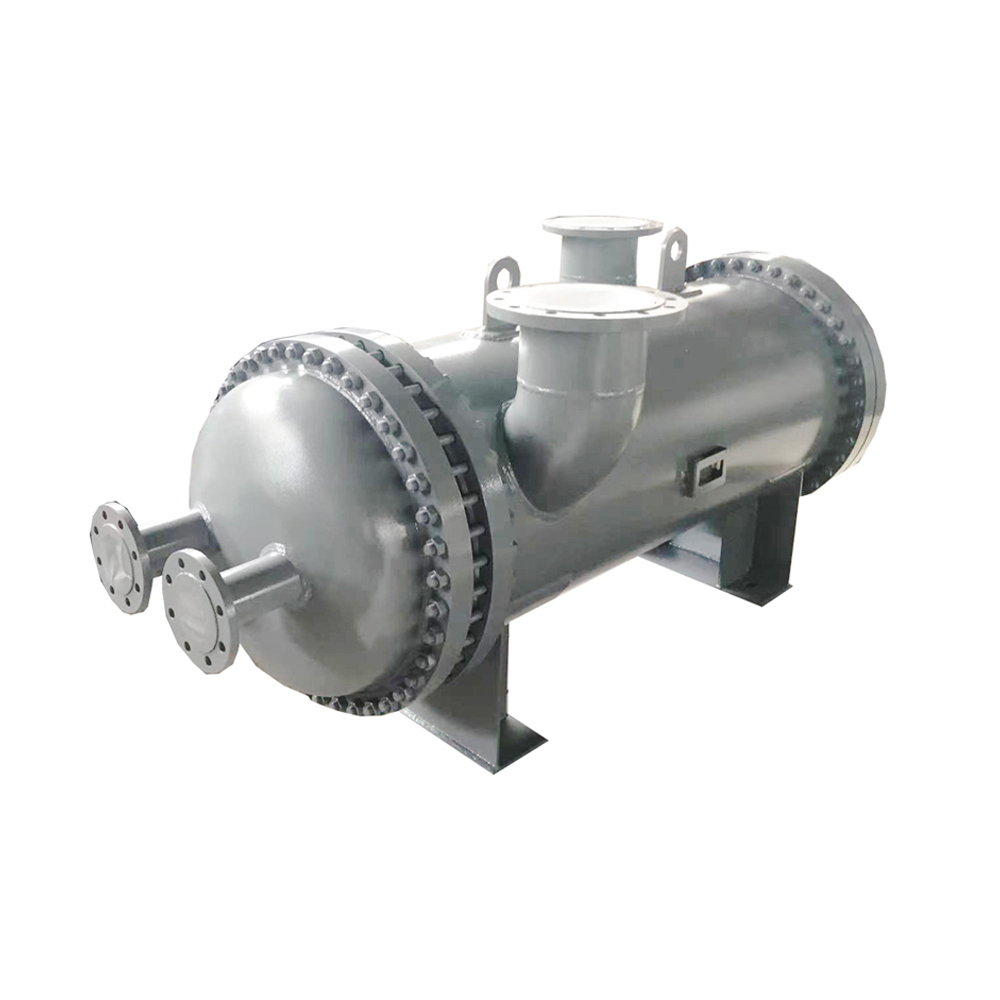
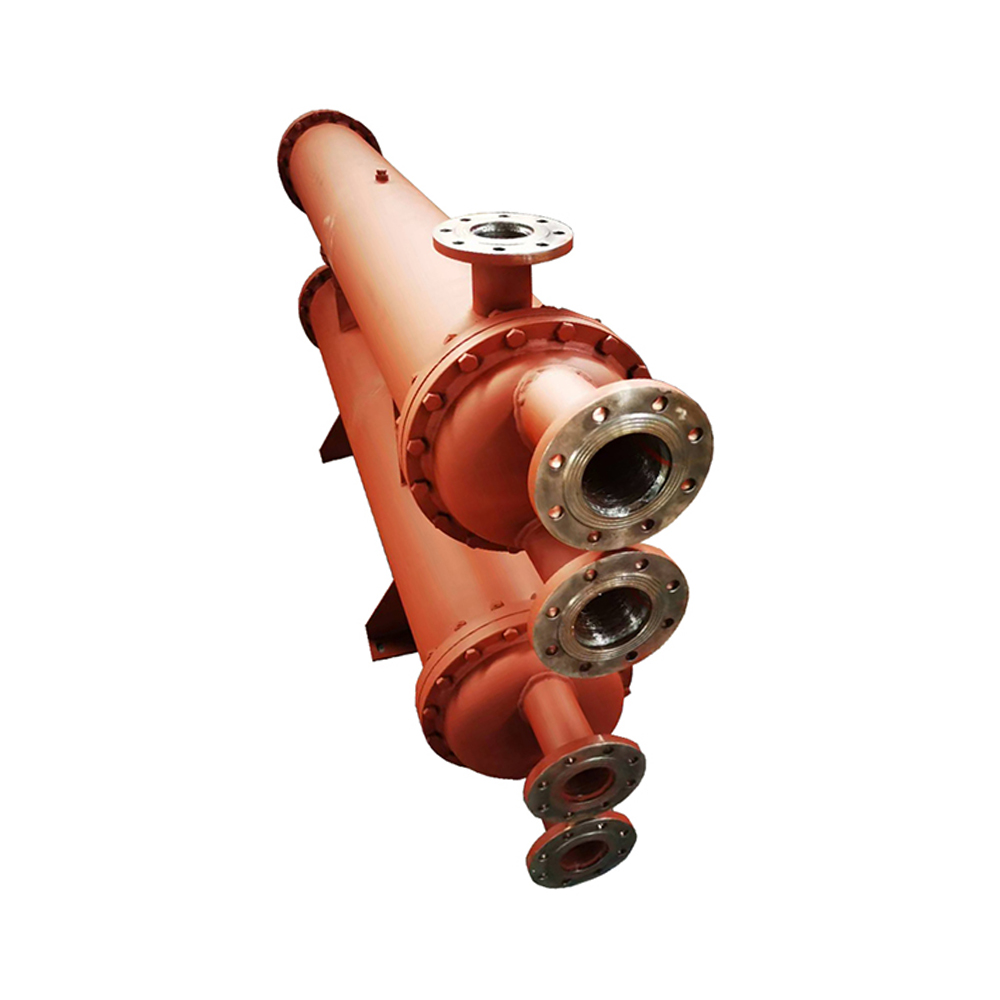
Best Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Cost: A Comprehensive GuideUnderstanding the cost of a shell and tube heat exchanger is crucial for any project involving heat transfer. This guide provides a detailed breakdown of factors influencing price, helping you make informed decisions.
Factors Affecting the Cost of a Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
Several key factors significantly influence the final cost of your
shell and tube heat exchanger. Understanding these elements is vital for accurate budgeting and project planning.
1. Material Selection
The choice of material directly impacts the cost. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and various alloys. Stainless steel, for example, offers superior corrosion resistance but comes at a higher price than carbon steel. The specific alloy selected will also influence the overall cost. Choosing the right material depends on the application's operating conditions, including temperature, pressure, and the nature of the fluids involved.
2. Design and Size
The design complexity and overall size of the
shell and tube heat exchanger are major cost drivers. Larger units naturally require more material and labor, leading to increased expenses. Custom designs, involving specialized configurations or performance requirements, tend to be more expensive than standard units. Accurate sizing based on the heat transfer needs is critical to avoid overspending on unnecessary capacity.
3. Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process impacts cost significantly. Advanced manufacturing techniques, like precision machining or specialized welding, can improve efficiency and performance but increase the overall cost. The manufacturer's experience and production capabilities also affect price. A reputable manufacturer with efficient processes may offer competitive pricing.
Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd offers a range of high-quality
shell and tube heat exchangers produced through efficient and reliable manufacturing processes.
4. Additional Features and Accessories
The inclusion of additional features or accessories, such as insulation, nozzles, or pressure relief valves, adds to the overall cost. These features often enhance safety, efficiency, or ease of maintenance. The necessity of such features should be carefully considered in relation to budget and specific application requirements.
Estimating the Cost: A Practical Approach
Accurately estimating the cost of a
shell and tube heat exchanger requires considering the factors discussed above. While providing a precise cost without specific project details is impossible, we can illustrate a general cost range. Small, standard units may start at a few thousand dollars, while larger, custom-designed units can cost tens of thousands or more.
Tips for Minimizing Costs
Several strategies can help minimize the cost of your
shell and tube heat exchanger without compromising performance. Optimize design: Careful design considerations can lead to more efficient and cost-effective units. Consult with experienced engineers to ensure the optimal design for your specific application. Select appropriate materials: Choose materials that meet your performance needs without unnecessary expense. A cost-benefit analysis can help guide your decision-making process. Consider used equipment: If appropriate for your application, exploring used or refurbished equipment can lead to significant cost savings. Always ensure proper inspection and testing before use. Partner with experienced suppliers: Working with reputable suppliers such as
Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd can result in cost-effective solutions tailored to your specific needs.
Conclusion
The cost of a
shell and tube heat exchanger is a multifaceted issue influenced by material, design, manufacturing, and additional features. By understanding these factors and employing cost-saving strategies, you can obtain a high-quality heat exchanger that meets your requirements while remaining within budget. Remember to always consult with experienced professionals for guidance and accurate costing.