This guide provides a comprehensive overview of tube in tube heat exchangers, exploring their design, applications, advantages, disadvantages, and selection criteria. We'll delve into the different types, materials, and considerations for optimal performance, helping you choose the best solution for your specific needs. Learn how to maximize efficiency and minimize operational costs with the right tube in tube heat exchanger.
Understanding Tube in Tube Heat Exchangers
What are Tube in Tube Heat Exchangers?
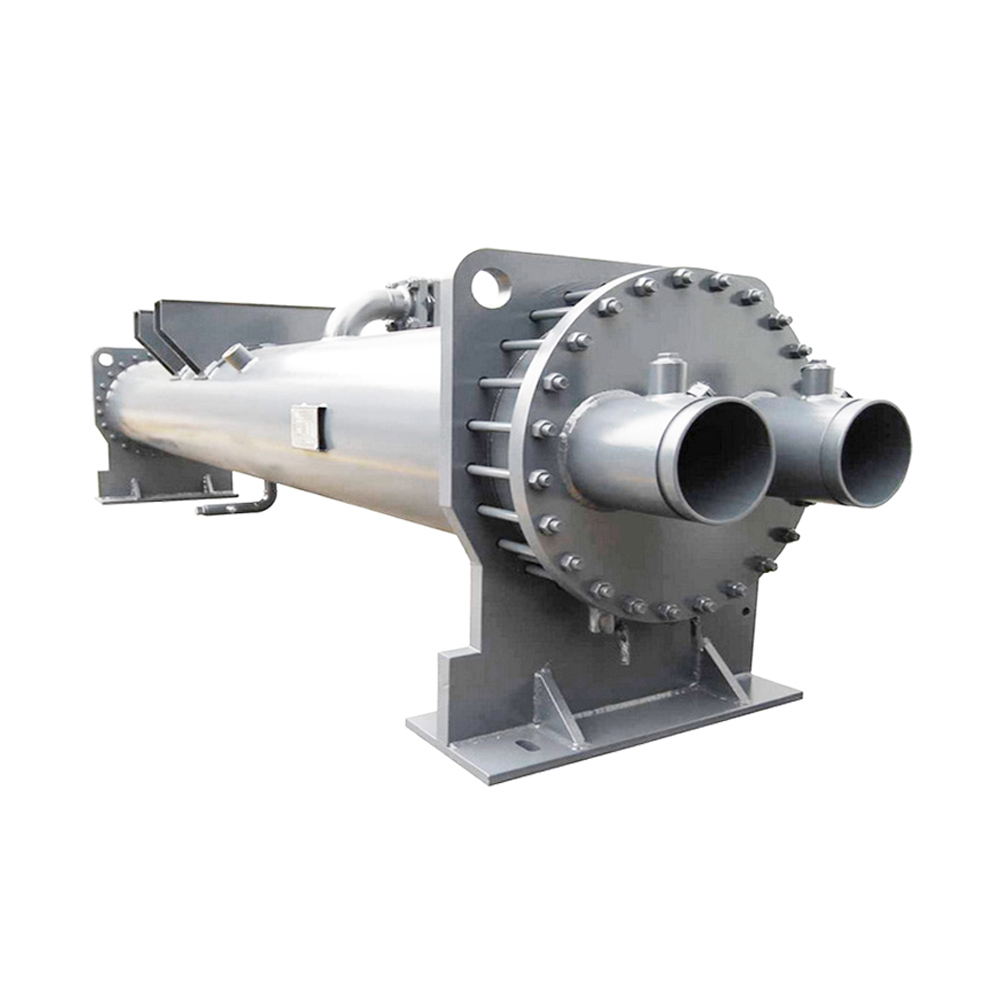
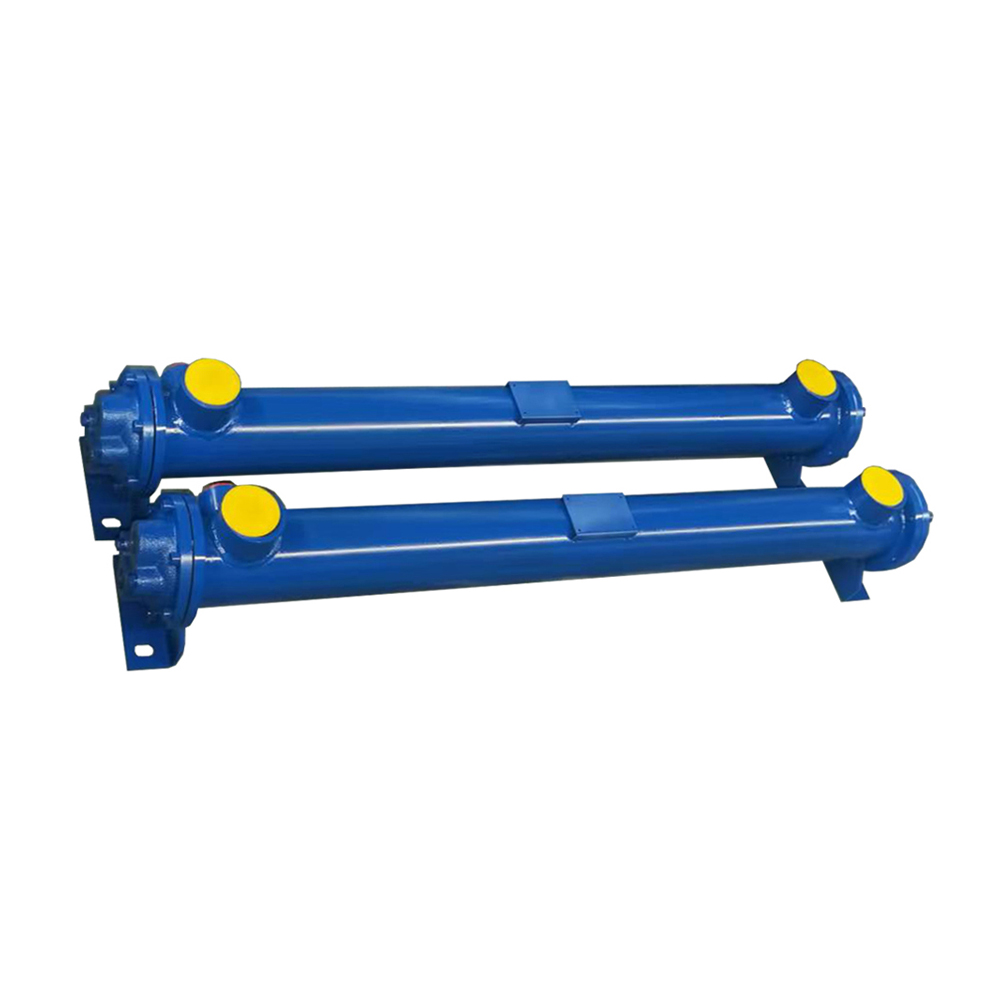
Tube in tube heat exchangers, also known as double-pipe heat exchangers, are a simple yet effective type of heat exchanger consisting of two concentric tubes. One fluid flows through the inner tube, while the other flows through the annulus (the space between the inner and outer tubes). Heat is transferred between the two fluids through the tube walls. Their straightforward design makes them easy to manufacture and maintain. This simplicity often makes them a cost-effective solution for various applications. For more advanced solutions or larger-scale operations, you may consider other heat exchanger types; however, for many applications, tube in tube heat exchangers offer a robust and reliable solution.
Types of Tube in Tube Heat Exchangers
Several configurations exist, categorized mainly by the flow arrangement of the two fluids:
- Countercurrent flow: Fluids flow in opposite directions, resulting in the highest possible heat transfer efficiency.
- Cocurrent flow (parallel flow): Fluids flow in the same direction, leading to lower efficiency than countercurrent flow but often simpler in design.
- Crossflow: One fluid flows perpendicularly to the other. This arrangement is less common in tube in tube heat exchangers but can be useful in specific applications.
The choice depends on factors such as required heat transfer rate, temperature differences, and pressure drop constraints.
Materials and Applications
Common Materials
The material selection for tube in tube heat exchangers is crucial for corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and pressure handling capabilities. Common materials include:
- Stainless steel: Offers excellent corrosion resistance and high strength.
- Copper: Possesses high thermal conductivity, making it suitable for applications requiring efficient heat transfer.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and cost-effective, but less corrosion-resistant than stainless steel.
- Titanium: Highly resistant to corrosion, often used in demanding environments.
The specific material is chosen based on the fluids being handled and the operating conditions.
Applications of Tube in Tube Heat Exchangers
Their versatility makes tube in tube heat exchangers suitable for a wide range of applications, including:
- Heating and cooling processes in various industries
- HVAC systems
- Chemical processing
- Food and beverage processing
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Waste heat recovery
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
Some key advantages include simplicity of design, ease of manufacturing and maintenance, relatively low cost, and good performance for many applications. They are often favored for their robustness and reliability in less demanding environments.
Disadvantages
Limitations include lower heat transfer efficiency compared to some other heat exchanger types (e.g., shell and tube), limited heat transfer surface area, and potential for fouling and scaling. The relatively small surface area can make them unsuitable for high-capacity applications.
Selecting the Right Tube in Tube Heat Exchanger
Factors to Consider
When selecting a tube in tube heat exchanger, consider factors such as:
- Required heat transfer rate
- Fluid properties (viscosity, density, thermal conductivity, etc.)
- Operating temperature and pressure
- Material compatibility
- Space constraints
- Maintenance requirements
Careful consideration of these factors is vital for optimizing performance and ensuring longevity.
Case Studies (Examples of Applications)
Example 1: Heating a Process Fluid
A chemical plant uses a stainless steel tube in tube heat exchanger to heat a viscous chemical solution using steam in the annulus. The countercurrent flow arrangement maximizes heat transfer efficiency, ensuring the process fluid reaches the desired temperature.
Example 2: Cooling a Lubricating Oil
In a manufacturing facility, a copper tube in tube heat exchanger cools lubricating oil circulated through machinery. The high thermal conductivity of copper aids in efficient heat dissipation, minimizing operational costs.
Conclusion
Tube in tube heat exchangers offer a simple, efficient, and cost-effective solution for numerous heat transfer applications. Understanding their design, materials, advantages, and limitations is crucial for making informed decisions and selecting the appropriate heat exchanger for specific needs. For more information on high-quality heat exchangers, visit Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd. They offer a range of solutions for various industrial needs. Remember to carefully evaluate your requirements to determine the optimal configuration and materials for your specific application.

























.jpg)
