This comprehensive guide explores the world of condensers, covering their types, applications, selection criteria, and maintenance. We'll delve into the specifics to help you understand how condensers work and choose the right one for your needs, whether it's for industrial cooling, HVAC systems, or other applications. Learn about different condenser designs, their advantages and disadvantages, and factors to consider for optimal performance and longevity. This guide also explores troubleshooting common condenser issues.
Types of Condensers
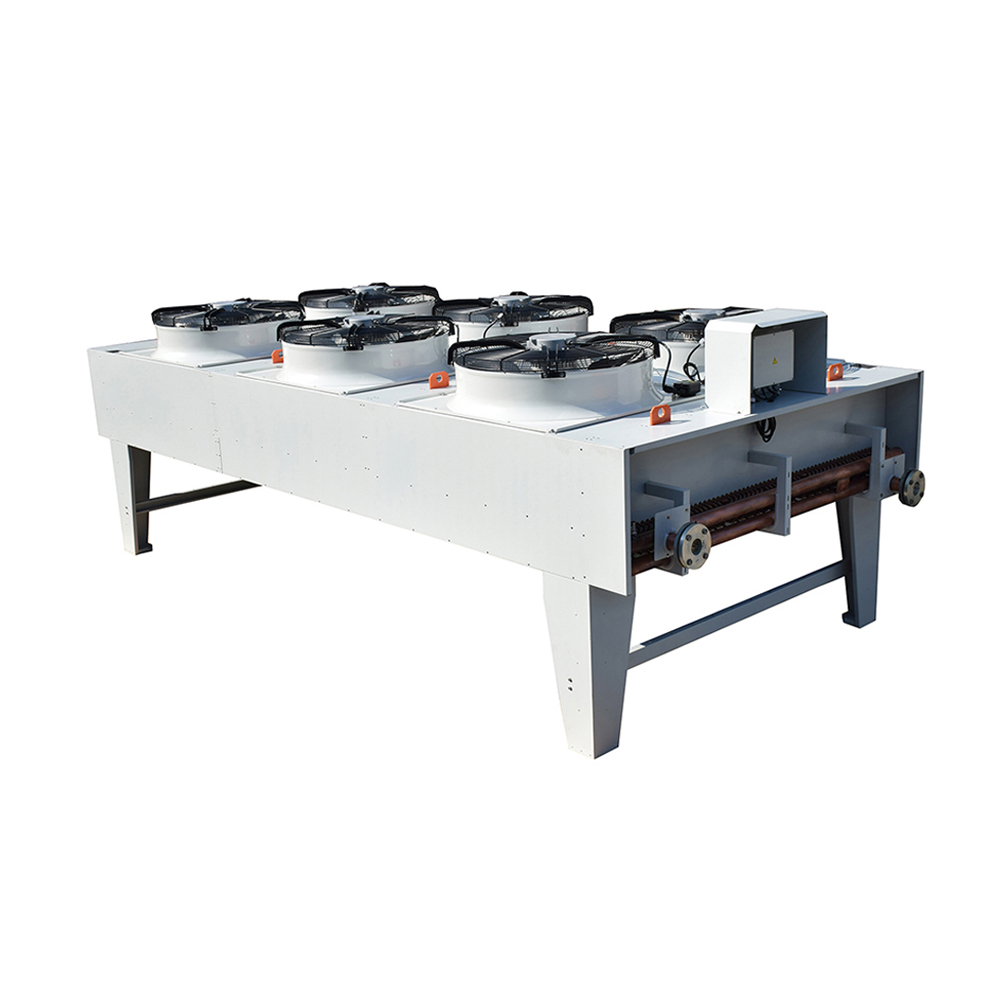
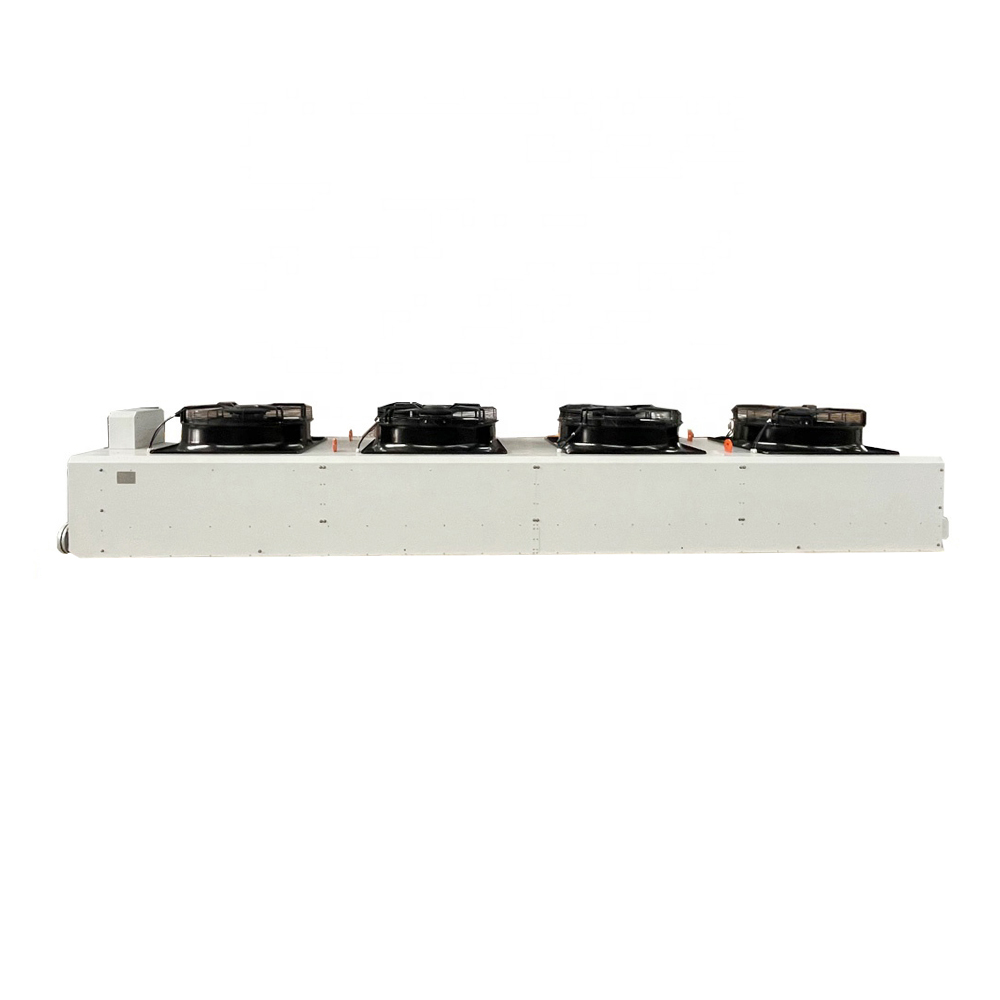
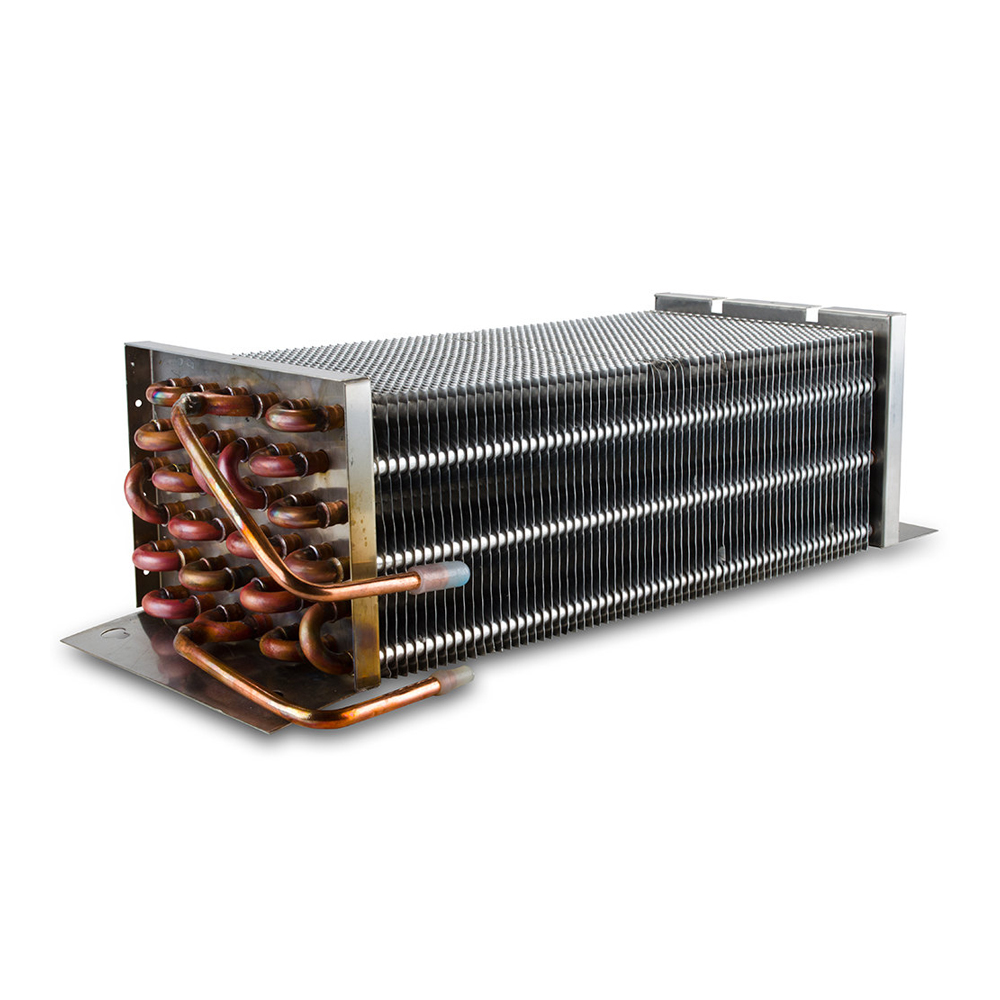
Air-Cooled Condensers
Air-cooled condensers are widely used due to their simplicity and relatively low cost. They utilize fans to blow air across finned tubes containing the refrigerant, dissipating heat into the surrounding atmosphere. These condensers are ideal for smaller applications and where water is scarce. However, their efficiency can be impacted by ambient temperature and airflow.
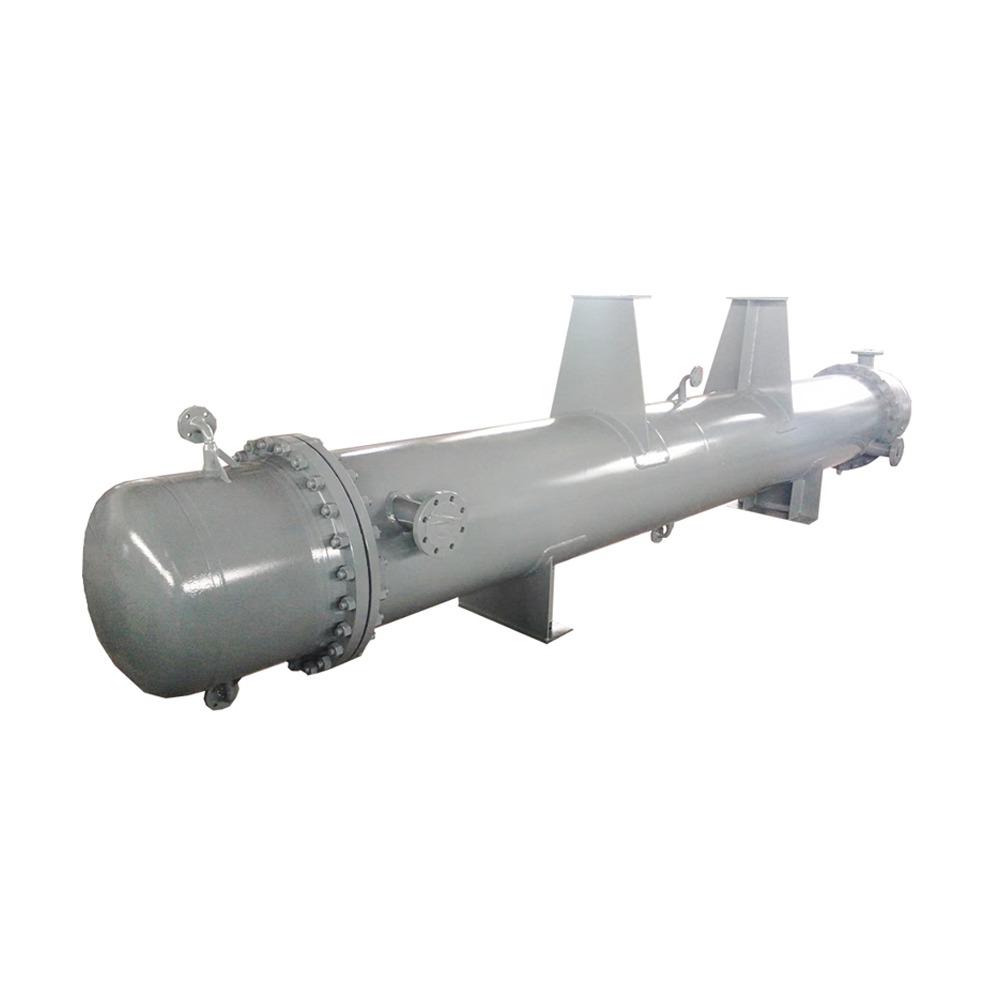
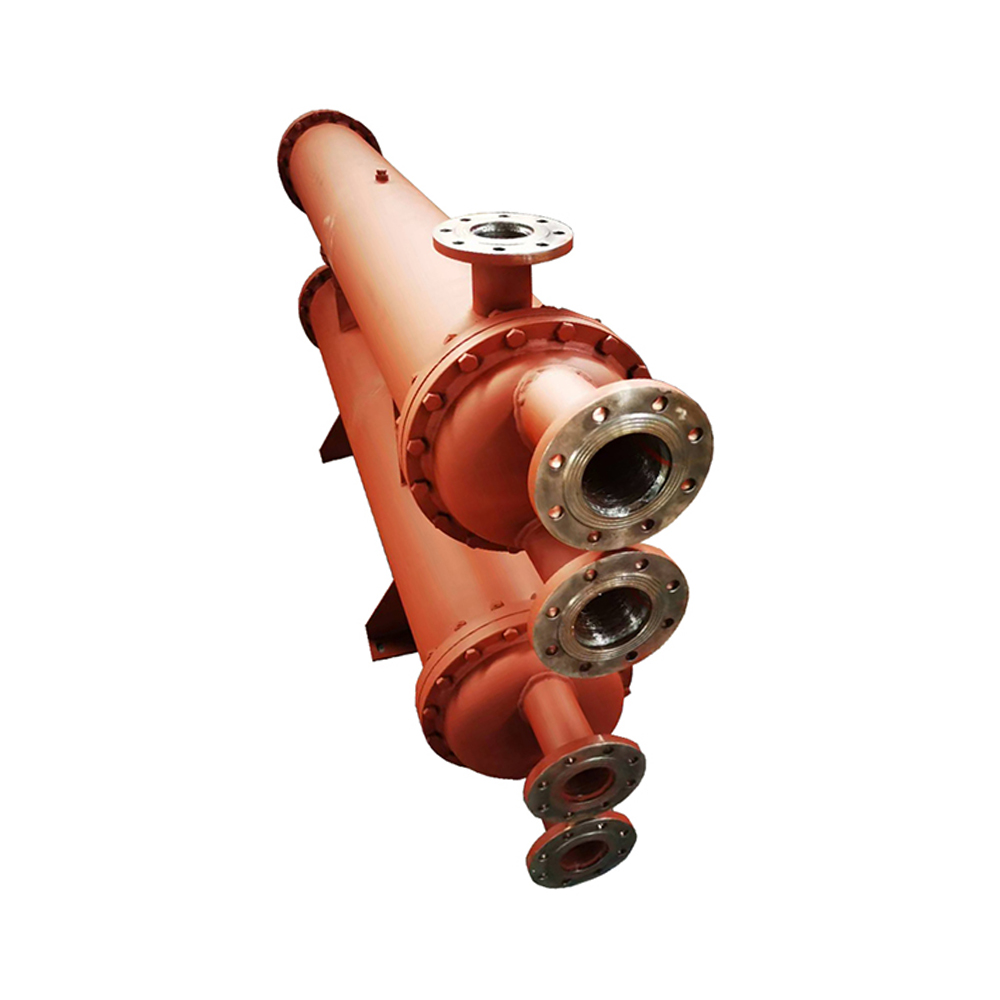
Water-Cooled Condensers
Water-cooled condensers use water to remove heat from the refrigerant. They are generally more efficient than air-cooled condensers, especially in hot climates. Water-cooled condensers are commonly employed in larger industrial refrigeration systems and power plants. The efficiency depends heavily on the availability of cooling water and its temperature.
Evaporative Condensers
Evaporative condensers combine air and water cooling for increased efficiency. Water is sprayed over the condenser coils, and air is blown across them. As the water evaporates, it absorbs heat, resulting in a more efficient cooling process. This type is particularly suitable for applications where water conservation is a concern, offering a balance between air and water-cooled systems.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Condenser
Selecting the appropriate condenser requires careful consideration of several factors:
Capacity
The condenser must have sufficient capacity to handle the heat load generated by the system. This is determined by the refrigeration system's cooling capacity (measured in tons or kW).
Operating Conditions
Ambient temperature, airflow, and water availability significantly influence condenser performance. Consider these factors when determining the type and size of condenser.
Refrigerant Type
Different refrigerants have varying properties, and the condenser must be compatible with the refrigerant used in the system. Check compatibility with your specific refrigerant to ensure optimal function.
Maintenance Requirements
Consider the ease of maintenance for each condenser type. Some condensers require more frequent cleaning or servicing than others. Regular maintenance can extend a condenser's operational life.
Condenser Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal condenser performance and longevity. Common issues include:
- Clogged fins: Regular cleaning of the fins is necessary to ensure efficient heat transfer.
- Low refrigerant levels: Regular refrigerant level checks are essential to prevent performance degradation.
- Faulty fans or pumps: Check for proper functionality to ensure sufficient airflow or water circulation.
Comparison of Condenser Types
| Feature | Air-Cooled | Water-Cooled | Evaporative |
| Efficiency | Lower | Higher | Moderate to High |
| Cost | Lower | Higher | Moderate |
| Water Usage | None | High | Moderate |
For high-performance industrial cooling solutions, consider exploring the options available at Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd. They offer a wide range of condenser solutions tailored to various industrial needs.
This information is for general guidance only. Always consult with a qualified professional for specific applications and installations.














.jpg)