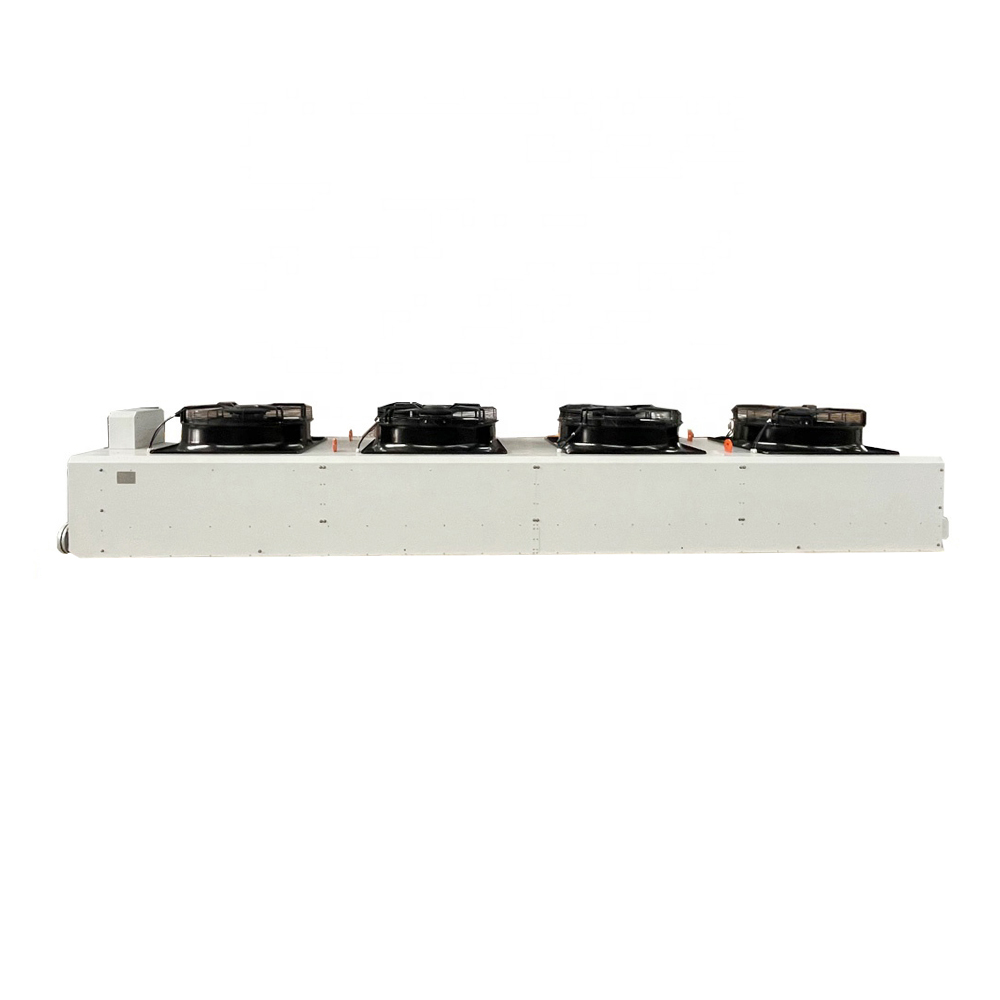
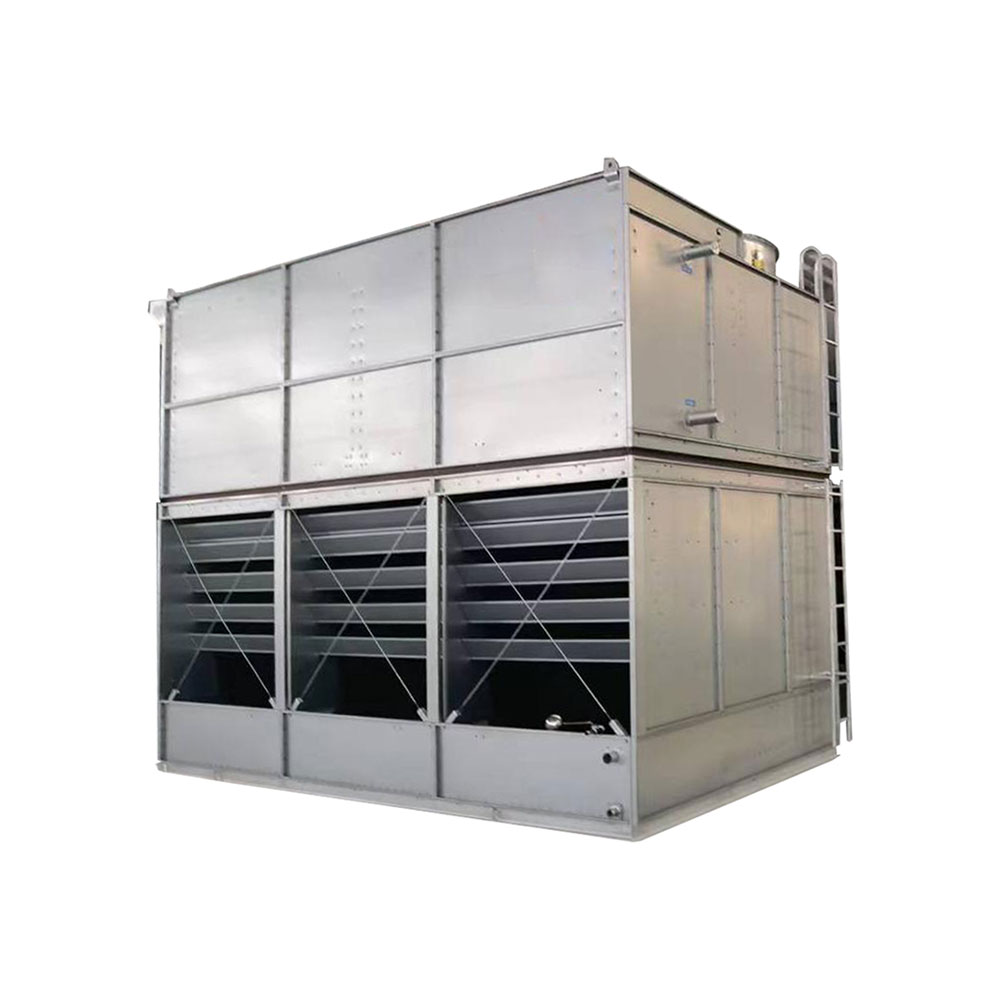
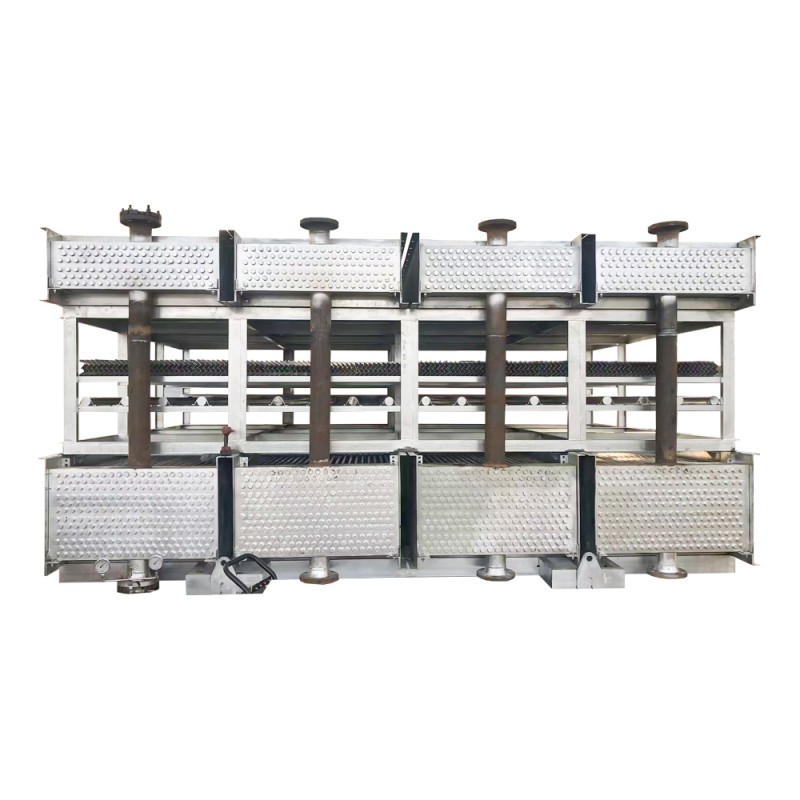
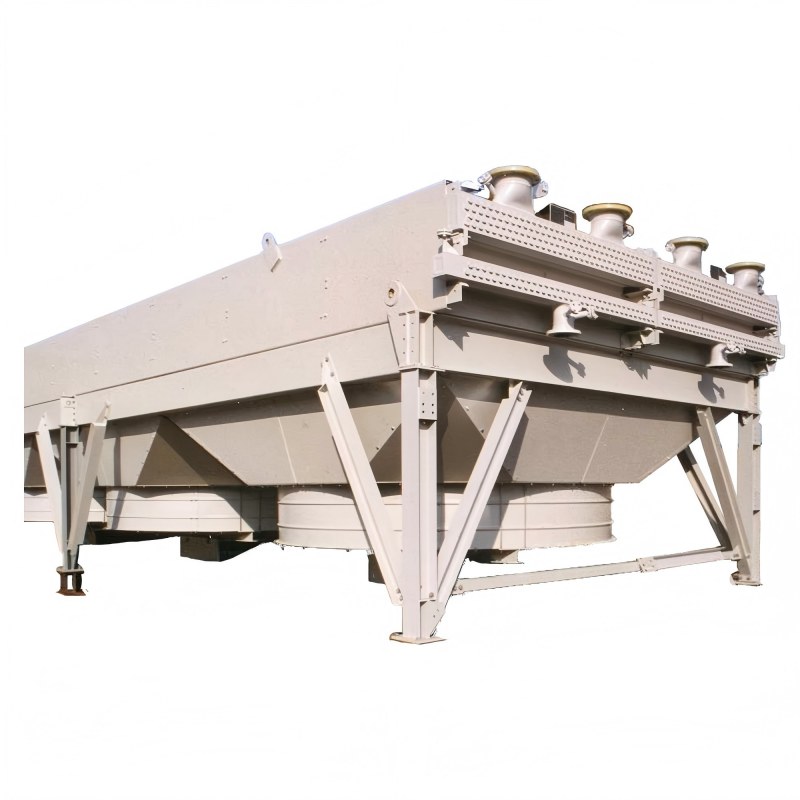
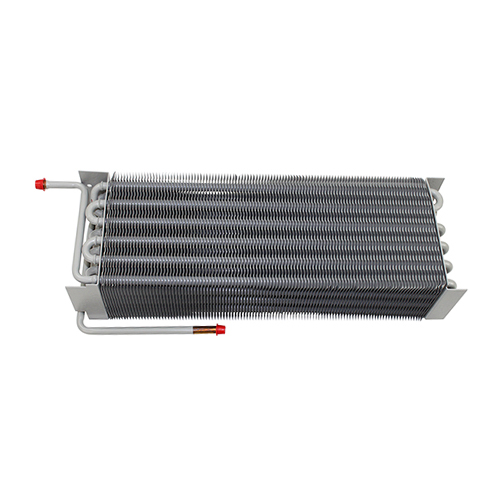
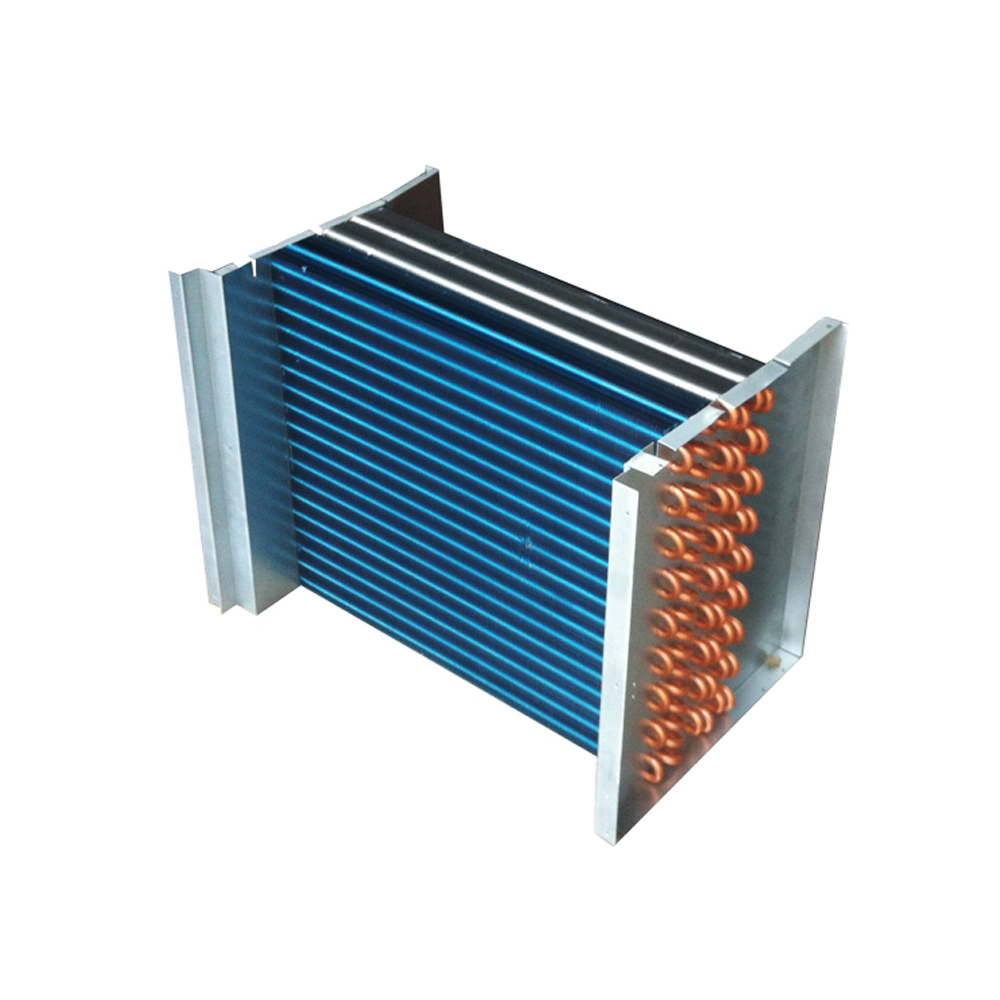
The Intricacies of Air Cooled Condensers
Air cooled condensers often get overshadowed by their water-cooled counterparts, but their significance, especially in regions with water scarcity, is undeniable. There's a subtle elegance in their simplicity that belies the engineering precision required to get them right. Let's explore the fine details that make these systems tick and address some common misconceptions.
Understanding Air Cooled Condensers
To begin, air cooled condensers operate on a relatively straightforward principle: they transfer heat from the refrigerant to the ambient air. Unlike water-cooled systems, they don't rely on a constant water supply—something that appeals to regions where water is a scarce resource.
However, it's not all straightforward. There are varying designs, and selecting the appropriate one is more than just plugging in specs. For instance, the efficiency can dramatically vary based on the fan type, fin surface, and ambient conditions. Something that might be overlooked is the altitude of where it's being used. Every bit of elevation affects performance.
Companies like Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd have been pioneering solutions. By investing in advanced research and practical designs, SHENGLIN ensures their condensers perform well under different environmental pressures.Learn more about their innovations.
Common Pitfalls in Implementation
A rookie mistake I’ve seen more times than I'd like to admit is underestimating the impact of the ambient temperature on these units. An air cooled condenser that performs impeccably in a temperate climate can struggle in hotter regions. The efficiency drop seems subtle, yet it’s enough to throw off entire systems if not accounted for.
Maintenance is another overlooked aspect. These condensers gather dust, pollen, and debris more than most imagine. And this accumulation drastically impacts heat transfer efficiency. Routine cleaning isn’t just preventive; it's essential for optimal performance.
I’ve also noted that improper spacing during installation can lead to restricted airflow. The end result? A not-so-efficient system that leads to higher operational costs over time. Leave enough clearance around the unit; it's simpler than retrofitting a fix later.
The Role of Innovations
Technological advancements have added new dimensions to condenser design. Variable speed fans, for instance, adjust to cooling demands dynamically, conserving energy. Such innovations can provide substantial savings, especially in industrial settings.
SHENGLIN's role in the cooling industry is marked by constant adaptation to these shifts. Specializing in industrial cooling technologies, they have implemented solutions that promise energy efficiency and reliability, catering to the unique demands of each client.
Another area is the emerging materials for fins and tubes, which offer improved thermal conductivity. Don’t underestimate the impact of material science—it could redefine future designs.
Tackling Specific Challenges
As with any system, unique challenges pop up in specific scenarios. Coastal installations, for instance, face corrosion challenges due to saline air, which standard galvanization methods might not fully withstand. Here, specialized coatings or materials become indispensable.
I recall a case where a poorly insulated piping system led to severe energy losses. Sometimes, it's not just about the condenser unit but the whole system. Addressing these peripheral issues ensures maximum effectiveness.
Climate considerations often dictate condenser choice. In particularly dry and sandy areas, sand infiltration can block fins, reducing efficiency. Protective barriers or strategic siting can mitigate this risk but requires foresight during planning phases.
Integrating into Broader Systems
It's not just about the condenser itself, but how it integrates into the larger HVAC or refrigeration system. Misalignments can lead to inefficiencies. A precision-engineered condenser won't perform if upstream systems are lacking.
Institutions like Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co.,Ltd excel in creating integrated solutions that consider these broader challenges. The synergy of components makes a world of difference in overall efficiency.
Ultimately, as we delve into these intricacies, we see that air cooled condensers are far more than peripheral installations; they're central to sustainable cooling solutions. Every detail matters—from design to maintenance, and integration to innovation.