Fin type heat exchangers are crucial components in various industrial and commercial applications, facilitating efficient heat transfer between two fluids. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of these devices, covering their design principles, different types, material selection, advantages, and disadvantages. Understanding fin type heat exchangers is crucial for optimizing thermal performance and system efficiency. We'll also look at specific examples and considerations for choosing the right heat exchanger for your needs.
Types of Fin Type Heat Exchangers
Several types of fin type heat exchangers exist, each designed to optimize performance for specific applications. The choice depends on factors such as fluid properties, pressure drop requirements, and heat transfer needs.
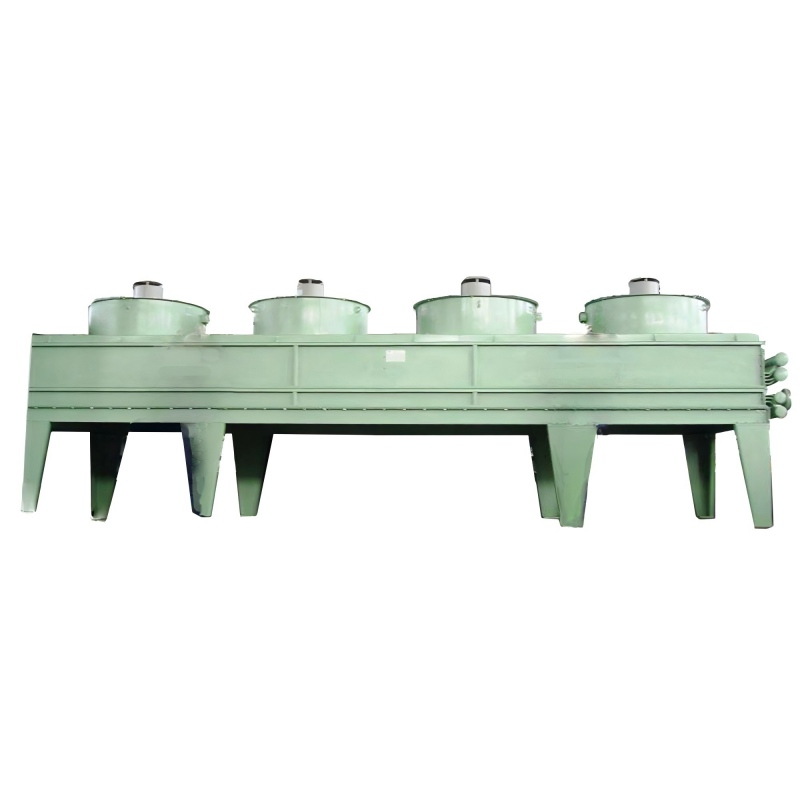
Plate Fin Heat Exchangers
Plate fin heat exchangers are characterized by their compact design and high surface area-to-volume ratio. They consist of thin, corrugated plates with fins pressed or brazed onto them. These are commonly used in HVAC systems and other applications requiring high efficiency in a small space. They are often made from aluminum or copper due to their excellent thermal conductivity.
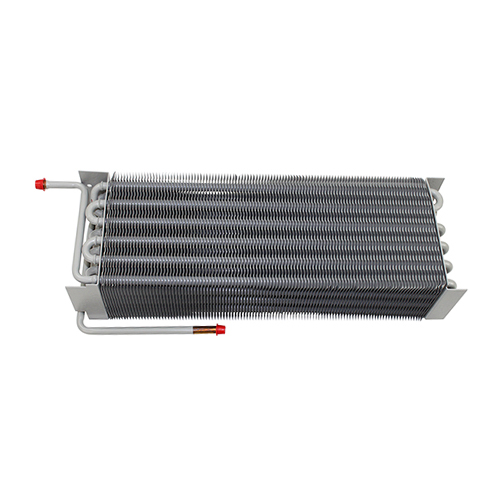
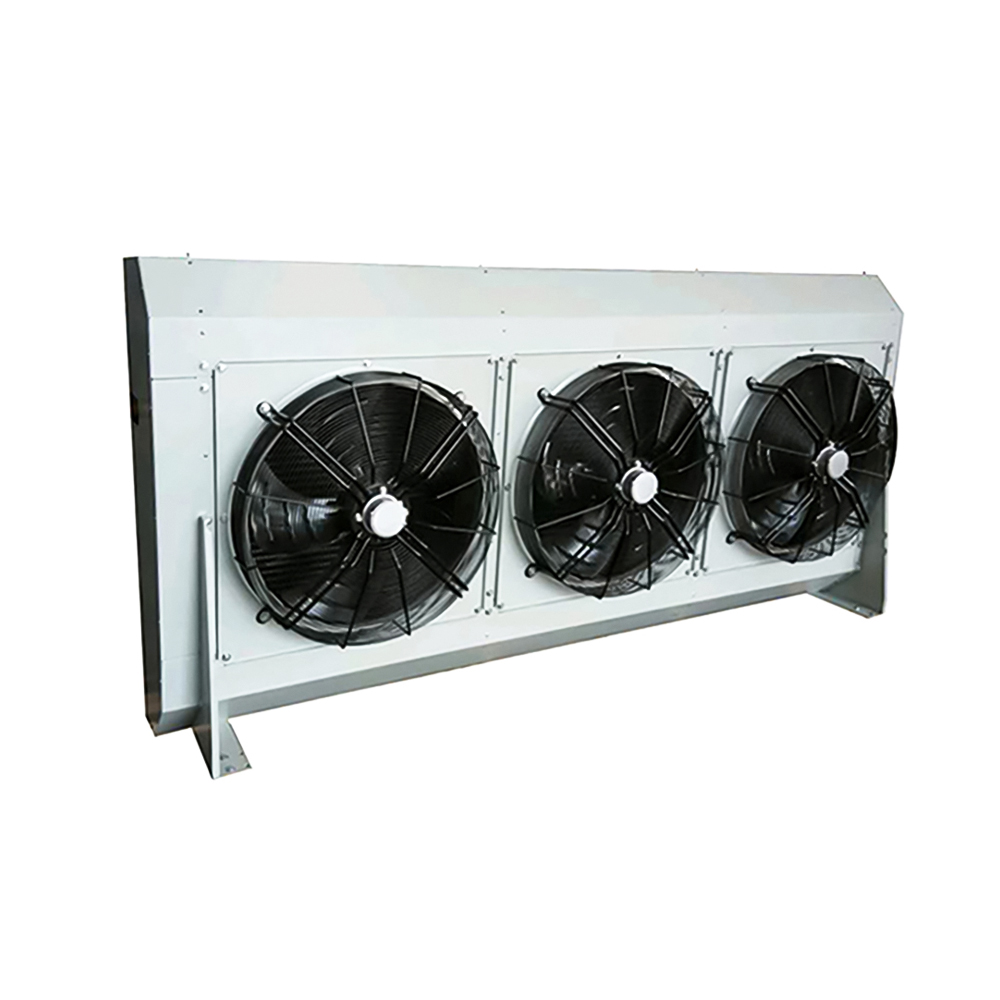
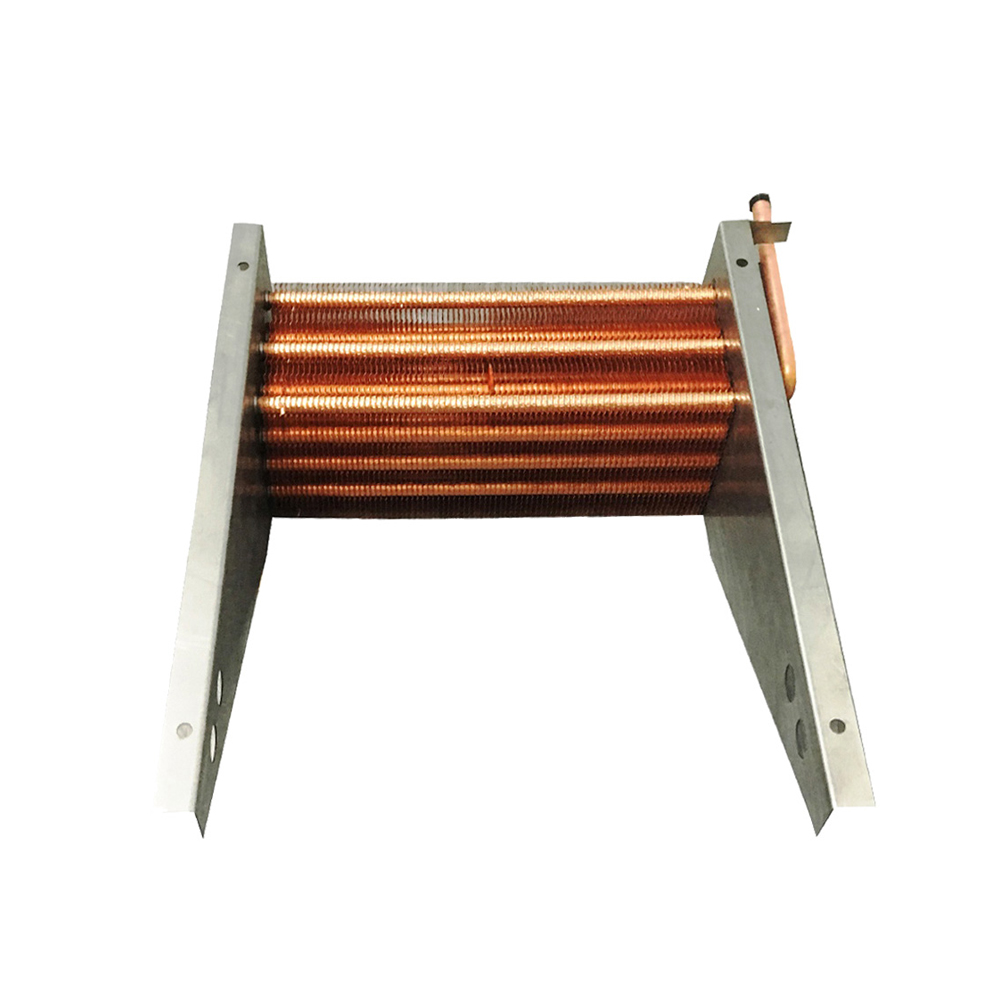
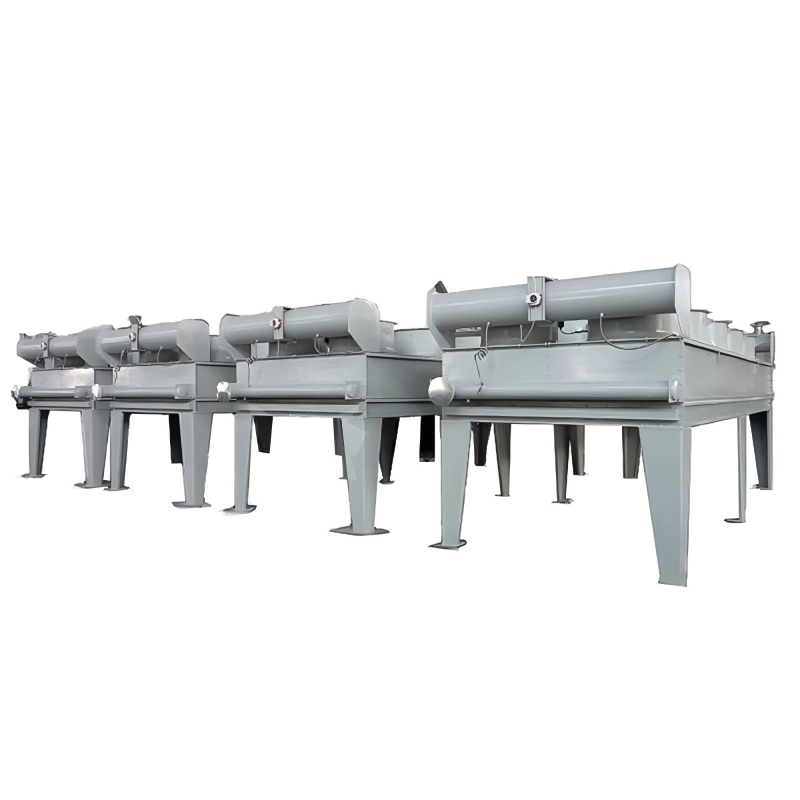
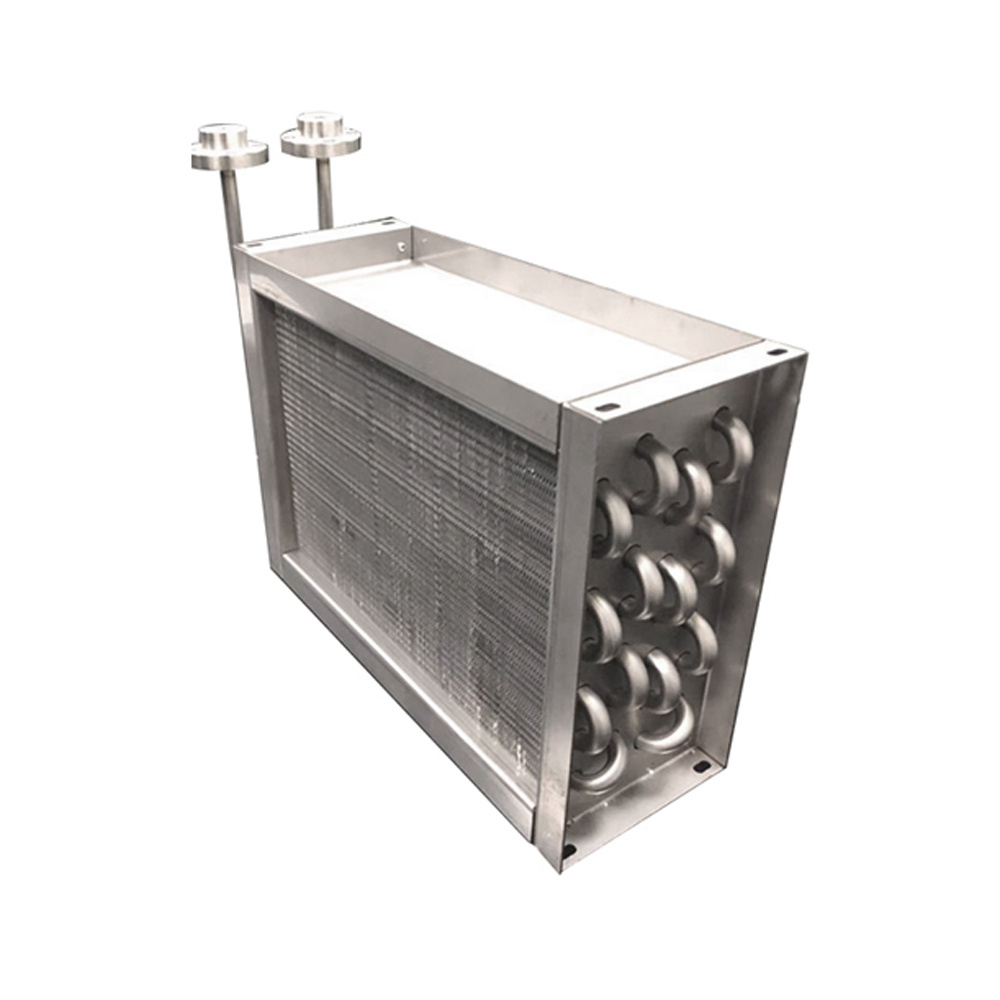
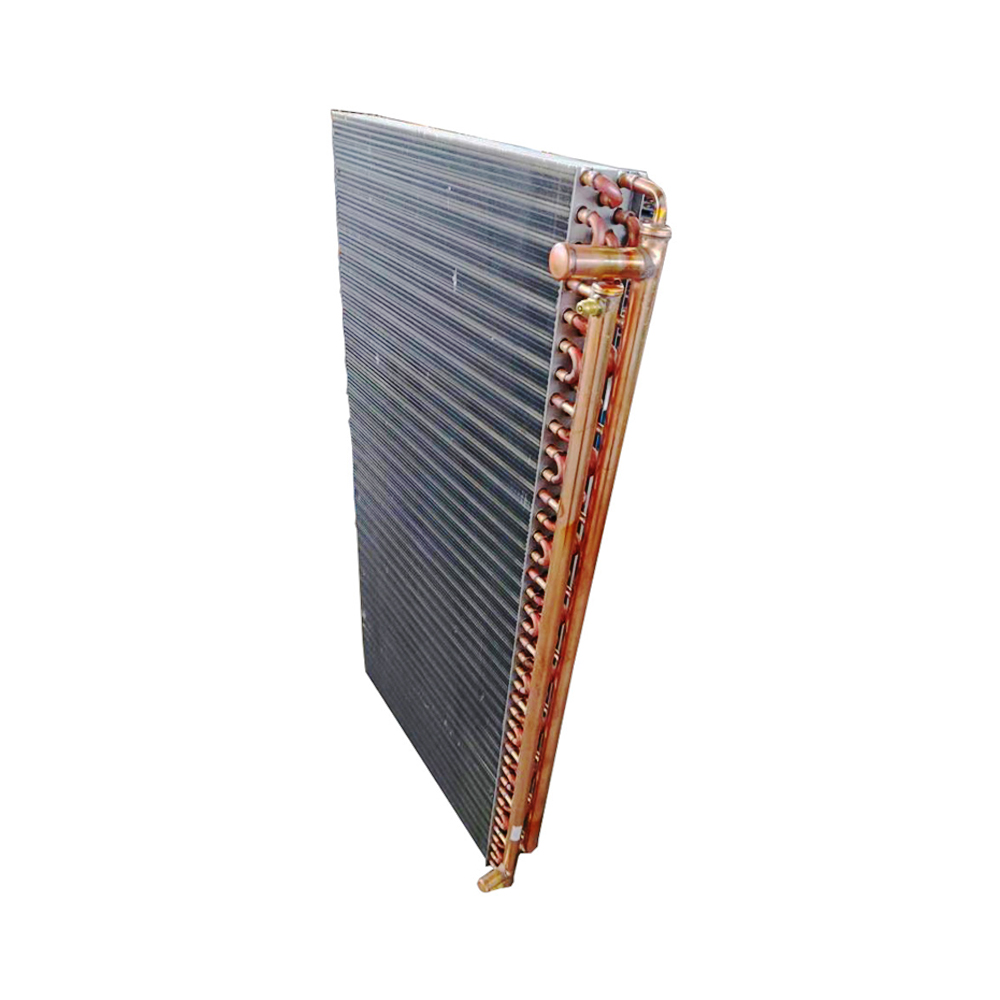
Tube Fin Heat Exchangers
Tube fin heat exchangers are characterized by tubes with fins attached to enhance heat transfer. These fins can be either on the inside or outside of the tubes, depending on the application. This type is frequently employed in power generation, refrigeration, and air conditioning systems, often utilizing materials like copper, aluminum, or steel.
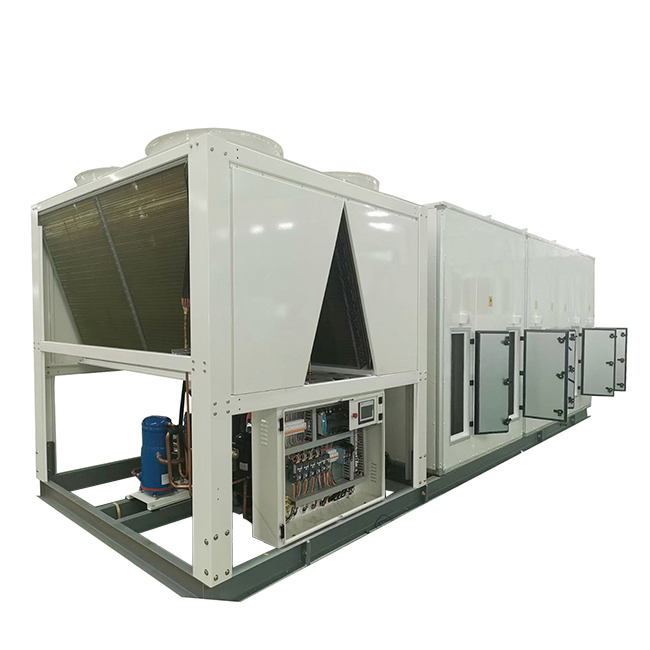
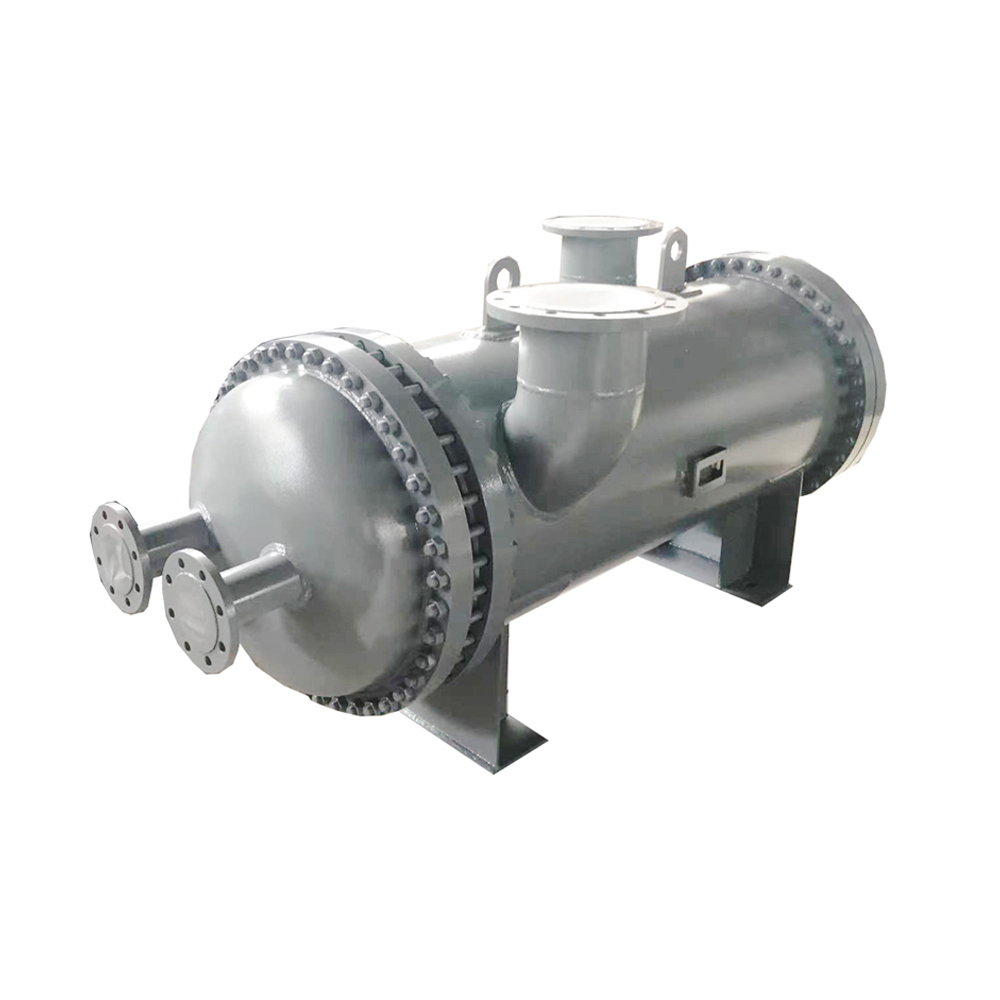
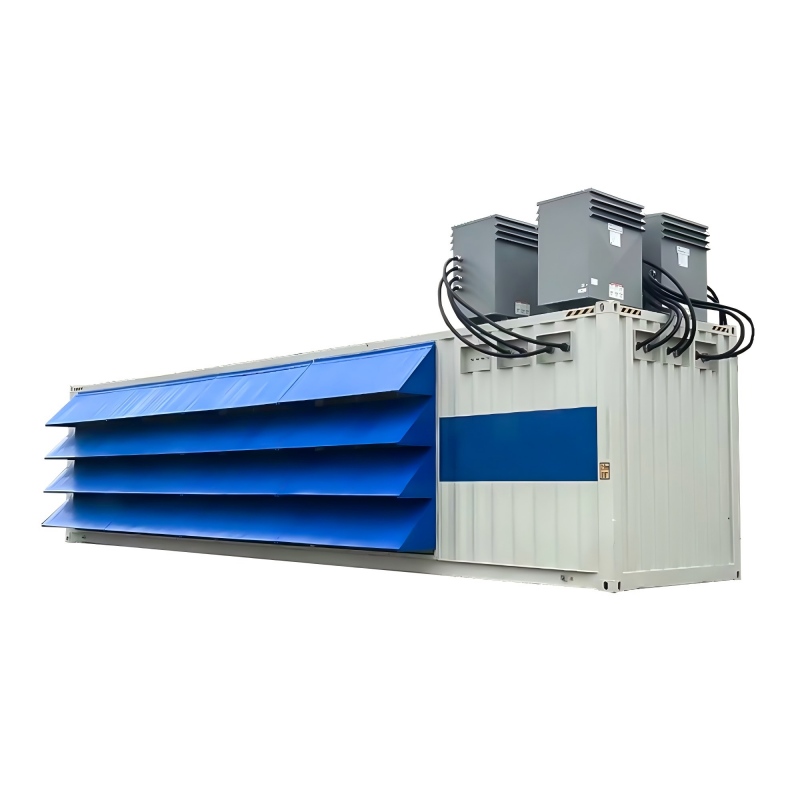
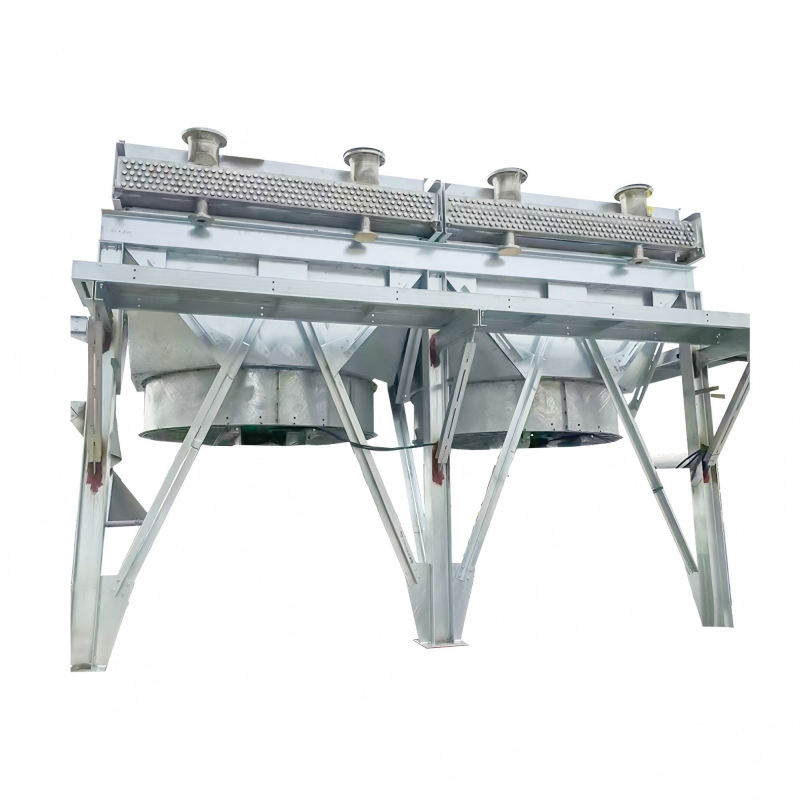
Compact Heat Exchangers
Compact heat exchangers are designed to maximize heat transfer surface area within a minimal volume. They frequently use complex geometries and multiple flow paths to achieve optimal performance. These are prevalent in aerospace and automotive applications where weight and space are critical concerns. Materials commonly used include aluminum alloys, stainless steel, and titanium.
Material Selection for Fin Type Heat Exchangers
The choice of material significantly impacts the performance and longevity of a fin type heat exchanger. Key considerations include thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and cost.
| Material | Thermal Conductivity | Corrosion Resistance | Cost |
| Aluminum | High | Moderate | Low |
| Copper | Very High | High | Moderate |
| Stainless Steel | Moderate | Very High | High |
Table 1: Material Comparison for Fin Type Heat Exchangers
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fin Type Heat Exchangers
Fin type heat exchangers offer several advantages but also come with some limitations.
Advantages:
- High heat transfer efficiency due to increased surface area.
- Compact design, ideal for space-constrained applications.
- Variety of designs and materials to suit different needs.
Disadvantages:
- Potential for fouling and reduced efficiency over time.
- Pressure drop can be significant in certain designs.
- Cost can vary depending on material and complexity.
Selecting the Right Fin Type Heat Exchanger
Choosing the appropriate fin type heat exchanger requires careful consideration of various factors. These include the specific application, fluid properties, required heat transfer rate, pressure drop limitations, and available space. Consulting with a specialist from a reputable company like Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd can provide valuable assistance in selecting the optimal solution for your needs. They offer a range of high-quality fin type heat exchangers designed for various industrial applications.
Conclusion
Fin type heat exchangers are essential components in countless industrial and commercial applications. Understanding their different types, materials, and selection criteria is vital for maximizing thermal efficiency and overall system performance. By considering the factors discussed in this guide, you can make informed decisions to optimize your heat transfer needs.


















.jpg)









