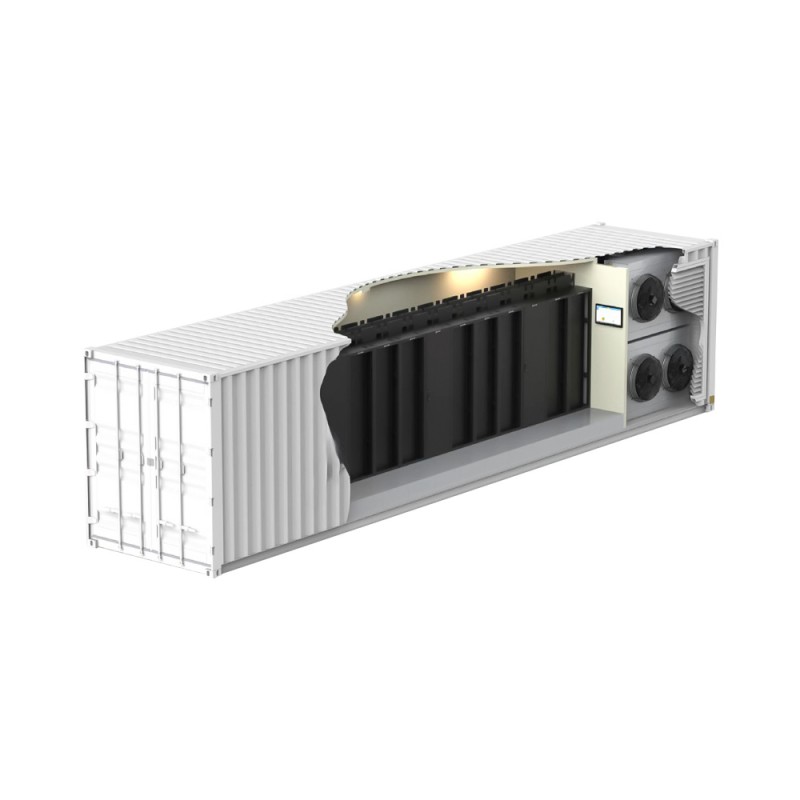
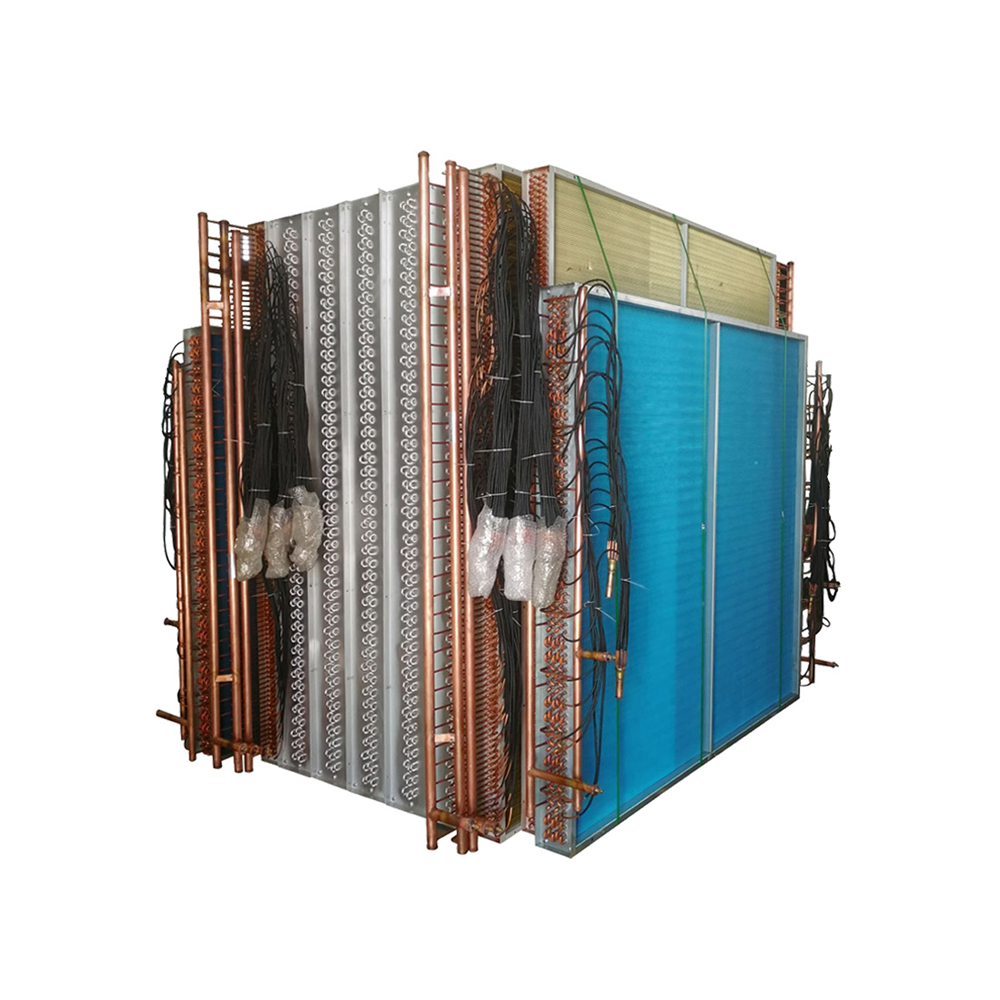
This comprehensive guide explores the world of heat exchangers, covering their types, applications, selection criteria, and maintenance. Learn how to choose the optimal heat exchanger for your specific needs, from understanding fundamental principles to navigating the complexities of various designs. We'll delve into practical examples and considerations to ensure you make informed decisions for efficient thermal management.
Types of Heat Exchangers
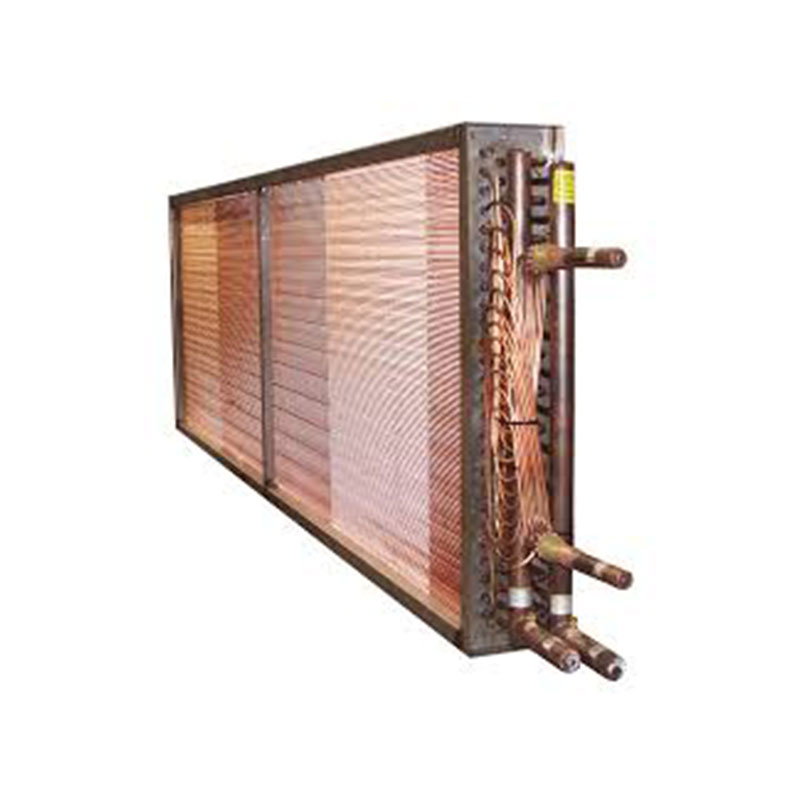
Plate Heat Exchangers
Plate heat exchangers are known for their high efficiency and compact design. They consist of a series of corrugated plates stacked together, creating numerous channels for the fluids to flow through. The large surface area allows for efficient heat transfer. Plate heat exchangers are commonly used in various industries, including food processing, HVAC, and pharmaceuticals. Their compact size makes them ideal for space-constrained applications. However, they can be more susceptible to fouling and require regular cleaning.
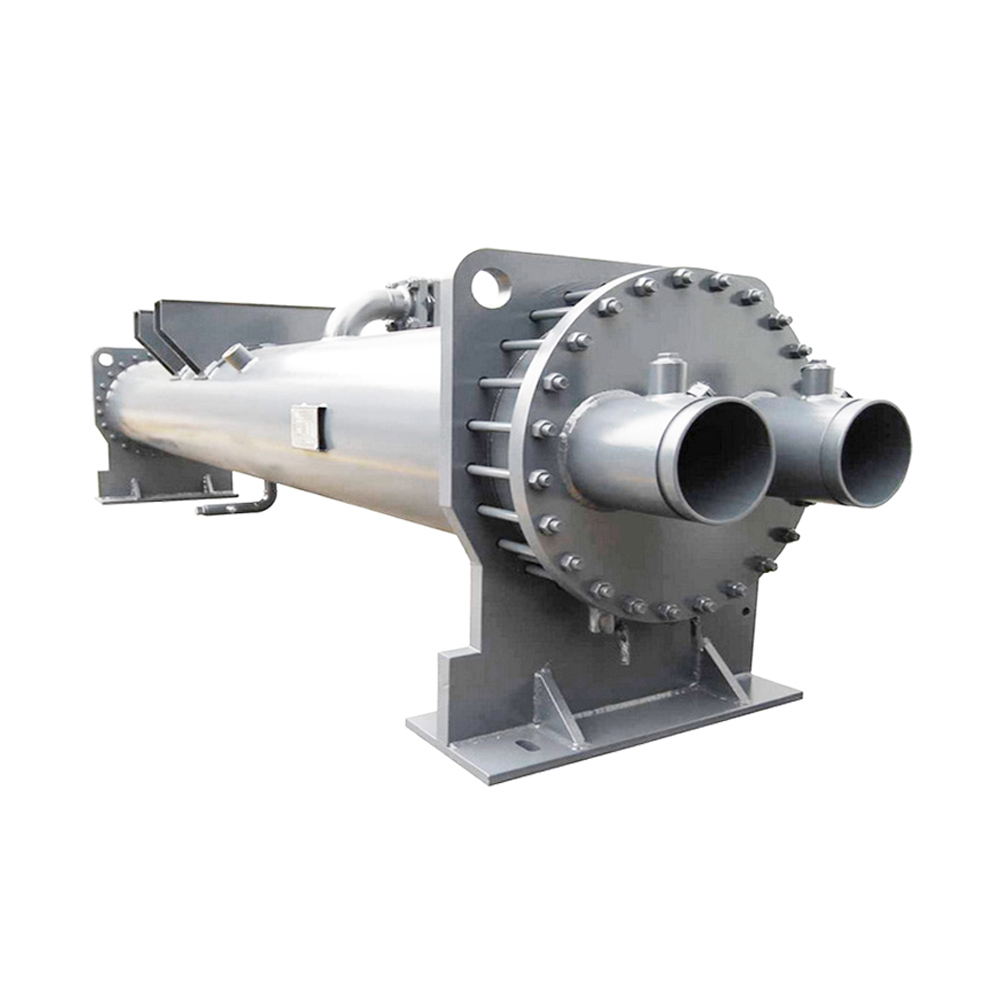
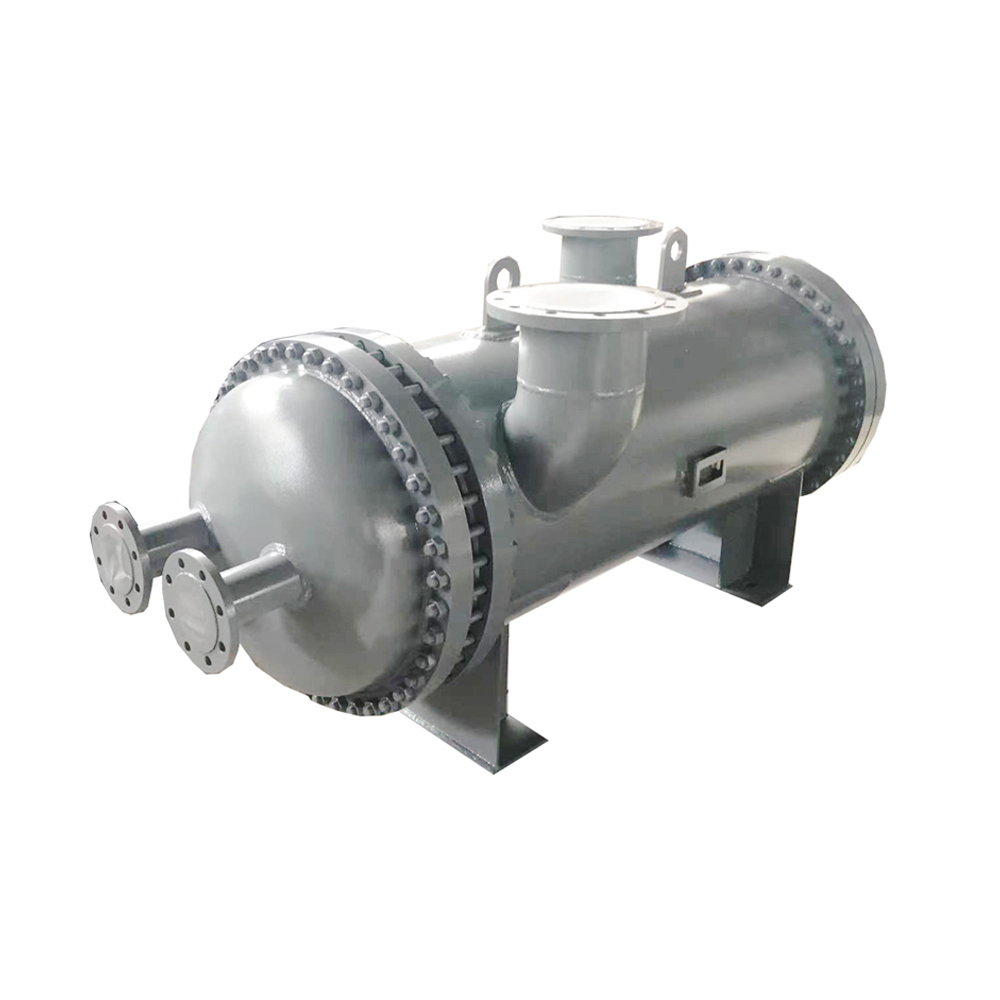
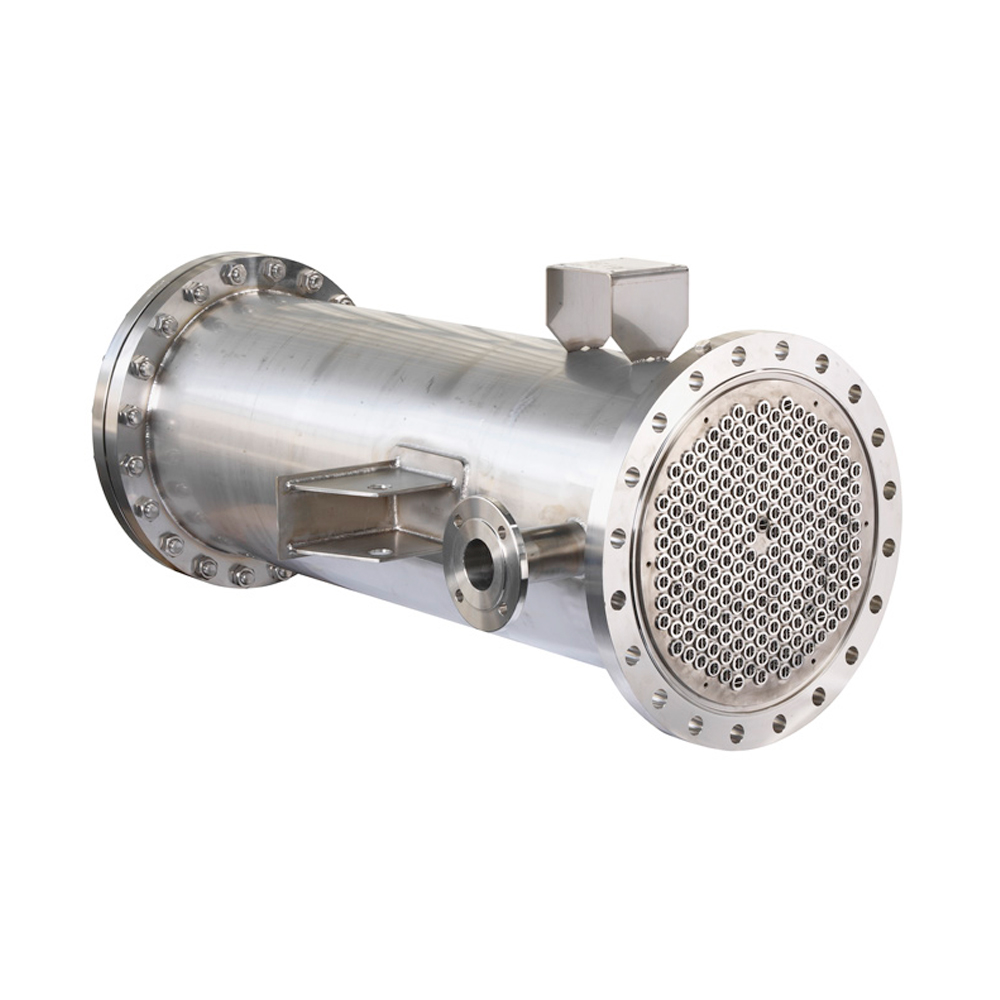
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
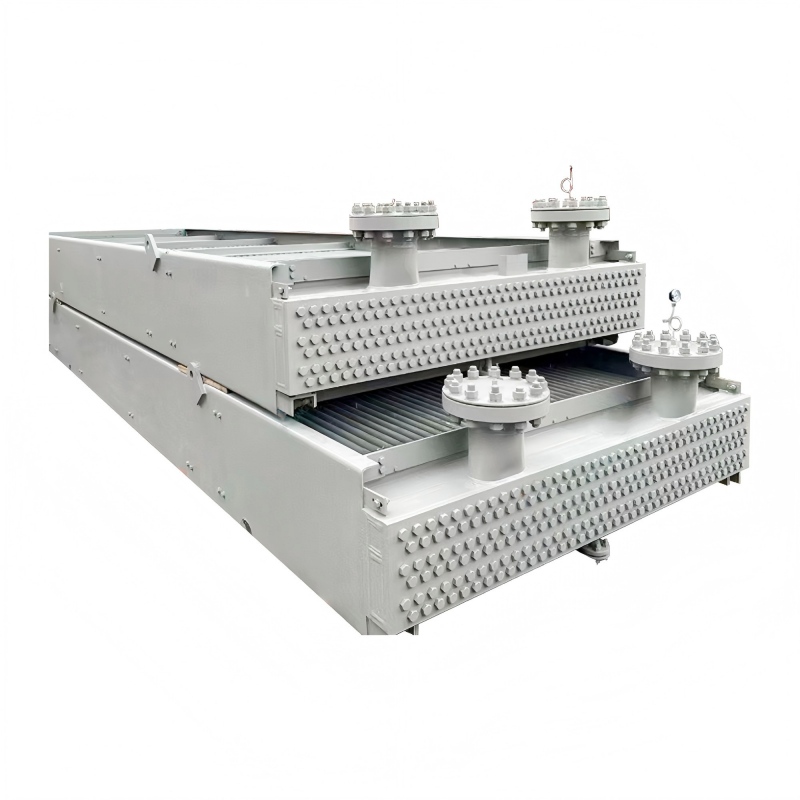
Shell and tube heat exchangers are robust and widely used in industrial applications. They consist of a bundle of tubes housed within a cylindrical shell. One fluid flows through the tubes, while the other flows across the tubes in the shell. This design allows for a large heat transfer area and can handle high pressures and temperatures. Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd (https://www.ShenglinCoolers.com/) is a leading manufacturer of high-quality shell and tube heat exchangers, offering a wide range of customized solutions. However, they can be bulky and more expensive than other types.
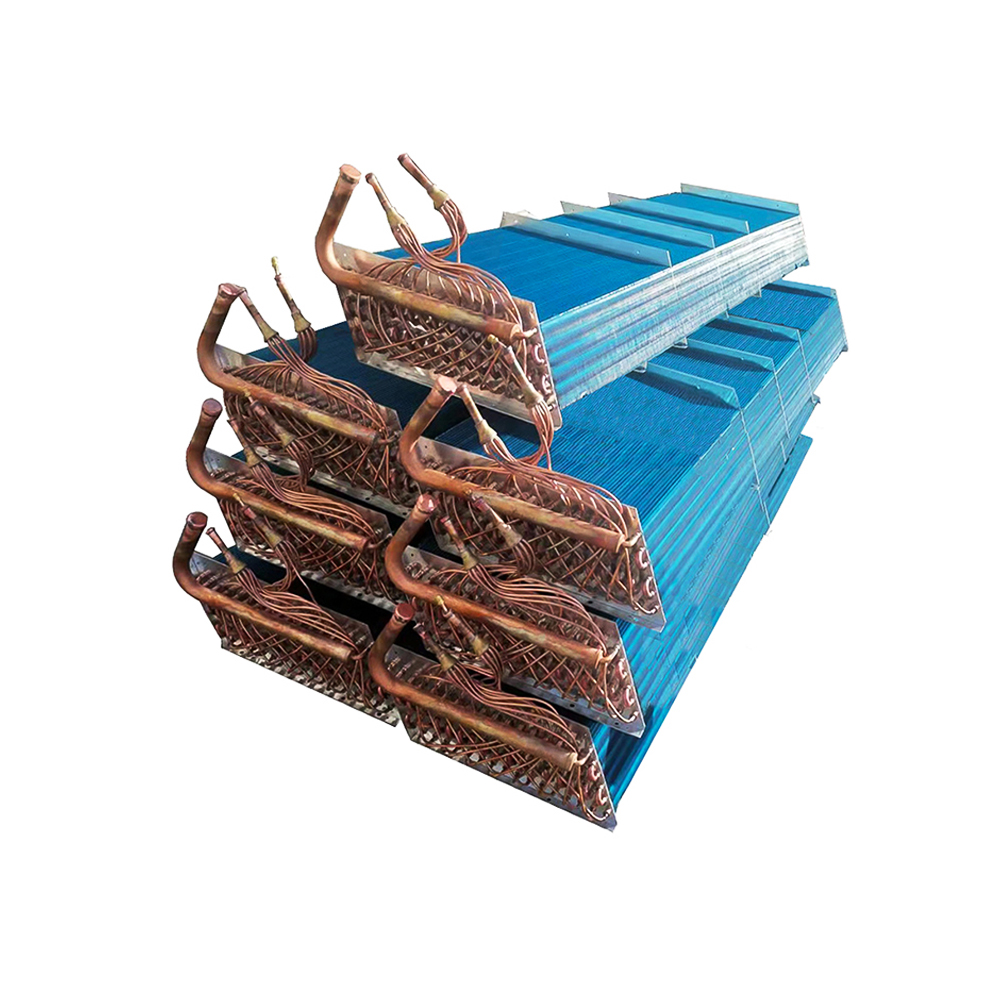
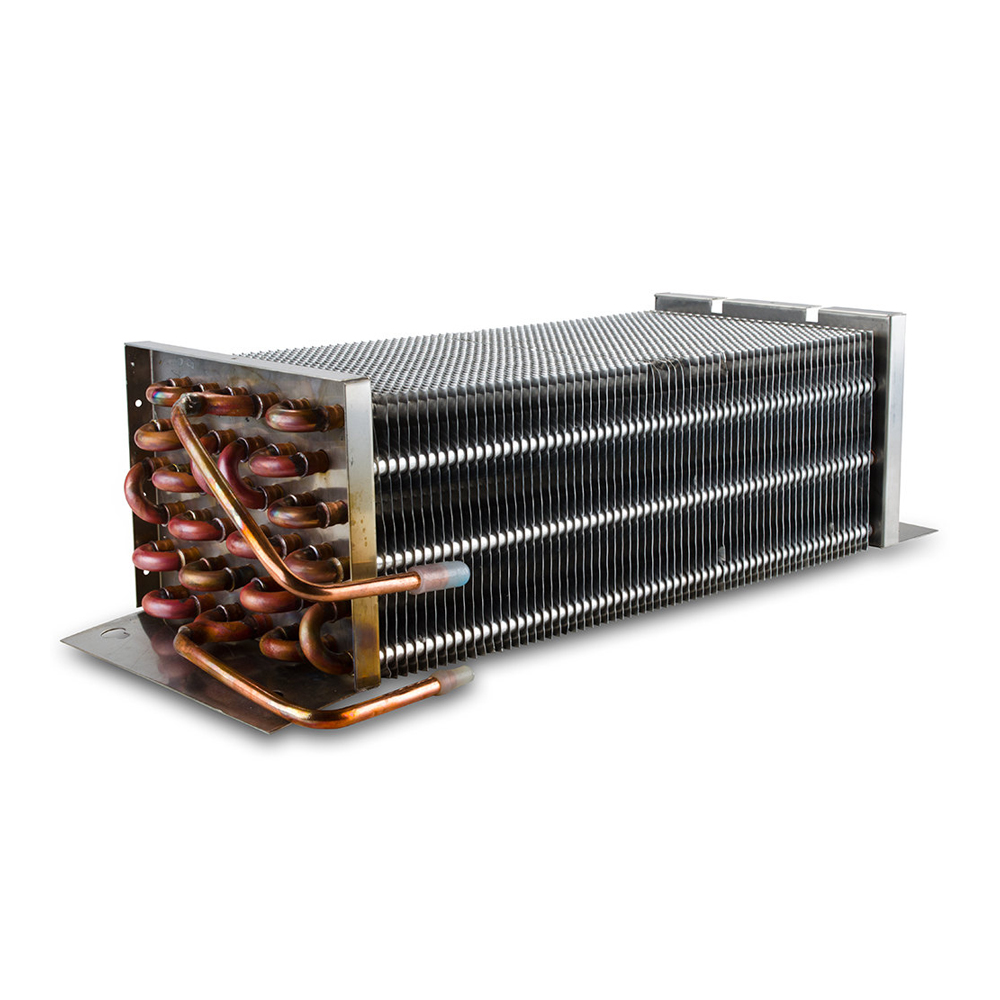
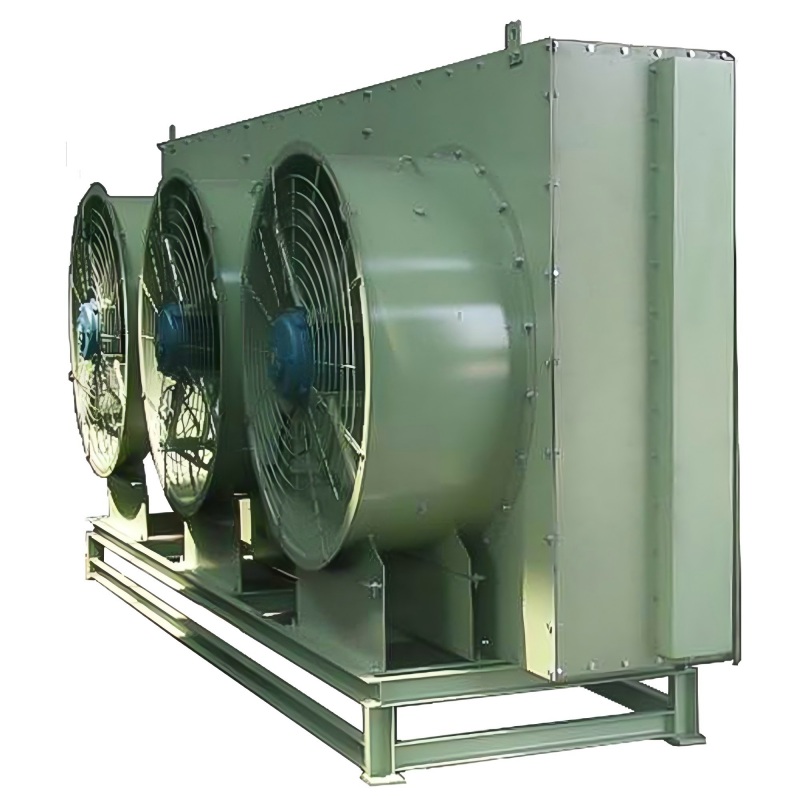
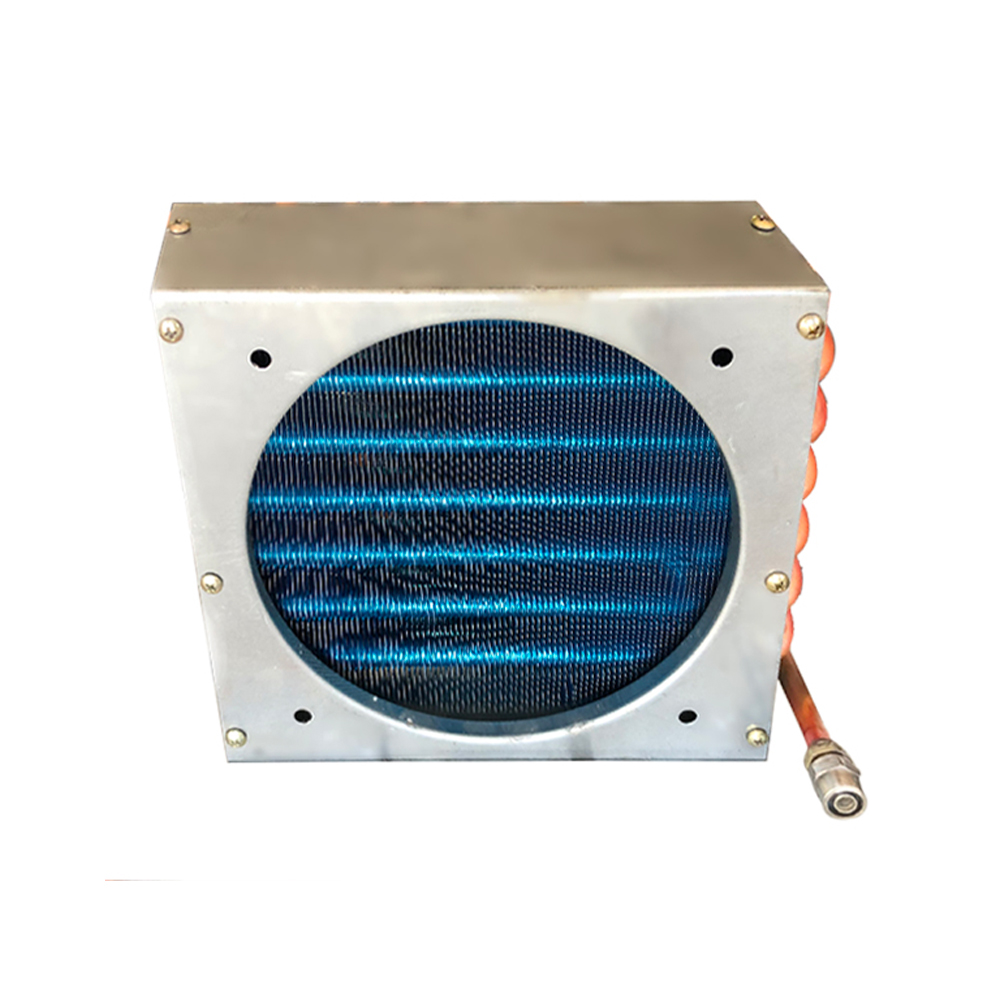
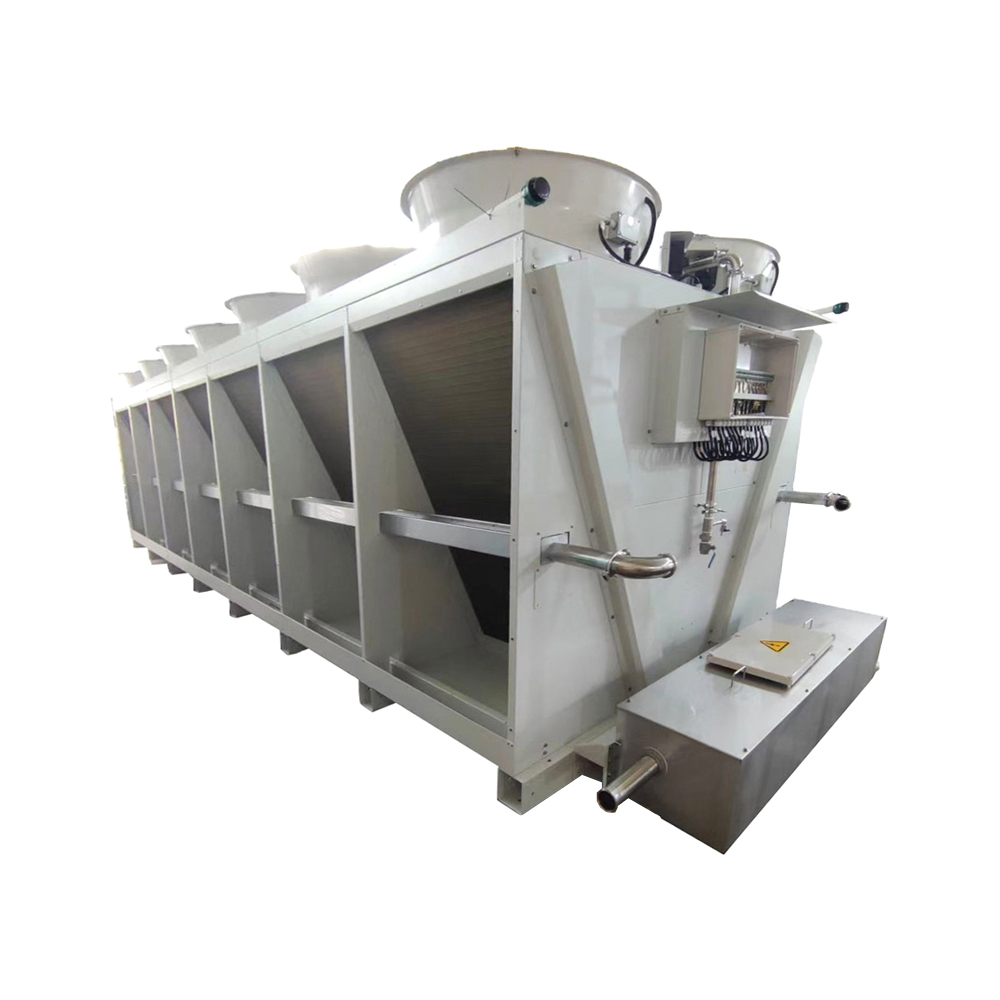
Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers
Air-cooled heat exchangers utilize air as the cooling medium. They are commonly used in applications where water is scarce or expensive. These heat exchangers often incorporate fins to increase the surface area for heat transfer to the surrounding air. They are generally less efficient than water-cooled systems but offer simplicity and lower maintenance requirements. The selection of a suitable fin design is crucial for optimal performance. Factors like air flow rate and ambient temperature significantly impact efficiency.
Other Types
Other types of heat exchangers include spiral heat exchangers (known for their self-cleaning capabilities), and scraped surface heat exchangers (ideal for viscous fluids). The choice depends heavily on the application's specific requirements and constraints.
Selecting the Right Heat Exchanger
Choosing the appropriate heat exchanger involves considering several factors:
- Fluid Properties: Viscosity, specific heat, and fouling tendencies of the fluids involved.
- Temperature Difference: The temperature difference between the hot and cold fluids affects the heat transfer rate.
- Pressure: Operating pressures determine the design requirements of the heat exchanger.
- Flow Rate: The desired flow rates of the fluids influence the size and design of the heat exchanger.
- Space Constraints: The available space dictates the size and type of heat exchanger that can be used.
- Budget: The cost of the heat exchanger and its maintenance must be considered.
Heat Exchanger Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of heat exchangers. This includes regular cleaning to remove fouling, inspection for leaks or damage, and appropriate chemical treatments to prevent corrosion.
Comparison Table: Common Heat Exchanger Types
| Type | Efficiency | Cost | Maintenance | Applications |
| Plate | High | Moderate | Moderate | Food processing, HVAC |
| Shell and Tube | Moderate | High | Moderate | Industrial applications |
| Air-Cooled | Low | Low | Low | Applications where water is scarce |
This information is for general guidance only. Specific requirements will vary depending on the individual application. Always consult with a qualified engineer to determine the best heat exchanger solution for your specific needs.














.jpg)