This comprehensive guide explores the design, operation, and applications of shell and tube heat exchangers. We'll delve into the various types, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for selecting the right exchanger for your specific needs. Learn about key parameters, maintenance, and troubleshooting tips. Whether you're an engineer, technician, or simply curious about this crucial piece of industrial equipment, this article provides a detailed overview.
Types of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Fixed Tubesheet Heat Exchangers
Fixed tubesheet heat exchangers are the most common type. The tubes are rigidly fixed to the tubesheets, simplifying construction but limiting thermal expansion capabilities. This type is best suited for applications with minimal temperature differences between the fluids. They are robust and relatively inexpensive to manufacture. However, potential for tube damage due to thermal stress exists.
U-Tube Heat Exchangers
In a U-tube heat exchanger, the tubes are bent into a U-shape, allowing for thermal expansion without putting excessive stress on the tubesheets. This design is advantageous for high-temperature applications and situations where cleaning is required. Access to both sides of the tubesheets allows easy tube cleaning. However, U-tube exchangers can be more expensive than fixed tubesheet designs, and cleaning the U-bends themselves can be challenging.
Floating Head Heat Exchangers
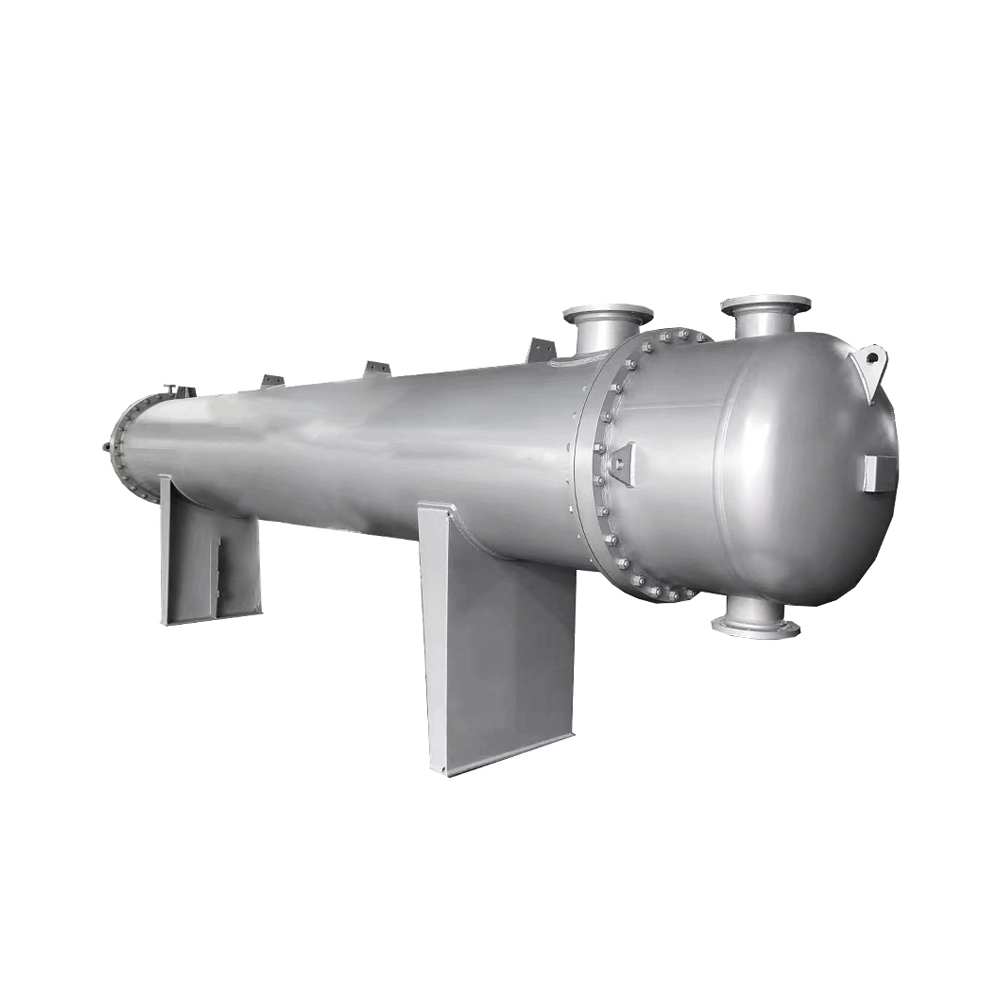
Floating head heat exchangers are designed to accommodate significant thermal expansion. One tubesheet is fixed, while the other is allowed to float, accommodating the expansion and contraction of the tubes. This design is ideal for applications with substantial temperature differences or pressure variations. Although more complex and expensive, they provide superior durability and reliability in demanding environments. Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd (https://www.ShenglinCoolers.com/) offers a range of high-quality floating head shell and tube heat exchangers.
Key Parameters and Considerations
Selecting the appropriate shell and tube heat exchanger requires careful consideration of several key parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
| Fluid Properties | Viscosity, density, specific heat, thermal conductivity, and corrosiveness are crucial. |
| Temperature Difference | The temperature difference between the hot and cold fluids impacts heat transfer efficiency and exchanger design. |
| Pressure | Operating pressure affects material selection and exchanger design. |
| Heat Duty | This refers to the amount of heat that needs to be transferred. |
| Fouling | The build-up of deposits on heat transfer surfaces reduces efficiency. Regular cleaning is necessary. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Advantages:
- High heat transfer efficiency
- Can handle high pressures and temperatures
- Wide range of fluids and applications
- Relatively easy to maintain and clean (depending on the type)
Disadvantages:
- Can be expensive
- Can be bulky and require significant space
- Potential for fouling and scaling
- Complex design for some types
Applications of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Shell and tube heat exchangers are used across numerous industries, including:
- Power generation
- Chemical processing
- Oil and gas refining
- Refrigeration
- HVAC systems
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is essential for optimal performance and longevity of a shell and tube heat exchanger. This includes regular inspections, cleaning, and potential repairs. Troubleshooting involves identifying and addressing issues such as reduced heat transfer efficiency, leaks, or fouling. Regular cleaning is crucial to maintain efficiency. The specifics of maintenance and troubleshooting will depend heavily on the type of shell and tube heat exchanger installed and the fluids used.
For further information on selecting and maintaining your shell and tube heat exchanger, consult with a specialist such as Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd. (https://www.ShenglinCoolers.com/).