This guide provides a comprehensive overview of China heating and cooling coils, covering their types, applications, selection criteria, and key considerations for optimal performance. We delve into the factors influencing efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions for your specific needs. Learn about different coil materials, fin designs, and manufacturing processes prevalent in the Chinese market.
Types of Heating and Cooling Coils
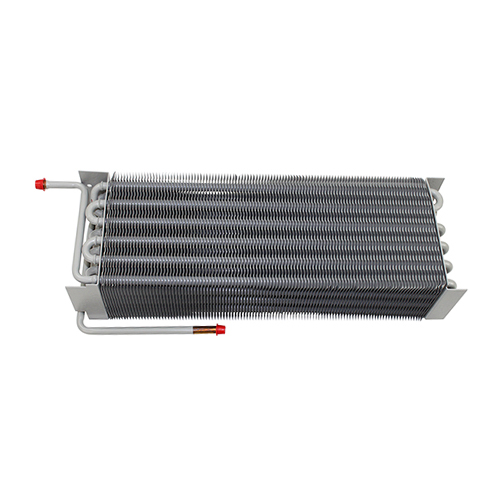
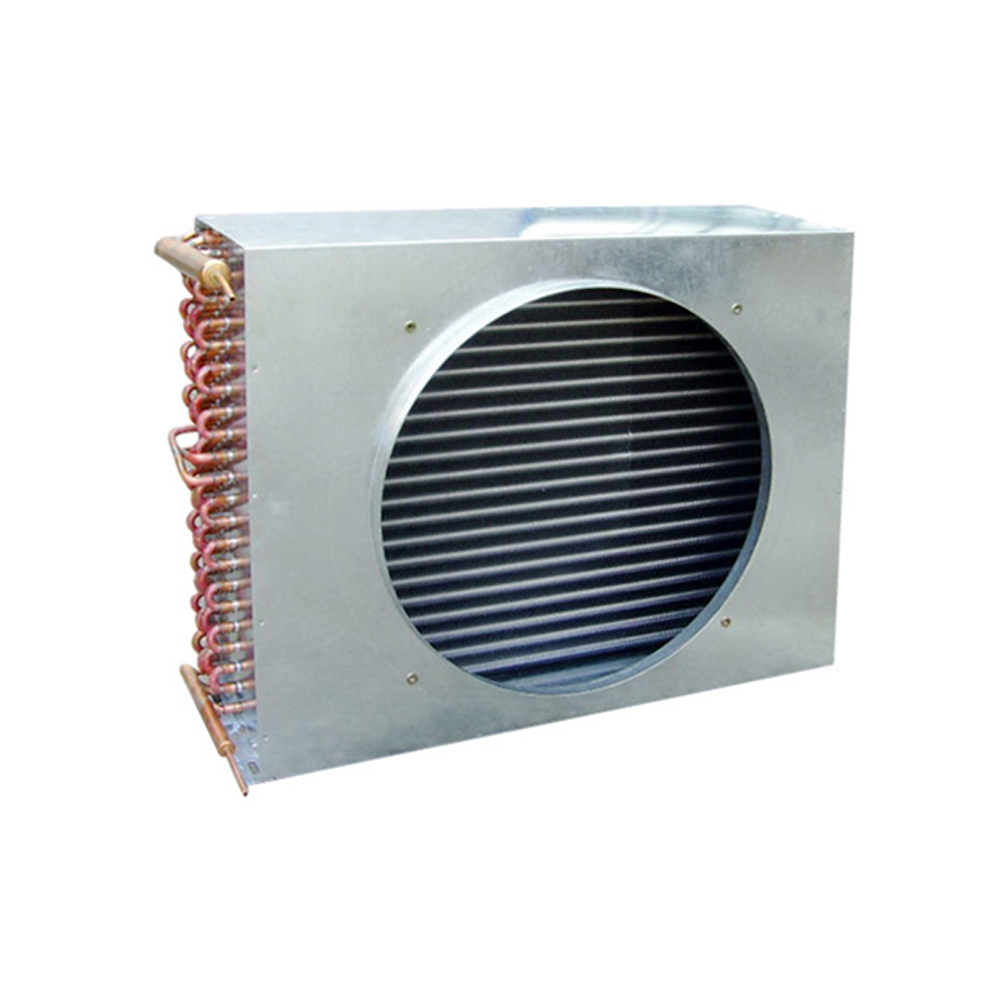
Finned Tube Coils
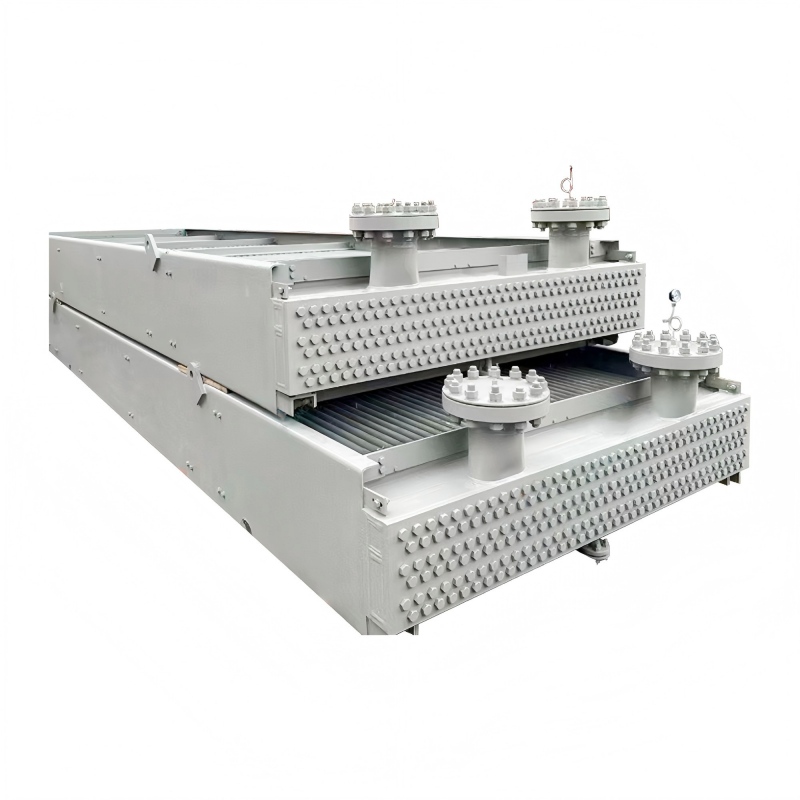
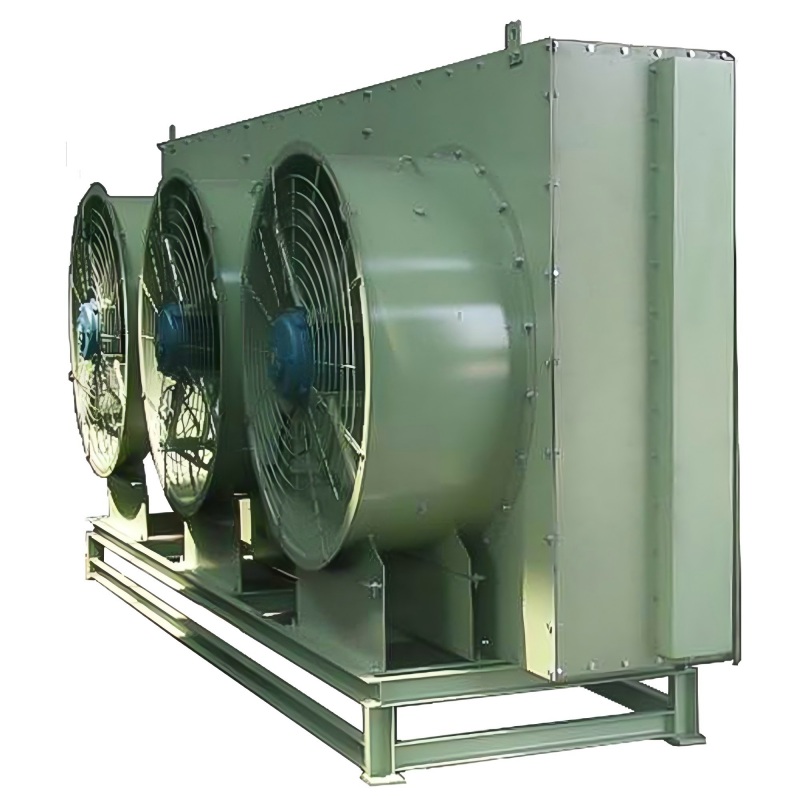
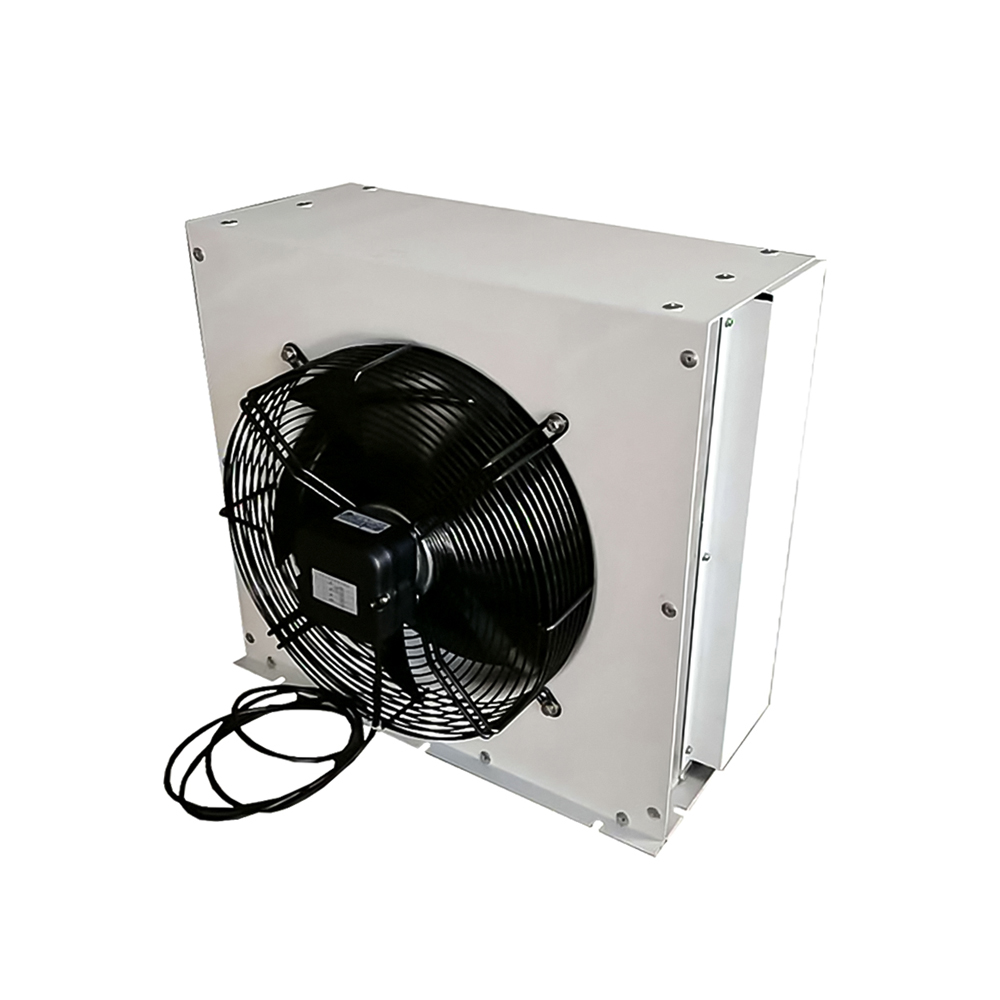
China heating and cooling coils frequently utilize finned tube designs. These coils consist of tubes with fins attached to enhance heat transfer. The fins increase the surface area, leading to improved efficiency. Different fin materials (aluminum, copper) and geometries (plain, louvered, wavy) influence performance characteristics. The choice depends on factors such as the operating temperature, fluid type, and pressure drop requirements. For more information on high-quality China heating and cooling coils, explore options from reputable manufacturers like Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd.
Plate Coils
Plate coils offer a compact and efficient solution for various applications. They are constructed from thin metal plates, welded or brazed together to form channels for fluid flow. Plate coils are particularly well-suited for applications with limited space. Their high heat transfer rates contribute to efficient China heating and cooling coils solutions.
Other Coil Types
Other types of coils exist, each with specific applications. These can include spiral coils, microchannel coils, and custom-designed coils tailored to specific requirements. The selection of the appropriate coil type for a particular project necessitates careful consideration of the application's unique demands.
Factors to Consider When Selecting China Heating and Cooling Coils
Material Selection
The choice of material for the tubes and fins is crucial. Copper offers excellent heat transfer properties but can be more expensive than aluminum. Aluminum is a cost-effective alternative with good thermal conductivity. Stainless steel is frequently chosen for its corrosion resistance in specific applications. The material selection for your China heating and cooling coils directly impacts longevity and performance.
Fin Design and Spacing
Fin density and geometry influence heat transfer efficiency and pressure drop. A higher fin density generally leads to improved heat transfer but also increases pressure drop. The optimal fin design is a compromise between these two factors, which depend on the specific application and fluid characteristics. The right China heating and cooling coils will account for these details.
Coil Dimensions and Configuration
The dimensions of the coil – length, width, and height – directly affect its heat transfer capacity and space requirements. The coil configuration, such as the number of rows and passes, also impacts performance. These design elements need careful consideration when selecting China heating and cooling coils.
Efficiency and Durability
The efficiency of a China heating and cooling coil is influenced by several factors, including the material used, the fin design, and the overall design of the coil. Durability is often a key concern, and the selection of corrosion-resistant materials can significantly extend the lifespan of the coil. Proper installation and maintenance practices also play an important role in ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Comparison of Different Coil Materials
| Material | Heat Transfer | Cost | Corrosion Resistance |
| Copper | Excellent | High | Good |
| Aluminum | Good | Low | Moderate |
| Stainless Steel | Moderate | Medium | Excellent |
Remember to always consult with experienced HVAC professionals when selecting and installing China heating and cooling coils to ensure optimal performance and safety.