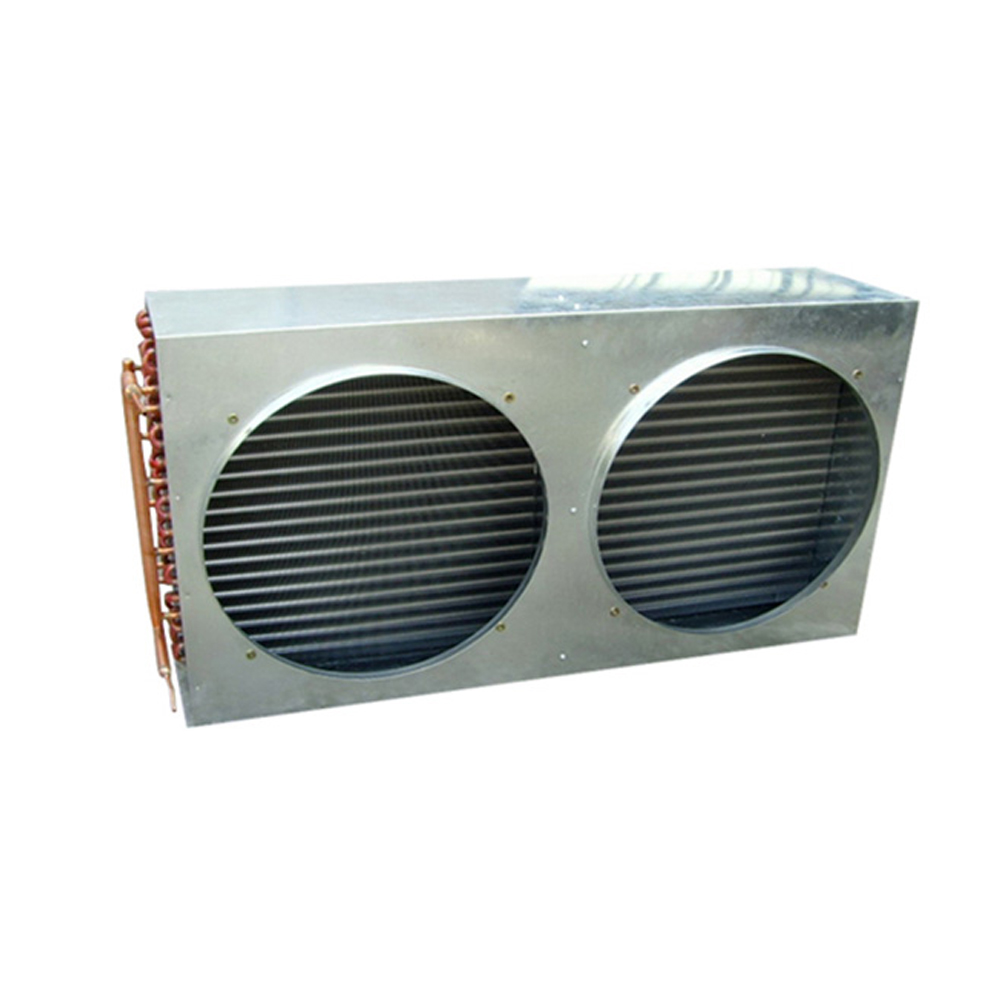
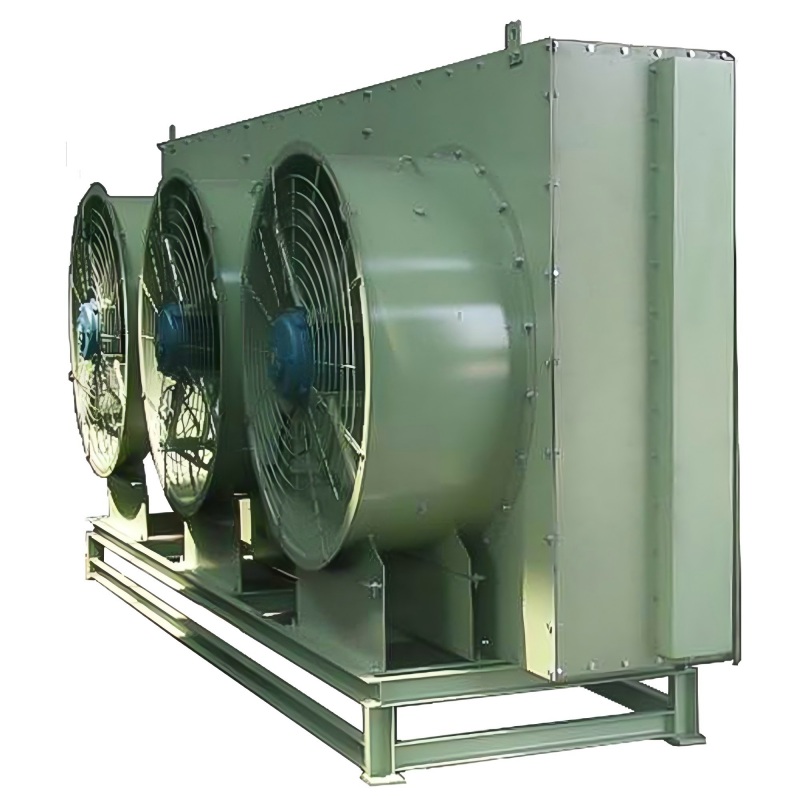
Razumijevanje i implementacija horizontalnog suhog hlađenja
Ovaj sveobuhvatni vodič istražuje horizontalno suho hlađenje sustava, s pojedinostima o njihovoj funkcionalnosti, prednostima, primjenama i razmatranjima za uspješnu implementaciju. Ispitat ćemo različite vrste sustava, istražiti njihovu učinkovitost i utjecaj na okoliš te ponuditi praktične savjete za odabir pravog sustava za vaše specifične potrebe. Naučite kako optimizirati svoju strategiju hlađenja pomoću ove dubinske analize.
.jpg)
Što je horizontalno suho hlađenje?
Horizontalno suho hlađenje je metoda odvođenja topline iz procesne tekućine (često vode) korištenjem zraka kao rashladnog medija bez potrebe za izvorom vode poput rijeke ili rashladnog tornja. To se postiže izmjenjivačem topline, koji obično ima vodoravni raspored rebrastih cijevi, gdje vrući fluid prolazi kroz cijevi, a toplina se prenosi na okolni zrak. Ovaj postupak ima posebnu prednost u regijama s nedostatkom vode ili ekološkim ograničenjima korištenja vode.
Vrste vodoravnih sustava suhog hlađenja
Kondenzatori hlađeni zrakom
Zrakom hlađeni kondenzatori su uobičajena vrsta horizontalno suho hlađenje sustav koji se koristi u raznim industrijama. Često su favorizirani zbog svog kompaktnog dizajna i relativno jednostavnog rada. Učinkovitost zrakom hlađenih kondenzatora može varirati ovisno o čimbenicima poput temperature okoline i brzine zraka. Pravilna veličina ključna je za optimalnu izvedbu.
Evaporativni suhi rashladni tornjevi
Ovi sustavi kombiniraju prednosti suhog hlađenja i hlađenja isparavanjem. Iako primarno koriste zrak za hlađenje, oni uključuju malu količinu hlađenja isparavanjem kako bi se povećala učinkovitost, osobito pri visokim temperaturama okoline. Ovaj pristup nudi ravnotežu između potrošnje vode i rashladnog kapaciteta. Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co., Ltd nudi inovativna rješenja u ovom području.
Prednosti horizontalnog suhog hlađenja
Horizontalno suho hlađenje nudi nekoliko ključnih prednosti:
- Očuvanje vode: Eliminira ili značajno smanjuje potrošnju vode u usporedbi s tradicionalnim mokrim sustavima hlađenja.
- Ekološka prihvatljivost: Smanjuje utjecaj na okoliš povezan s korištenjem vode i mogućnost onečišćenja vode.
- Smanjeni operativni troškovi: Niži troškovi vode i tretmana doprinose dugoročnim uštedama.
- Fleksibilnost lokacije: Može se postaviti u područjima s ograničenim pristupom vodi.
Čimbenici koje treba uzeti u obzir pri odabiru vodoravnog sustava suhog hlađenja
Odabir odgovarajućeg horizontalno suho hlađenje sustav uključuje pažljivo razmatranje nekoliko čimbenika:
- Zahtjevi za kapacitet hlađenja: Sustav mora biti dimenzioniran tako da zadovolji specifične potrebe za disipacijom topline aplikacije.
- Temperatura okoline i klima: Klimatski uvjeti značajno utječu na performanse sustava. Više temperature okoline zahtijevaju veće sustave ili dodatne strategije hlađenja.
- Raspoloživi prostor: Fizički otisak sustava treba procijeniti u odnosu na raspoloživi prostor.
- Proračun i ROI: Procijenite početni trošak ulaganja, operativne troškove i dugoročni povrat ulaganja.
Studije slučaja i primjene
Horizontalno suho hlađenje nalazi primjenu u različitim sektorima, uključujući proizvodnju električne energije, industrijske procese i podatkovne centre. Brojne uspješne studije slučaja pokazuju njihovu učinkovitost u različitim klimatskim i operativnim okruženjima. Na primjer, elektrane u sušnim regijama uspješno su iskoristile horizontalno suho hlađenje kako bi se potrošnja vode svela na najmanju moguću mjeru uz održavanje pouzdane izlazne snage. kontakt Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co., Ltd za specifične primjere i prilagođena rješenja.
Usporedba vodoravnog i okomitog suhog hlađenja
| Značajka | Horizontalno suho hlađenje | Vertikalno suho hlađenje |
| Zahtjevi prostora | Često zahtijeva veći otisak | Može biti prostorno učinkovitiji |
| Održavanje | Općenito lakši pristup za održavanje | Može biti veći izazov zbog okomitog rasporeda |
| trošak | Može varirati ovisno o veličini i složenosti | Može varirati ovisno o veličini i složenosti |
Napomena: Ova usporedba pruža opći pregled; specifični troškovi i aspekti održavanja ovisit će o individualnom dizajnu sustava i proizvođaču.
Zaključak
Horizontalno suho hlađenje sustavi predstavljaju održivo i sve popularnije rješenje za učinkovito i ekološki odgovorno odvođenje topline. Pažljivim razmatranjem čimbenika o kojima se govori u ovom vodiču, možete odabrati i implementirati sustav koji optimizira vašu strategiju hlađenja i ispunjava vaše specifične operativne zahtjeve. Za više informacija ili raspravu o vašem projektu, molimo kontaktirajte Shanghai SHENGLIN M&E Technology Co., Ltd.









.jpg)






