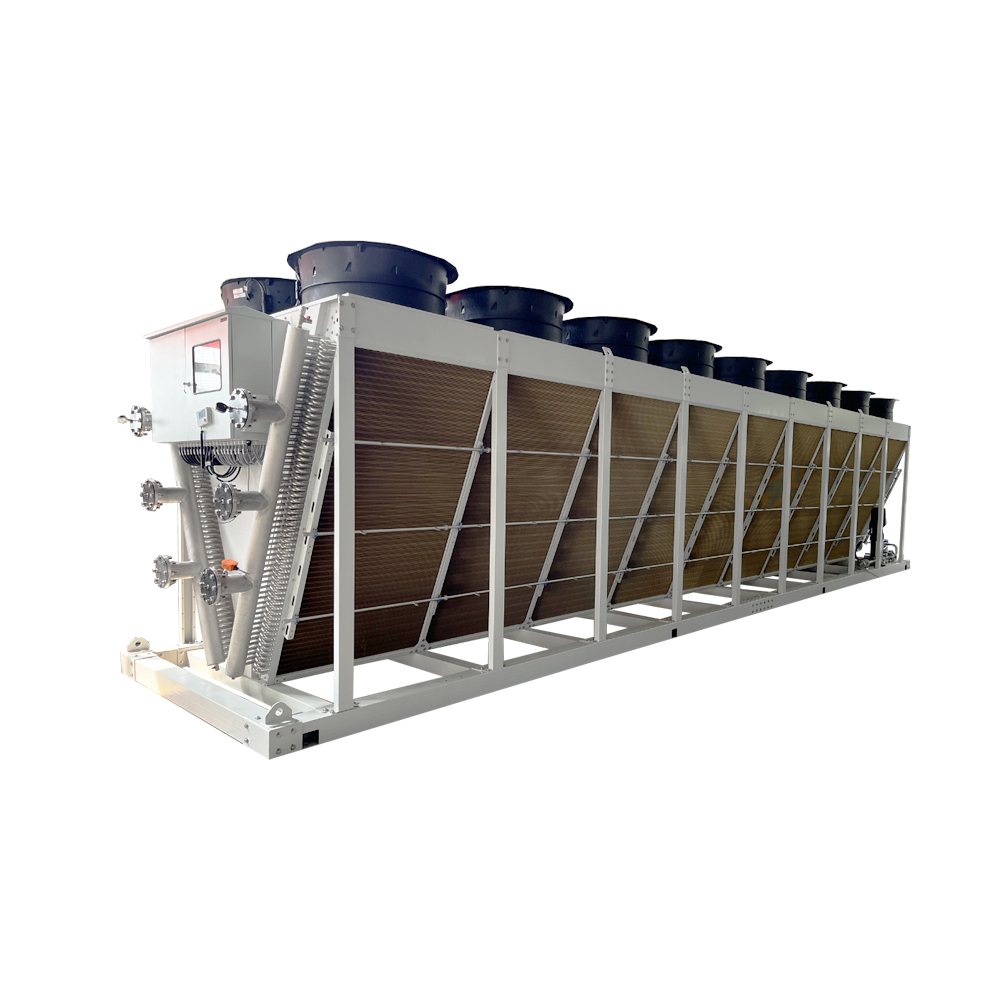
This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of dry cooling towers, offering a detailed understanding of their functionality, applications, advantages, and disadvantages. We'll delve into various types, crucial factors for selection, and provide insights to help you make informed decisions based on your specific needs. Learn about the environmental impact, maintenance considerations, and the role of dry cooling towers in efficient industrial processes.
What is a Dry Cooling Tower?
Unlike wet cooling towers that use water evaporation for heat dissipation, a dry cooling tower utilizes air as the primary cooling medium. Heat from a process, typically industrial, is transferred to the air via a heat exchanger. This method eliminates water usage, minimizing water consumption and reducing the environmental impact associated with water evaporation and the formation of plumes.
Types of Dry Cooling Towers
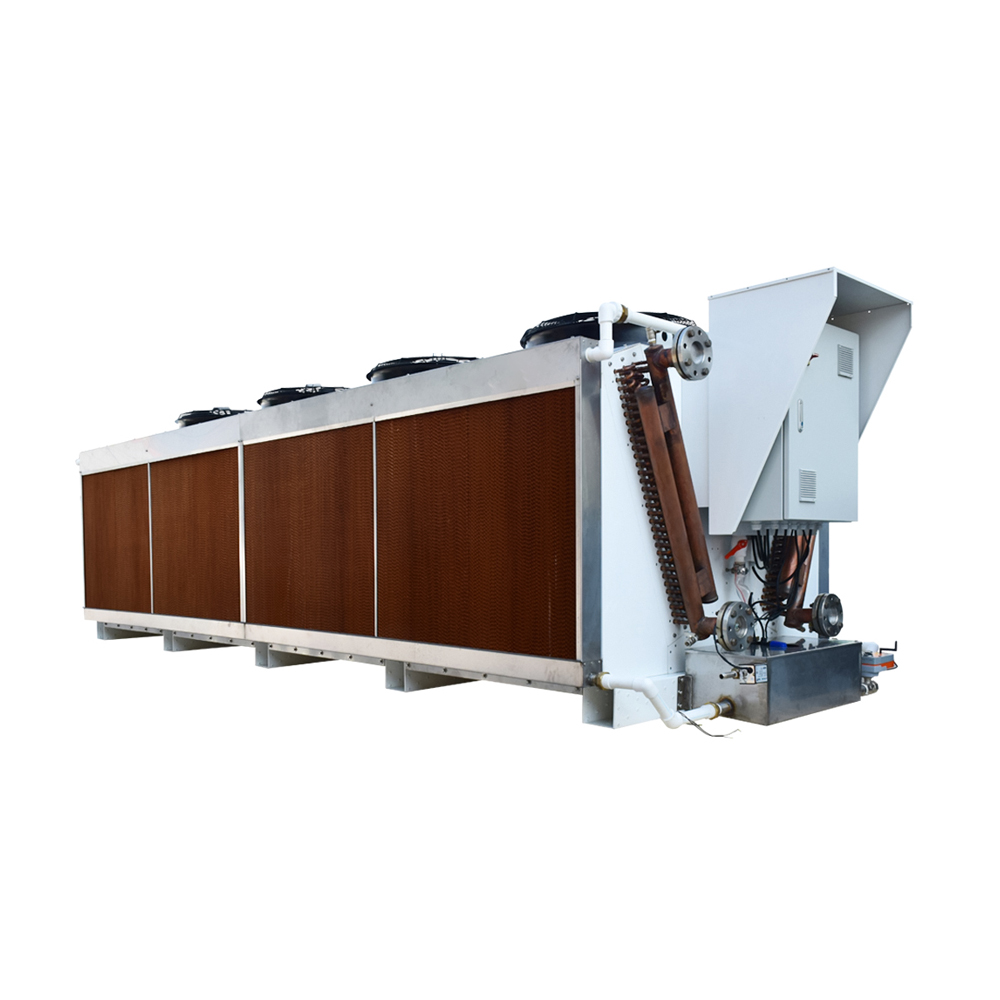
Air-Cooled Condensers
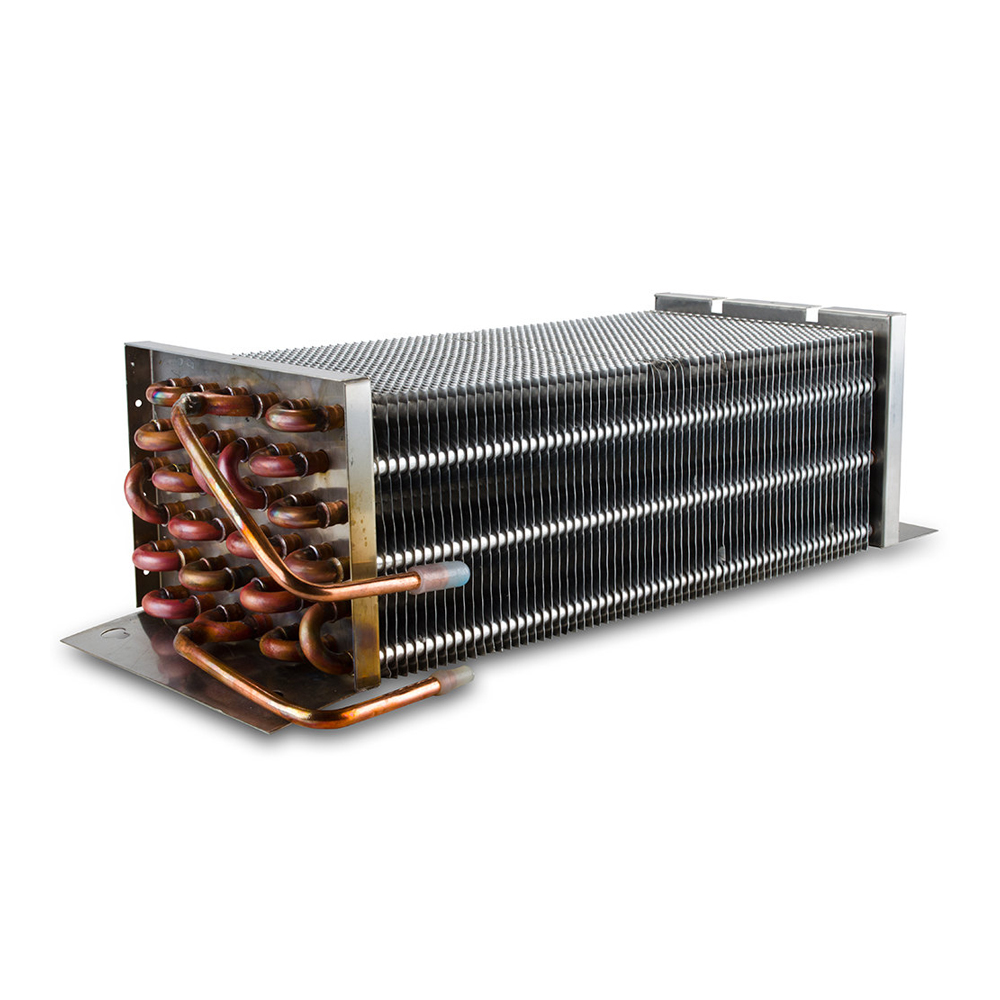
Air-cooled condensers are a common type of dry cooling tower. They directly cool the refrigerant or process fluid using air, often employing finned tubes for efficient heat transfer. This design is simple and reliable, making it suitable for various applications.
Indirect Dry Cooling Towers
Indirect dry cooling towers utilize a heat exchanger to separate the cooling air from the process fluid. This prevents air contamination and is beneficial in situations where air cleanliness is critical. These systems often offer higher efficiency than direct air-cooled systems.
Hybrid Cooling Towers
Combining the features of wet and dry cooling towers, hybrid systems offer a balance between efficiency and water consumption. They utilize both air and water for cooling, optimizing performance based on ambient conditions. This approach provides flexibility and adapts to varying environmental demands.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Dry Cooling Tower
Selecting the appropriate dry cooling tower requires careful consideration of several key factors:
| Factor | Description |
| Cooling Capacity | The amount of heat the tower needs to dissipate. This is determined by the process requirements. |
| Ambient Air Temperature | Higher ambient temperatures reduce the efficiency of dry cooling towers. |
| Space Requirements | Dry cooling towers often require a larger footprint compared to wet cooling towers. |
| Capital and Operating Costs | Initial investment and ongoing maintenance expenses should be considered. |
Table 1: Key factors influencing the selection of a dry cooling tower.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Dry Cooling Towers
Dry cooling towers offer several advantages but also have some limitations:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Reduced water consumption | Higher capital costs |
| Lower environmental impact | Lower efficiency compared to wet towers in some conditions |
| Reduced risk of scaling and corrosion | Larger footprint requirements |
Table 2: Advantages and disadvantages of dry cooling towers.
Maintenance and Operation
Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. This includes inspecting fans, cleaning heat exchangers, and monitoring for leaks or other issues. Proper maintenance helps extend the lifespan and efficiency of your dry cooling tower. For expert design, manufacturing, and installation of high-quality dry cooling towers, consider contacting Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd. They offer a range of solutions tailored to meet your specific cooling needs.
Conclusion
The selection of a dry cooling tower is a critical decision that involves careful consideration of several factors. By understanding the different types, advantages, and disadvantages, and by considering the specific operational requirements, you can make an informed choice that optimizes efficiency, minimizes environmental impact, and ensures cost-effectiveness for years to come. Remember to consult with experts like Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd to ensure the best solution for your specific needs.