This guide provides a detailed overview of China heat exchanger type shell and tube units, covering their design, applications, advantages, and considerations for selection. We'll explore various aspects to help you understand this crucial piece of equipment in various industrial processes. Learn about different materials, sizes, and efficiency considerations to make informed decisions for your specific needs.
Understanding Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Fundamentals of Shell and Tube Design
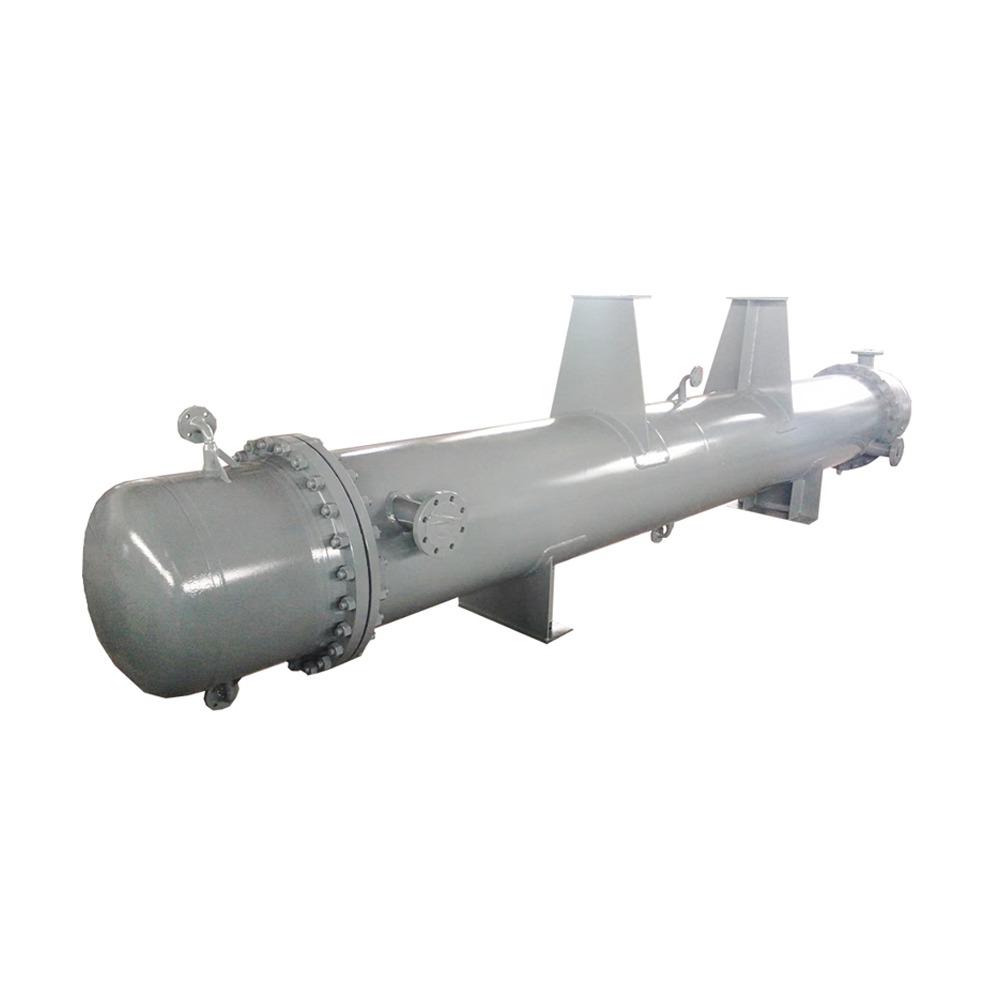
A China heat exchanger type shell and tube is a type of heat exchanger where one fluid flows through a bundle of tubes, while another fluid flows around the outside of the tubes within a shell. This design allows for efficient heat transfer between the two fluids. The tubes are often finned to increase surface area and improve heat transfer efficiency. The shell and tube arrangement enables high heat transfer rates, making them suitable for various high-temperature and high-pressure applications.
Materials Used in Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
The choice of material for a China heat exchanger type shell and tube depends heavily on the fluids being processed and the operating conditions. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel (various grades), copper, nickel alloys, and titanium. Each material offers a different level of corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and strength, influencing its suitability for specific applications. For example, stainless steel is often preferred for corrosive environments, while carbon steel is a cost-effective option for less demanding applications.
Types of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Several variations exist in the basic China heat exchanger type shell and tube design. These include variations in the number of tube passes, shell passes, and the arrangement of baffles within the shell. These design choices influence the overall heat transfer performance and pressure drop characteristics of the exchanger. Selecting the correct configuration is critical for optimal performance and longevity.
Applications of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Industrial Processes
China heat exchanger type shell and tube units find extensive use across various industries. Key applications include: power generation (steam condensers, feedwater heaters), chemical processing (reactors, distillation columns), oil and gas refining (crude oil preheating, fractionation), and HVAC systems (cooling and heating). Their ability to handle high temperatures and pressures makes them indispensable in many high-intensity industrial processes.
Specific Examples
Consider the use of shell and tube exchangers in the petrochemical industry for cooling down hot process streams before further processing. The robust design and high heat transfer efficiency are crucial for maintaining product quality and process safety. In power plants, large shell and tube condensers are essential for converting steam back into water, a vital step in the power generation cycle.
Selecting the Right Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
Factors to Consider
Choosing the appropriate China heat exchanger type shell and tube requires careful consideration of several factors. These include the fluids' properties (temperature, pressure, viscosity, corrosiveness), the required heat duty, the allowable pressure drop, the available space, and the budget. Consulting with a heat exchanger specialist can significantly aid in making the correct selection.
Performance and Efficiency
The efficiency of a China heat exchanger type shell and tube is influenced by factors such as the heat transfer area, the temperature difference between the fluids, and the flow rates. Optimization of these parameters is crucial for maximizing the efficiency and minimizing energy consumption. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and inspection, is essential to maintaining optimal performance.
Maintenance and Considerations
Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance, including cleaning to remove fouling and scaling, extends the lifespan and efficiency of a China heat exchanger type shell and tube. Fouling can significantly reduce heat transfer, leading to decreased efficiency and increased energy costs. Scheduled inspections should also be part of a preventative maintenance program to identify and address potential problems before they escalate.
For high-quality China heat exchanger type shell and tube units and expert advice, contact Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd.
Comparison of Different Materials
| Material | Corrosion Resistance | Thermal Conductivity | Cost | Typical Applications |
| Carbon Steel | Low | Moderate | Low | Non-corrosive applications |
| Stainless Steel (304) | Moderate | Moderate | Medium | Mildly corrosive applications |
| Stainless Steel (316) | High | Moderate | High | Highly corrosive applications |
| Titanium | Very High | High | Very High | Highly corrosive and high-temperature applications |
Note: The above cost and performance data are general guidelines. Actual values may vary depending on specific material grade and supplier.
Disclaimer: This information is for general guidance only and should not be considered professional engineering advice. Always consult with qualified engineers and professionals for specific applications.










.jpg)