This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of air cooled cooling towers, examining their functionality, various types, selection criteria, and maintenance considerations. We’ll delve into the advantages and disadvantages, helping you make informed decisions for your specific cooling needs. Learn how to choose the optimal system for maximizing efficiency and minimizing operational costs.
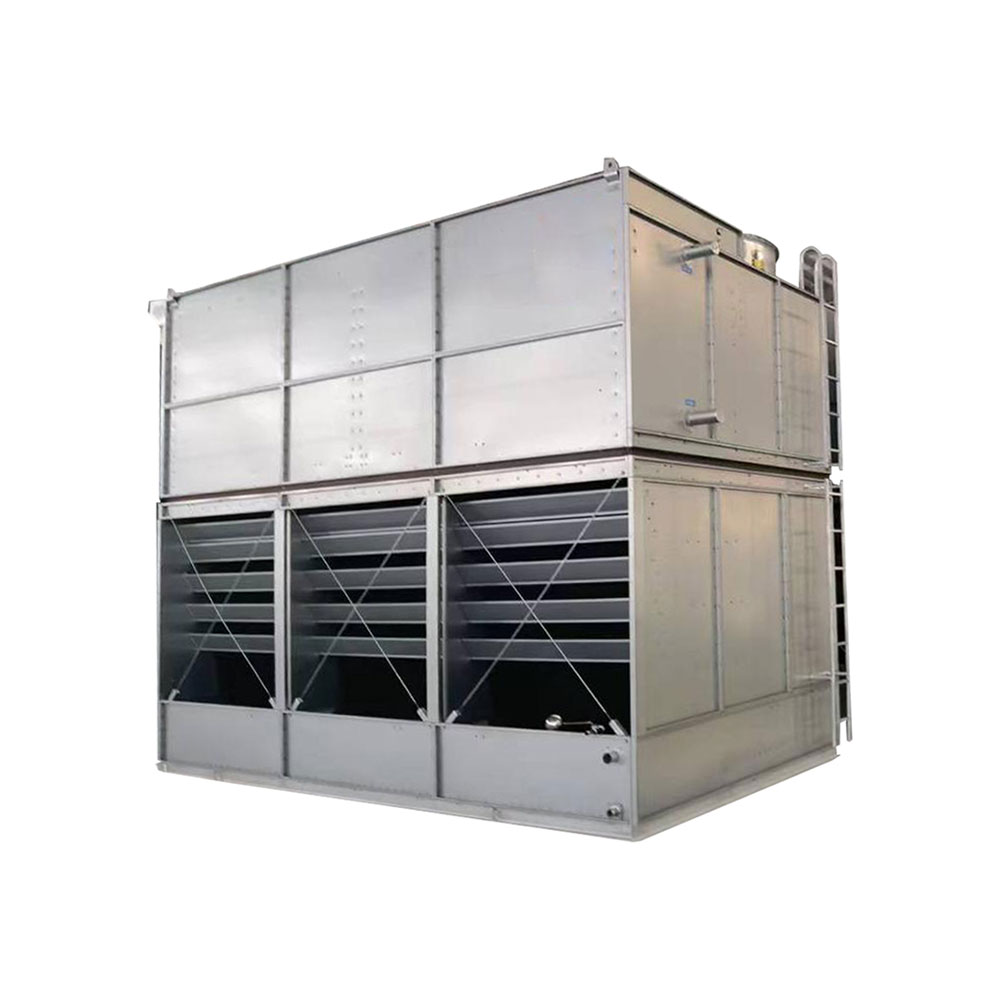
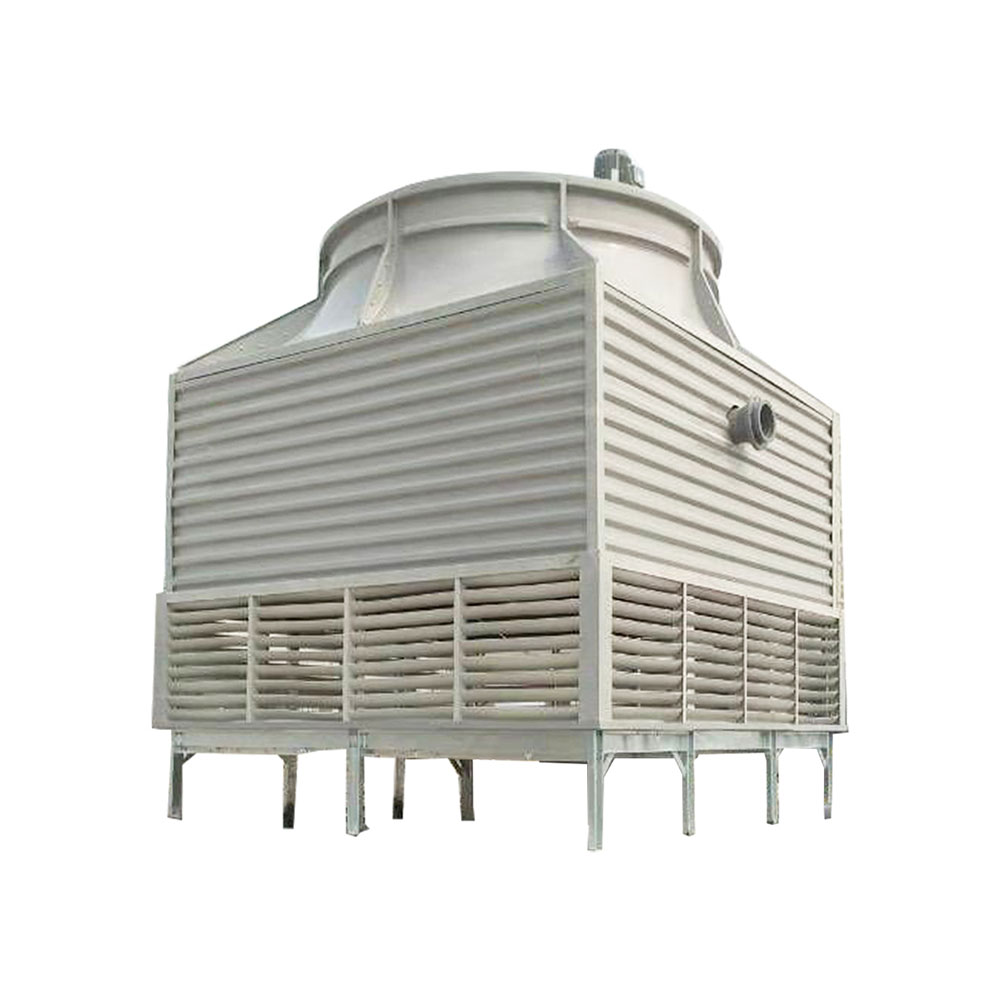
What is an Air Cooled Cooling Tower?
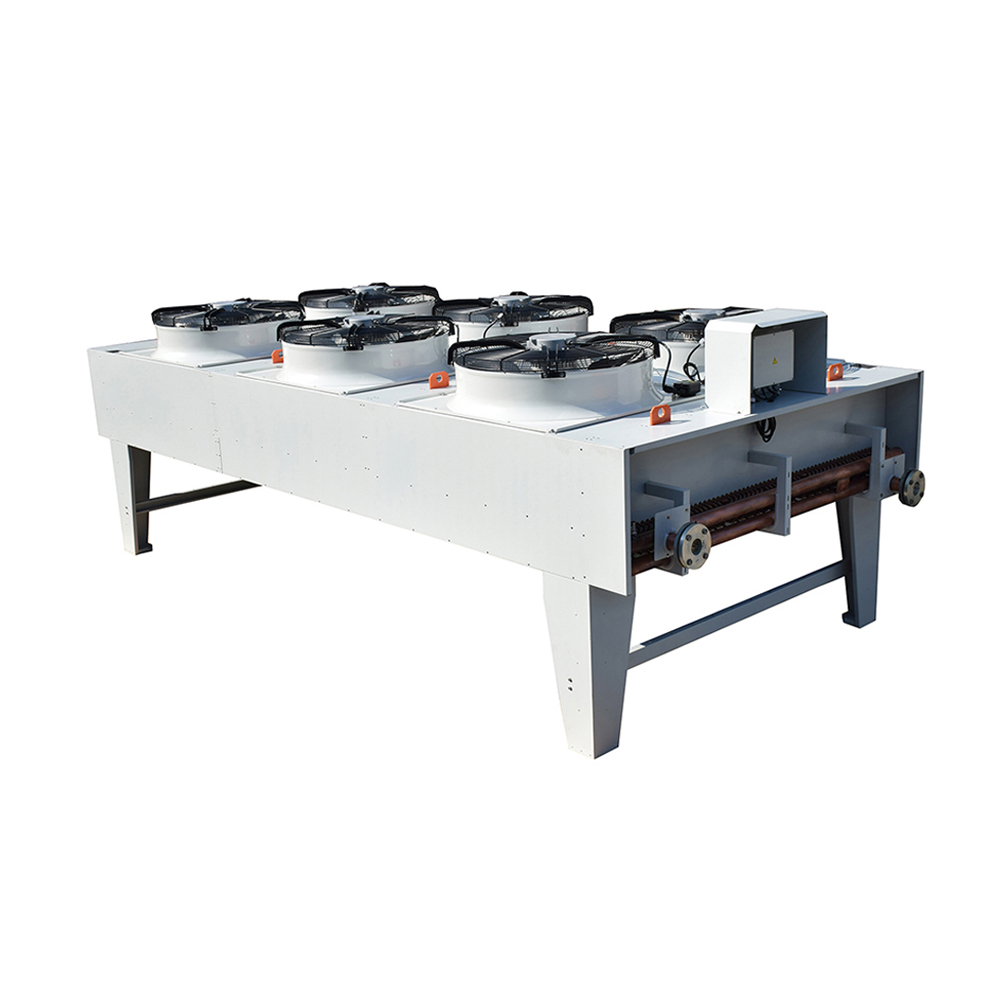
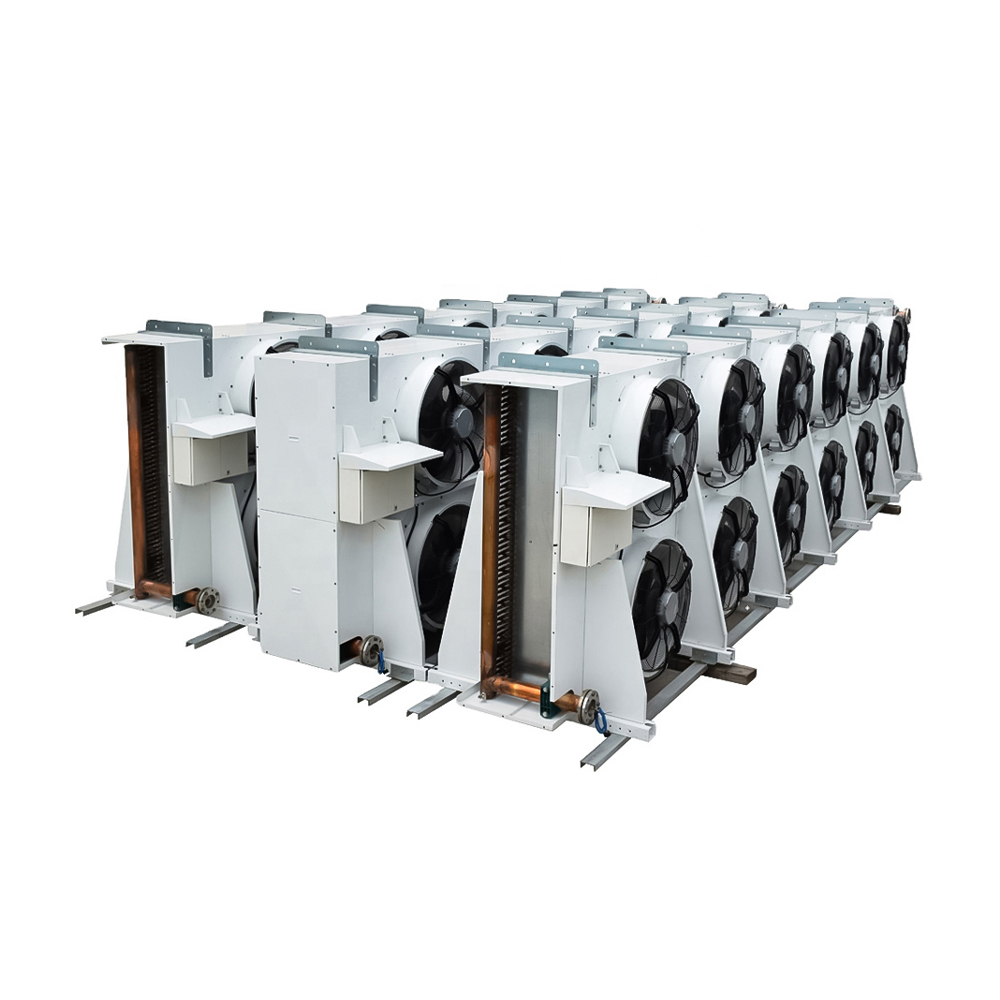
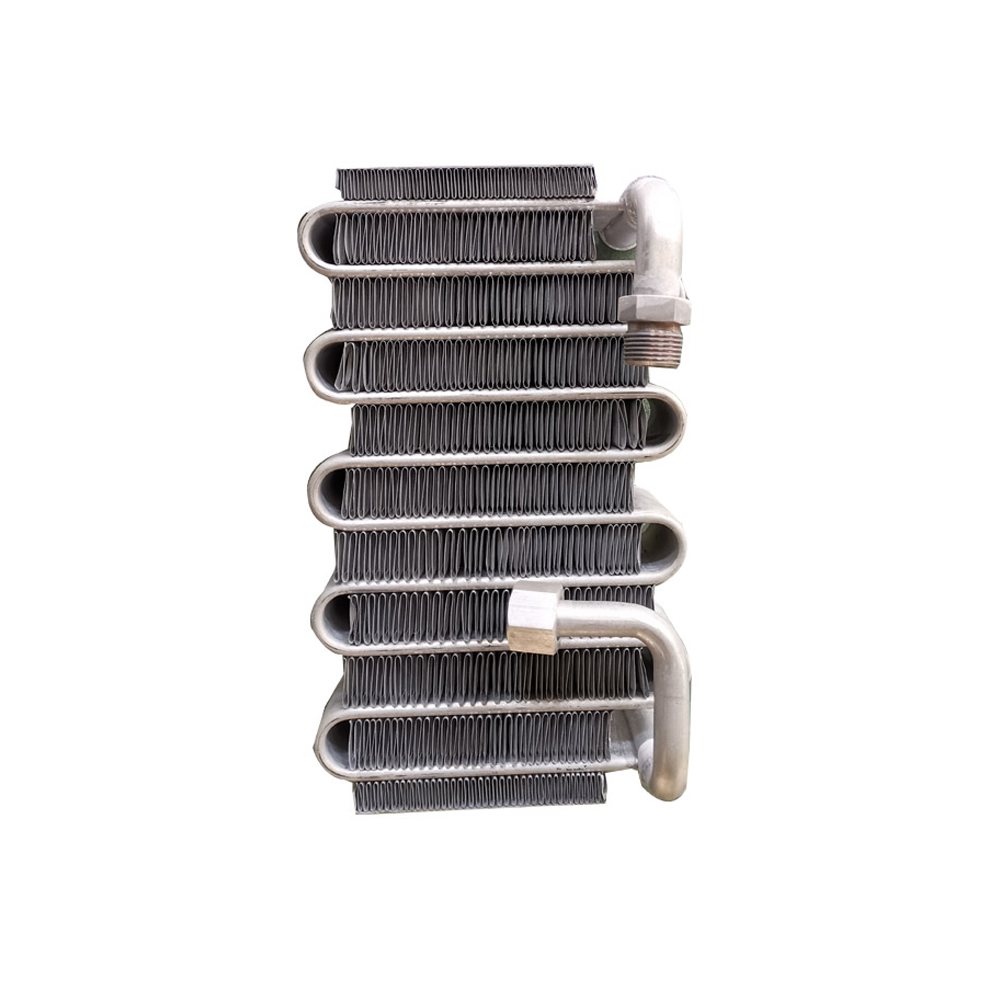
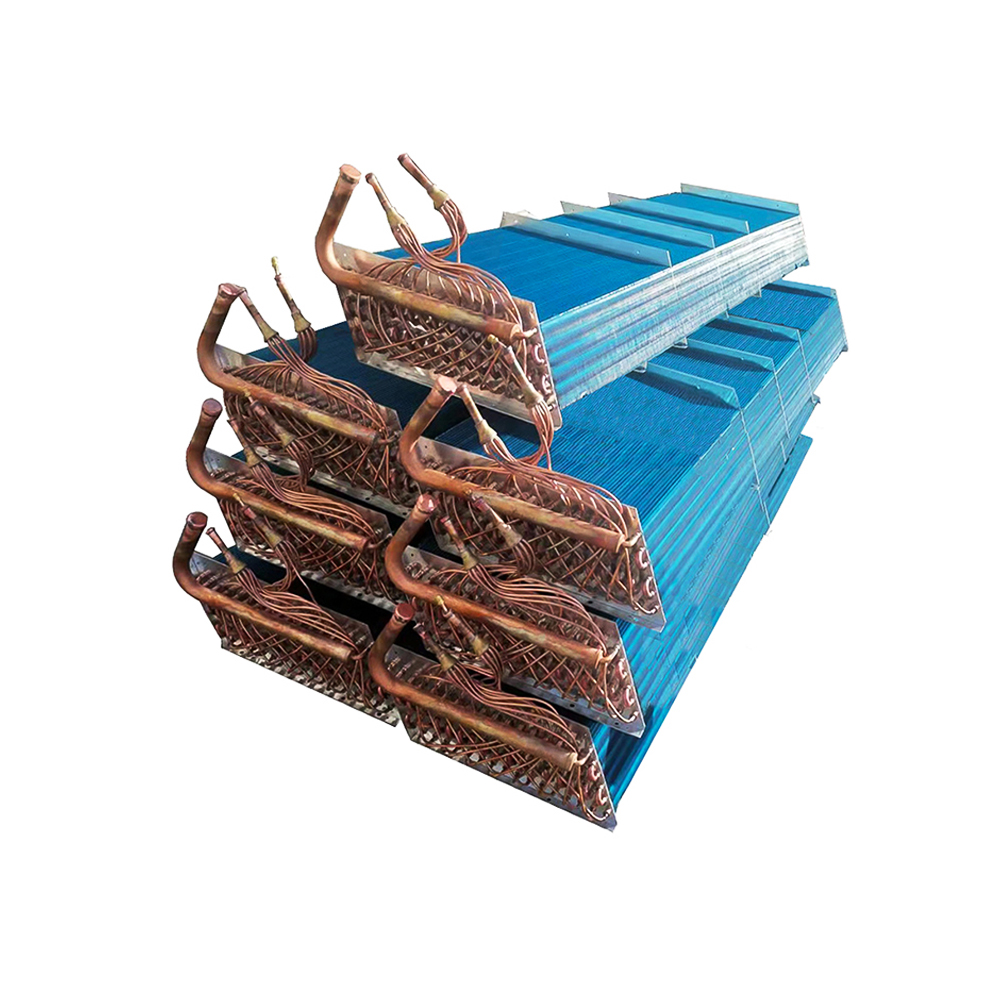
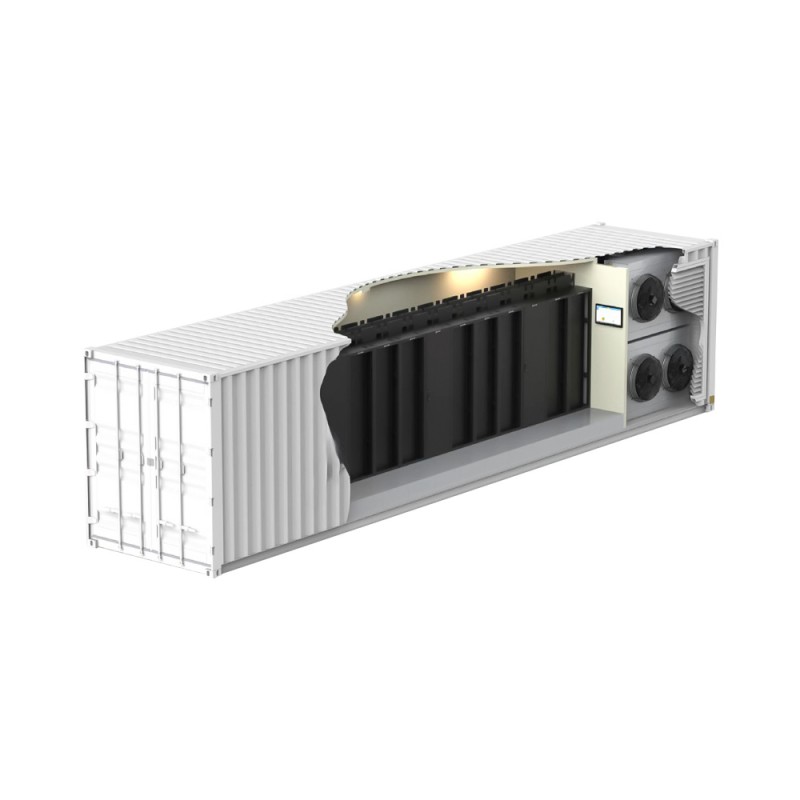
Unlike water-cooled counterparts, an air cooled cooling tower dissipates heat directly into the ambient air. This is achieved through a heat exchanger, usually involving a fan to enhance airflow across the finned surfaces. This process cools a liquid, typically water, used in industrial processes or HVAC systems. The system relies on the principle of convection to transfer heat from the liquid to the surrounding air. The absence of a water evaporation process makes them environmentally friendly, reducing water consumption compared to evaporative cooling towers.
Types of Air Cooled Cooling Towers
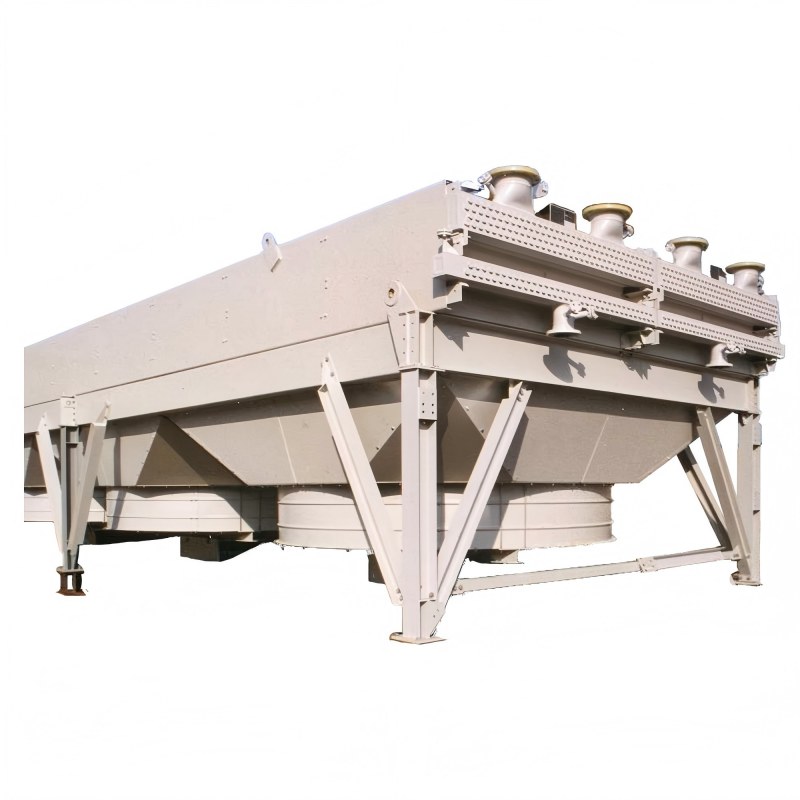
Air cooled cooling towers come in various designs, each suited for different applications and capacities. Key distinctions lie in their construction, heat transfer mechanisms, and overall efficiency.
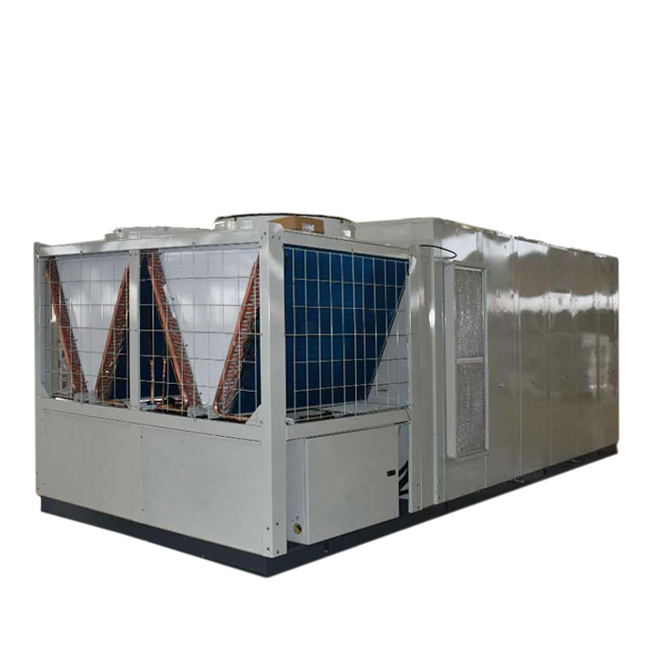
Induced Draft Cooling Towers
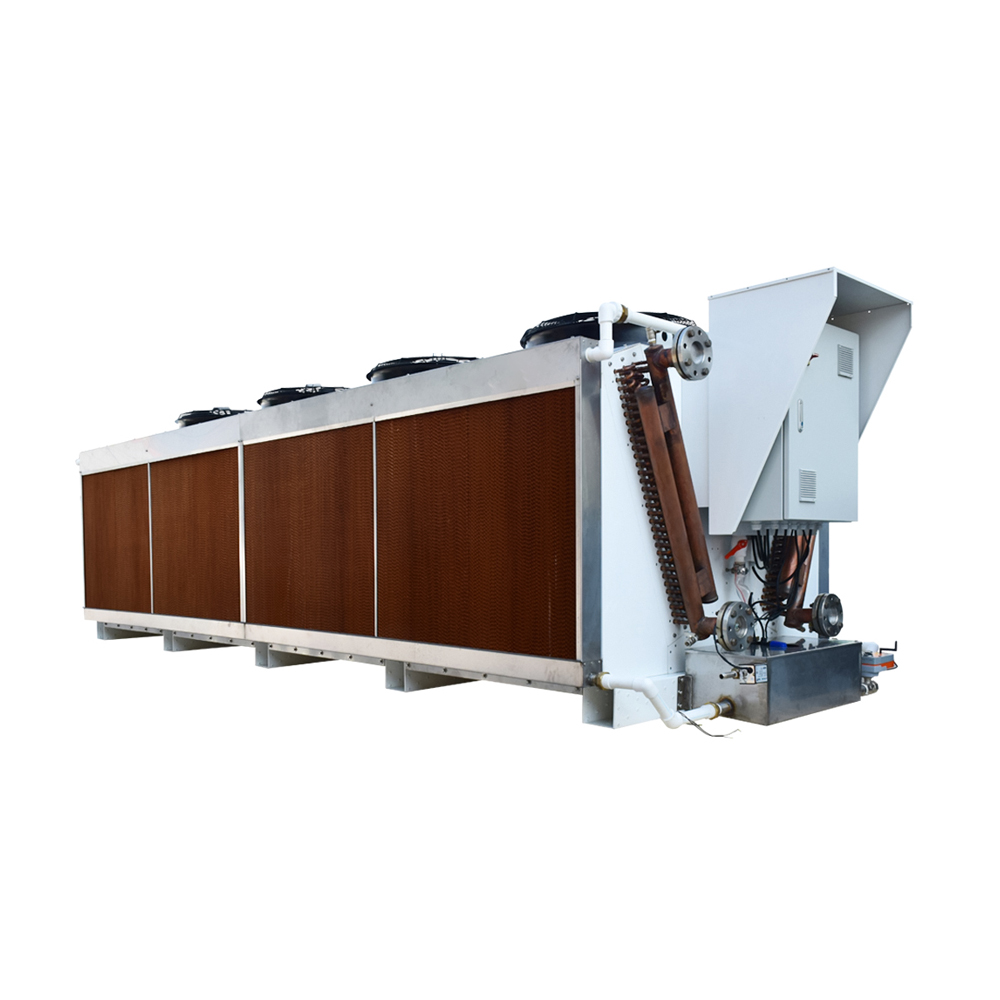
In induced draft towers, the fan pulls air through the heat exchanger, facilitating efficient heat transfer. This design often offers superior heat transfer performance and is popular in industrial settings demanding high cooling capacity. Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd (https://www.ShenglinCoolers.com/) offers a range of high-quality induced draft air cooled cooling towers.
Forced Draft Cooling Towers
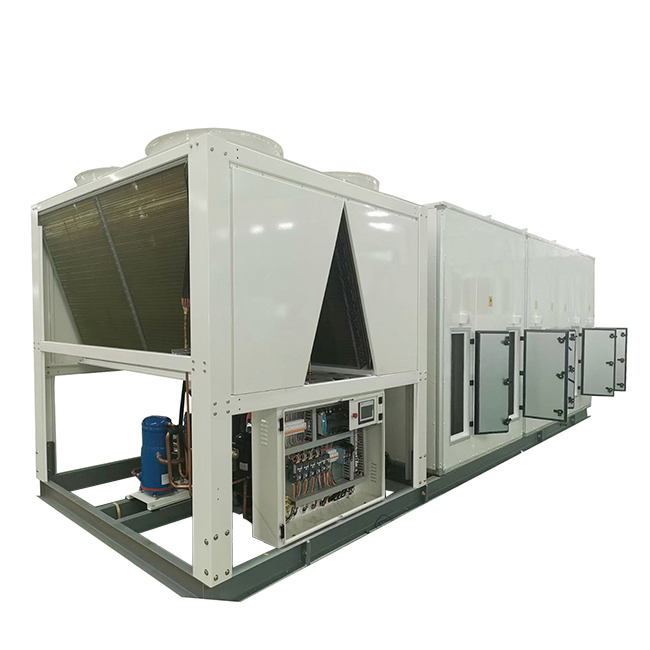
Forced draft systems utilize a fan to push air across the heat exchanger. This configuration is commonly preferred for compact installations and situations where airflow direction is critical. While generally less efficient than induced draft systems, they can be more cost-effective for certain applications.
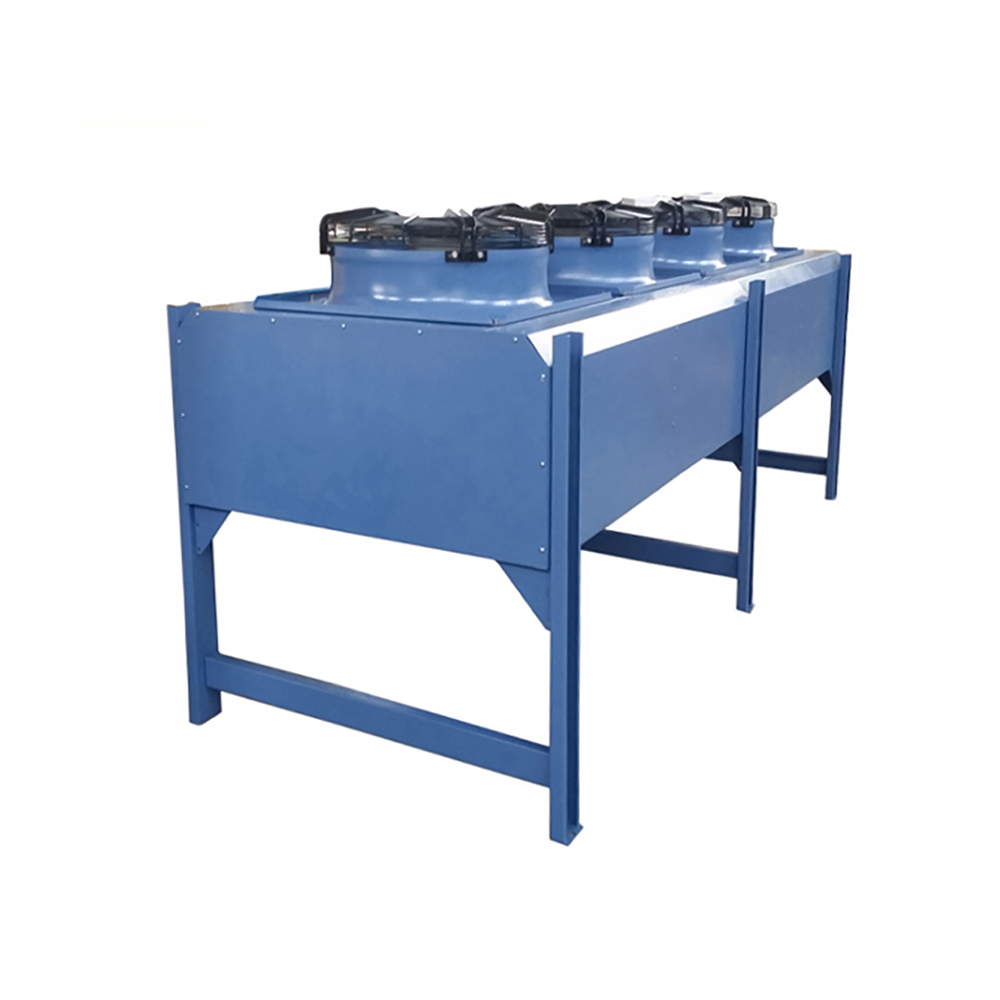
Dry Coolers
Dry coolers, a specific type of air cooled cooling tower, operate without any water evaporation. They are ideal for applications requiring high reliability and where water conservation is paramount. Their closed-loop design minimizes maintenance and reduces the risk of scaling and corrosion.
Selecting the Right Air Cooled Cooling Tower
Choosing the appropriate air cooled cooling tower involves careful consideration of several key factors:
Cooling Capacity
The cooling capacity required depends on the heat load of the system being cooled. Accurate estimation of this load is crucial for selecting a suitably sized tower. Underestimating the capacity can lead to insufficient cooling, while overestimating increases initial investment costs. Always consult with a specialist for accurate load calculations.
Ambient Air Temperature
The ambient air temperature significantly affects the efficiency of an air cooled cooling tower. Higher temperatures reduce cooling capacity. Choosing a tower capable of handling the highest anticipated ambient temperatures is essential for reliable performance. Consider climate data and seasonal variations when making this selection.
Water Flow Rate and Temperature
The water flow rate and inlet temperature significantly influence the heat transfer rate within the tower. Matching these parameters to the tower’s design specifications is important to ensure efficient and effective cooling.
Maintenance of Air Cooled Cooling Towers
Regular maintenance is critical for extending the lifespan and optimizing the performance of your air cooled cooling tower. This includes:
- Regular cleaning of fins and coils to prevent heat transfer degradation.
- Inspection of fan motors and belts for wear and tear.
- Monitoring of pressure drops across the heat exchanger.
- Periodic inspection for leaks and corrosion.
Air Cooled vs. Water Cooled Cooling Towers: A Comparison
Choosing between air cooled and water-cooled systems depends on several factors. The following table summarizes key differences:
| Feature | Air Cooled | Water Cooled |
| Water Consumption | Minimal | Significant |
| Efficiency | Generally lower at high ambient temperatures | Generally higher |
| Maintenance | Lower | Higher |
| Environmental Impact | Lower | Higher due to water consumption and potential chemical usage |
| Initial Cost | Often higher | Often lower |
Remember to always consult with professionals like Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd for expert advice tailored to your specific needs. The information provided here is for general guidance only and should not substitute professional engineering consultation.